Inflammation of the paraanal glands in cats is a dangerous condition that can lead to blood poisoning. Despite this, not all owners know about the location and significance of this important organ. This gap prevents timely detection of the problem, complicating further treatment. Familiarity with the causes and symptoms of the inflammatory process will help you avoid unpleasant consequences.
What are paraanal glands and where are they located?
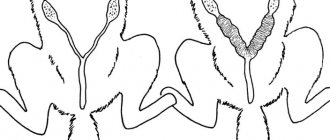
The anal glands in cats are small ball-shaped sacs located next to the anus on the inside. They perform an exocrine function, that is, they secrete a thick, sharp-smelling white or cream-colored secretion. Thanks to it, animals recognize each other by smell, attract the opposite sex and mark their territory. The secretion also participates in metabolic processes, facilitating the passage of feces.
More humane treatments
There are more humane ways to solve this problem. For example, you can use syntomycin liniment. To do this, apply the ointment to the inflamed area and do not let the cat lick the product for an hour. You can buy suppositories at the pharmacy that contain ichthyol - they must be placed in ¼ halves for 10 days.
But it is best, of course, to seek qualified help from a veterinarian. Do not allow your pets to develop such a disease; systematically monitor their health, in particular the anal glands. By these actions you will save yourself from problems, and the animal from suffering.
Why do problems occur with the glands?
The natural outflow of secretions occurs due to muscle contractions during bowel movements or the application of territorial marks. If the secretion is disrupted, then liquid begins to accumulate inside. Stagnation is accompanied by severe itching and inflammation.
The main causes of inflammation of the paraanal glands in cats include:
- too narrow excretory canals inherited by the animal from birth;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- prolonged diarrhea or constipation caused by too much or too little fiber in the diet, respectively;
- anal injuries;
- anal sphincter insufficiency;
- infection with bacteria or helminths;
- obesity, metabolic disorders and physical inactivity;
- low immunity.
The risk group includes pets that do not go outside. Due to low physical activity and lack of need to mark territory, these cats experience blockage of the paraanal glands.
Symptoms of the inflammatory process
When the excretory channels are blocked, the concentration and color of the exiting secretion changes. Gradually it becomes thicker and darker (even black). Curdled inclusions appear in it.
Due to the accumulated fluid, the glands increase in size. The resulting compactions can be detected by palpation. The act of defecation is accompanied by pain, so the animal behaves restlessly and constantly licks the anal area. In addition to the pain syndrome, severe itching occurs, which the pet tries to eliminate by riding on its butt. This symptom is similar to helminthic infestation.
Frequent licking worsens the condition of the coat - it becomes dull and falls out. Dandruff and increased fat content appear. Not only the anal area is affected, but also adjacent parts: the base of the tail, the sacrum, the inner side of the hind legs.
The resulting disturbances lead to a deterioration in appetite and general well-being. If a secondary infection occurs, the temperature may rise. The anus becomes swollen and looks dirty. An unpleasant odor appears that persists even after bathing. The cat constantly covers the anus with its tail, preventing palpation. Lameness may develop.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should be examined by a veterinarian. Timely diagnosis will prevent the development of complications.
Surgical methods of treatment
In recent years, veterinarians are increasingly promoting surgical methods for treating inflammation of the rectal sinuses. And this is far from accidental: practice shows that animals that have at least once suffered from inflammation of the glands will definitely have relapses, with a 100% probability. In fact, only removing the “root of trouble” will make your pet healthier. Currently, there are two therapeutic methods:
- Simple surgical excision of inflamed sinuses. The operation is very simple and quick and is performed under local anesthesia. An incision is made in the skin, the inflamed sinus is removed and cut off (there are nuances, but this is approximately what happens). The stump is sutured and disinfected. Already on the second day the animal can lead a normal life.
- A less common technique is to cauterize the inflamed glands with liquid nitrogen. After this, the inflamed tissues atrophy and subsequently the animal is no longer bothered.
In addition, surgical treatment methods include castration/sterilization. We have already mentioned above that when the gonads are removed, the intensity of inflammation of the sinuses quickly decreases.
When a problem can be solved on your own
You can clean up accumulated secretions on your own, but only after examination at a veterinary clinic. Diagnostics is necessary to exclude pathologies with similar symptoms: helminthiases, allergies, mental disorders.
Mechanical cleaning – what is it?
Mechanical cleaning is a rather unpleasant, but very effective procedure that involves manually removing accumulated secretions. It is part of the complex treatment of inflammation of the paraanal glands in cats and is its mandatory step. The remaining stages, including rinsing and taking antibiotics, are prescribed on an individual basis.
Cleaning at home
The ducts are cleaned in two ways: internal and external. The first one is not performed at home, since without proper preparation it can lead to injury to the anus or rectum.
To carry out external mechanical cleaning you must:
- Make sure you have an assistant. The procedure is unpleasant not only for the owner, but also for the animal, so it will have to be constantly restrained. For safety, secure the cat with a towel.
- Prepare latex gloves and old unnecessary clothing. The extracted secretion smells bad. If you are not careful, it can end up not only on you, but also on furniture. It is safer to carry out the procedure in the bathroom.
- Gently squeeze the anus area, clasping it on both sides with your fingers. At this moment, hold the napkin where the stagnant secretion will flow. Focus on the condition of the animal. Don't press too hard if you see it's causing him a lot of pain.
- Disinfect the anus with Chlorhexidine after the remainder of the discharge is released.
If the above manipulations do not bring any effect, consult a doctor. Thickened secretions can only be cleaned internally. Also, in case of severe pain, novocaine blockade is recommended.
It is best to discuss the frequency of preventative cleaning with your veterinarian. The rate of blockage varies from person to person. The procedure can be carried out every six months or once a month, and sometimes there is no need for repeated cleansing at all.
Symptoms of paraanal inflammation in cats
Inflammation in the anus area causes severe pain in the animal and the owner will definitely notice pain in the pet.
A cat with inflamed glands exhibits the following symptoms:
- constant licking by the cat of the area under the tail;
- the animal makes a minimum of movements, rarely gets up, does not play as before;
- anxiety appears with tactile contact in the tail area;
- the animal rolls its heel on the floor trying to get rid of excess secretory fluid;
- the cat emits a terrible aroma, the tail fur becomes greasy;
- walking is impaired;
- in severe cases, the temperature rises.
Read here Hepatitis in cats: types, photos and videos of symptoms, diagnosis of the disease and treatment
For greater clarity, take a look at the photo of paraanal inflammation in cats. When squeezed out of the swollen glands, a brown oily liquid appears, emitting a disgusting stench.
If you find these symptoms in your pet, you should immediately contact your veterinarian at the hospital. After examining the animal, the veterinarian will be able to determine the stage and severity of the disease.
Treatment by a veterinarian
It is better to entrust the first cleaning to a veterinarian. The owners are allowed to be present at the procedure, which helps to understand its nuances in practice. You will also have to seek help if purulent discharge or fever appears. Both symptoms are fraught with complications, so any manipulation at home is excluded.
After passing the tests, the pet is given an accurate diagnosis and prescribed treatment. Depending on the stage of the disease, rinsing, medications or surgery are prescribed.
Washing
Washing is carried out in advanced cases when the animal has developed an abscess or a fistula. The procedure involves injecting an antiseptic solution based on Miramistin, potassium permanganate or Chlorhexidine directly into the affected organ using a syringe without a needle. This helps reduce the thickness of the secretion and facilitates mechanical cleaning. After washing is completed, antibacterial ointment is placed inside the anus, and a collar is put on the cat to prevent licking the treated area.
Use of medications
The inflammatory process is relieved with syntomycin ointment or Levomekol applied to the anal area. Both drugs have not only anti-inflammatory, but also antimicrobial effects. On average, the course of treatment with ointment is 10 days. To prevent licking, a protective collar is put on the cat.
In addition to ointments, rectal suppositories are used, but strictly as prescribed by a doctor. If the process is started, they can harm the animal. Methyluracil is used to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues. If a pet is diagnosed with eczema or bacteria, it is treated with intramuscular injections of Dexafort, Tetracycline or Amoxicillin.
When may surgery be needed?
With frequent relapses, when mechanical cleaning does not bring the desired effect, the mustachioed patient is prescribed surgery. Also, removal of the paraanal glands in cats is carried out for abscesses and other advanced complications. In this case, the abscess is excised along with the inflamed organ and its ducts.
Despite the use of general anesthesia, the operation is a mild one. Rehabilitation is quick and rarely accompanied by complications. The absence of an organ does not have a negative impact on the condition and vital functions of the animal, but only eliminates further relapses.
The only possible complication is constipation. If it occurs soon after surgery, you should consult a doctor, since stagnation of feces can lead to suture divergence.
In what cases is it necessary to contact a veterinarian?
Sometimes the cat needs to be taken to the clinic immediately, without waiting until the pet becomes really ill. So, in what cases will you need to contact a veterinarian:
- Complete refusal of food and even water. The younger or older the animal, the sooner you need to take it to the clinic.
- Severe pain reaction. The cat cannot poop normally, moans and meows hoarsely. If these same signs are observed regardless of the pet’s desire to relieve itself, things are even worse.
- A sudden and sharp increase in general body temperature, intermittent fever, which greatly exhausts the cat.
- Copious discharge of pus from swollen abscesses under the tail. If you “endure”, then in such cases the cat can easily die from purulent peritonitis or sepsis.
Are there any complications?
Prolonged development of the inflammatory process is fraught with the development of abscess, sepsis and adenosarcoma (tumor). Stagnant fluid creates an environment favorable for bacteria, stimulating their proliferation. Pathogenic microorganisms spread through the rectum, infecting neighboring organs and systems through the blood. Such extensive intoxication can be fatal. Also, opening an abscess can affect the integrity of the glands.
In addition to possible blood poisoning and cancer, the pathology is dangerous due to possible chronicity. In this case, the animal experiences frequent relapses - they negatively affect the general condition and cause secondary diseases. Chronic inflammation is treated only surgically.
Abscess
An abscess of the paraanal glands is an inflammation of this organ, which is accompanied by the formation of pustules. It occurs against the background of complications of blockage of passages.
An abscess can be recognized by the following signs:
- redness;
- swelling;
- fluctuations;
- bald spots around the anus;
- necrosis;
- discharge of pus;
All this is accompanied by general manifestations of the disease: malaise, soreness, decreased activity. Quite often cats begin to limp because of this. Prolonged lack of treatment can lead to inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue, tissue necrosis and blood poisoning.
If an abscess develops, it is necessary to mechanically clean the glands, rinse the sinus, and administer antibiotics. You also need to do everything possible to prevent the development of a secondary infection. If necessary, the cat is given local anesthesia and sedatives are also administered. In rare cases, when an abscess develops, punctures of the paraanal glands are made.
Gland problems in kittens
Inflammations occurring in kittens are very rare. In most cases, the owner is to blame for breaking the feeding rules. Also at risk are babies born prematurely or weakened by other diseases.
Due to the fragility of the child’s body, it is better to entrust treatment to a veterinarian. The introduction of rectal suppositories, lavage and mechanical cleaning are contraindicated for kittens. It is preferable to use anti-inflammatory ointments. The exact dosage and method of use should be obtained from your doctor.