Sometimes it happens that a cat cannot pee, sits in the litter box for a long time and tensely, meows loudly, moans, screams, does not allow her belly to be touched, and is afraid to go into the litter box. If you notice that bloody or purulent stains have appeared in the tray, or after much suffering the cat is going to the toilet with blood, you need to urgently contact a veterinarian and deal with the problem.
Signs of difficulty urinating in cats
The cat's body produces 50–200 ml of urine per day. The volume depends on the individual characteristics of the animal, drinking regime, gender, age and other factors. Due to the large amount of liquid they drink and the small size of their bladder, small kittens can void up to 10 times a day. After 1 month, babies relieve themselves about 5–7 times a day. After 3 months, the number of visits to the tray is reduced to 4–6. Adult males empty their bladder up to 5 times a day, and females - up to 3. For the latter, a single visit to the litter box during the day may be an individual norm.
Changes in posture and gait, arching of the back and aggression when trying to touch the lower abdomen may indicate inflammation and pain in the bladder area
The danger is the lack of urination for 24–36 hours in adult cats and cats and for 16–24 hours in children. Acute urine retention often causes the death of pets, so you need to act quickly. Other symptoms may also indicate problems with visiting the litter box: unsuccessful attempts to relieve yourself, plaintive meowing during the process, changes in the appearance of urine, etc. The diagnosis should be entrusted to a veterinarian, but it is important to describe the pet’s condition in as much detail as possible. For example, when my cat began to have problems urinating, she began to relieve herself on the carpets and bed. At first I scolded her, but then I realized that my pet was in pain, she associated discomfort with the tray, so she tried to find a soft surface.
What to do
If you notice that the cat has begun to pee less often, you need to pay attention to his behavior and the urine itself: it should not contain foreign inclusions - blood, mucus, stones, etc. These impurities, along with rare visits to the toilet, indicate serious violations, which is why prompt action is required on the part of the owner.
In such a situation, you only need to do one thing - contact a veterinarian, who will prescribe the appropriate treatment (antispasmodics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, a catheter for artificial drainage of urine or, in extreme cases, surgery).
Until the cat arrives for an appointment, you can put a warm heating pad on his belly and crotch. This may help your cat pee. But under no circumstances should you massage your stomach! Such actions will only increase the pain and will not bring any benefit.
Any cat can get sick and stop writing fully - both sterilized and not undergone such an operation. A special risk group includes “elderly” pets over 10 years old. They require even more care, regular veterinary checkups and home monitoring.
For all cats, prevention is equally important, thanks to which such a problem should not arise that the pet will not be able to write normally. Adhering to these measures is essential to maintaining the health of the animal.
© shutterstock
Why can't a cat go small?
The complete absence of urination in an adult animal is due to blockage of the tubules. Theoretically, this could happen, for example, due to the formation of adhesions as a result of prolonged cystitis or acute inflammation of neighboring internal organs, but most often the problem lies in urolithiasis. In such cases, the ducts are blocked by stones, sand and blood clots formed as a result of damage to the mucous membranes. Due to irritation of the internal lining, internal edema occurs, and the tubules narrow even more. Similar symptoms in most cases are observed when stones pass through the ducts. Lack of urination with urolithiasis is more common in cats, because the urethra is wider in cats.
In cats, when passing through small stones or sand, as well as in cats, the possibility of emptying with urolithiasis remains, but the urine becomes bloody or the color of meat slop
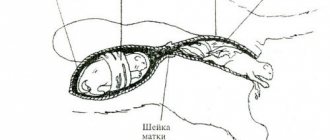
In kittens, delayed bowel movements can also be associated with pathologies of internal organs, congenital anomalies and inflammation, but usually the symptom occurs due to a banal lack of reflex. The mother helps babies defecate when they lick their bellies. Due to stimulation by the rough tongue, the muscles relax, and the contents of the intestines and bladder freely leave the body. At first, the cat licks the feces, so the owners may think that the kitten is not relieving itself. The most characteristic sign of lack of urination is an enlarged abdomen.
If the owner is convinced that there is a problem or doubts arise, it is better to play it safe and help the baby. You need to take a coarse cloth, gauze, cotton swab or any other material with a similar texture. It is moistened in warm water (about +39°C), then the kitten’s belly is massaged first, then the groin and anus area. This will cause the muscles to relax and release urine and feces if the intestines and bladder are full.
Video: how to help a small kitten go to the toilet
If the cat does not pee at all - anuria
With anuria, the kidneys lose their ability to produce urine. Experts associate this disease with partial or complete renal failure. When the disease occurs, the water-salt balance and acid-base metabolism are disrupted - intoxication of the cat's body occurs. Experts distinguish between acute and chronic forms of the disease.
Symptoms in the acute form:
- dejected state;
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- refusal of treats;
- rapid pulse;
- urination either stops altogether or decreases significantly;
- change in the shade of mucous membranes to a pale color;
- swelling;
- decrease in temperature indicators;
- a distinct smell of urine from the mouth of the mustache;
- dehydration.
If the disease occurs chronically, then the manifestations are hidden for a long time. Usually the first signals make themselves felt when 65-75% of nephrons are no longer working. Healthy kidney cells are overloaded because they take on all the work.
The first obvious manifestation of chronic anuria is very strong thirst and frequent trips to the litter box (polyuria). Afterwards, other symptoms signal themselves: emaciation, refusal to eat, diarrhea, vomiting, unpleasant odor of urine from the mouth, the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, dull fur, irritability and passivity.
In the advanced form of the disease, when therapy no longer produces results, tremors, convulsions, coma and lethargy appear (the mustache falls into a state of sleep).
This disease is fatal to the pet and requires professional supportive care. It cannot be cured, but you can alleviate the condition of your beloved four-legged friend with the help of veterinarians. Therefore, if you find that the cat does not pee, take him to the veterinary clinic.
Why does a cat walk small often, but little by little?
Frequent emptying of the bladder can be associated with 2 opposing conditions: cavity overflow or hypersensitivity. In the first case, the cause is a disruption of the central nervous system. Due to some circumstances, the nerve endings cannot transmit a reliable signal about the level of bladder filling. This causes the cat to leak urine. This condition is rare in animals and is characterized by the absence of acute symptoms. The pet does not feel any discomfort and defecates involuntarily. Problems with the central nervous system can be caused by damage to the spine, previous acute urinary retention with death of nerve cells and congenital structural abnormalities.
Problems with urination often accompany a spinal fracture; in such cases, the cat’s gait changes and he suffers from severe pain
Bladder hypersensitivity is many times more common. In this case, the animal tries to relieve itself, but this is not always successful. The pet is disturbed by false urges. The need to visit the tray appears even when a small portion of urine occurs. This may be due to a mechanical decrease in the volume of the bladder or inflammation of its walls. The first sometimes occurs as a result of an enlargement of neighboring organs (uterus, ovaries, prostate gland, etc.) in the presence of their pathologies.
Much more often the bladder itself becomes inflamed. In most cases, this occurs due to cystitis or urolithiasis. The diseases can be combined: if the urinary ducts are damaged by stones, the risk of infection increases. Bacteria can enter the kidneys and cause the development of pyelonephritis. Sometimes urethritis occurs - damage to the urinary canal.
Prevention
After a urine blockage, lifestyle changes may be necessary to prevent a recurrence of this life-threatening condition. Several factors have been identified as potential contributors to urethral blockage, including family stress and inadequate access to or consumption of water, poor quality feed, sedentary lifestyle, hard water, and fish feeding.
Below are steps your veterinarian may recommend to prevent future recurrences:
- Increase the amount of water your cat drinks. This “simple” strategy is strongly associated with reducing recurrent urinary blockage. Talk to your veterinarian about creative ways to get your cat to drink more water.
- Reviewing your pet's diet and feeding rations
- Your veterinarian may recommend a modified diet or prescribe a prescription therapeutic diet—perhaps one that can help dissolve certain types of crystals or stones
- Improving your pet's living conditions means enriching the environment. Making sure your cat feels safe and encouraging her to be active and in a good mood is an important way to help reduce or eliminate stress in the home. Improving housing conditions often includes proper control of litter tray cleanliness, as well as access to climbing structures, resting areas and scratching areas. Synthetic cat pheromones may help reduce stress and anxiety in some cats
Treatment
It is necessary to refrain from making an independent diagnosis and prescribing treatment. Only a veterinarian can competently assess the animal’s condition after palpation and ultrasound. Attempts to massage or palpate the bladder may rupture or dislodge stones!
Catheterization is recommended only as a last resort with confirmed urinary retention, since the procedure can increase inflammation
In case of acute urinary retention, the first step is to restore the outflow by puncturing the bladder through the abdominal wall or catheterization. After normalization of urine output, antispasmodics are prescribed to relax muscles and dilate the ducts, painkillers to alleviate the general condition and antibiotics to prevent infection. Depending on the diagnosis and the presence of complications, additional measures may be taken. For example, intravenous administration of drugs when there is a threat of developing renal failure.
Before changing your diet, it is important to consult a veterinarian, since feed formulations for different diseases of the urinary system differ greatly
During treatment, it is recommended to switch to wet food to reduce the degree of injury to irritated tissues. If necessary, the veterinarian can prescribe a therapeutic diet if the animal has kidney failure, cystitis or stones.
Urgent medical care
First aid in a veterinary clinic involves inserting a catheter.
Only a professional should insert a catheter, after first flushing the bladder with antiseptics. This operation is painful, so it is performed under general anesthesia. After catheterization, the veterinarian performs a series of tests to find the cause of urinary retention. Important: you should not insert a catheter often - after this procedure, swelling of the urinary tract occurs. If the doctor sewed in a catheter for several days, you need to keep the cat in a special collar during this time so that it does not injure itself and does not remove the catheter.
First aid
In the most difficult cases, surgery and the use of a catheter will be required to remove fluid from the cat's body. This procedure is quite painful, so it can only be performed by a qualified specialist. In some cases, such operations are performed using general anesthesia.
In most cases, painkillers are used and tinctures of medicinal herbs are given. Here are some of the herbs whose decoctions are recommended to be used in this case: rose hips, lavender, lingonberries, plantain, horsetail.
Often they prescribe one teaspoon of strawberry juice, boiled pumpkin, a hot bath for ten minutes (the cat is carefully lowered into the water up to the heart area)
In cases where all kinds of inflammatory processes appear, the pet needs to take medications that relieve inflammation.
At the same time, it is very important to complete the full course of treatment, and not stop it at the first signs of improvement in the cat’s condition.
It is necessary to include vitamin complexes in your daily diet, and add nettles to your food in the spring months. Walks and active games have a positive effect on the cat's condition.
Most diseases of the urinary system are chronic, so it is recommended to repeat the course of treatment constantly, as well as taking herbs and decoctions based on it.
Important: kidney collection is an excellent means for removing sand from an animal’s body. You can buy it at the pharmacy, but before doing so, consult a specialist
You can constantly give your cat water with decoctions of parsley, birch leaves, black currants and bearberry. The course of treatment in this case should last at least a month.