In many situations, cat owners know what causes this or that deviation in their pet’s health. But in some cases it is difficult to determine the cause on your own, because there are many of them. This also applies to cases where a cat has a swollen lower lip.
Before visiting the veterinarian, you should remember what the cat has been doing in recent days, how she spent her time, and whether she went outside. It would not be amiss to note changes in the animal’s behavior that have taken place recently. When communicating with a veterinarian, this data can be useful: with their help, the cause of the tumor will be established as accurately as possible.
Possible causes of swelling
Naturally, you can speculate for as long as you like what exactly caused the strange swelling on your pet’s lips, but only a veterinarian can make an accurate diagnosis based on the totality of the symptoms. You need to try to give as much information as possible about the disease and most likely your cat will be given one of the following diagnoses.
Swelling on the lip
Injury
Injuries are not uncommon for cats, including lip injuries. Most often, an animal injures its lips or gums by eating too hard food, bones, or licking cans of canned food. And even if your cat is a home cat and you carefully monitor his diet, he may secretly steal a bone or pull a dangerous can out of the trash can. Backyard animals are especially susceptible to lip injuries. They can be stung by a wasp or a bee, or injured by thorny bushes.
Lacerations on the lips caused by cat fights are not uncommon. Any damage to the delicate skin of the lips is dangerous due to secondary bacterial infection. Therefore, if you notice such an injury, be sure to treat it with an antiseptic and put the animal on a gentle diet. Give only soft food or porridge, exclude dry granular food or bones. In rare cases, when injuries on the lips are lacerated with severe bleeding, surgical intervention may be necessary - such wounds will need to be stitched.
Burn
Burns of the mouth and lips in cats can be thermal, chemical and electrical. Note that thermal burns are an atypical situation for cats; they do not rush to hot food, no matter how hungry they are. However, they may lick hot pans or grates. A chemical burn can occur if the animal has ingested some toxic substance, in which case poisoning can also occur.
A cat that has a bad habit of chewing wires can get a dangerous burn to its lips and mouth. This behavior can result not just in a burn, but also in death.
Therefore, a cat injured by electric current must be shown to a veterinarian. Mild forms of lip burns can be treated at home if the symptom is only mild redness. To do this, the affected area is washed with clean water and covered with sterile gauze or cloth.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis in cats is a local disease of the oral cavity. It is characterized by inflammation of the gums and the presence of a red border around the tooth.
Gingivitis in cats has the following symptoms:
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- inflamed, swollen gums, bleeding may occur;
- soreness in the gums and lips;
- drooling, poor appetite.
Gingivitis in the mouth
Gingivitis in cats can occur in chronic or acute form. The cause of this unpleasant disease can be dental diseases - plaque, tartar. As well as immune disorders, calcivirosis, rhinotracheitis virus and panleukopenia. Sometimes gingivitis is observed as a concomitant disorder with severe systemic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, liver or kidney failure. In principle, any state of immune depression makes the pet's mouth and lips especially vulnerable. Without treatment, gingivitis ends in tooth loss.
Eosinophilic granuloma
Another reason why a cat has a swollen lower lip can be eosinophilic granuloma. The disease is caused by an allergic reaction to insect bites, hypersensitivity to food or environmental components. It is expressed in damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips. The name eosinophilic granuloma supposedly comes from the name of the cells - eosinophils, which are the cause of the disease. Eosinophils belong to white blood cells, cells that are the basis of the body's immune system.
Manifestations of eosinophilic granuloma
With eosinophilic granuloma, swelling, papules, and plaques are observed in the animal’s oral cavity, and most often the disease is painless. But you should beware of the swallowing disorder that accompanies granuloma, which can lead to exhaustion of the animal. Diagnosis of granuloma can be complicated by the fact that fungal or bacterial lesions of the mucous membranes can have similar symptoms.
Cytology of smears should help, which in case of eosinophilic granuloma will contain an increased number of eosinophils. To treat granuloma, the first step is to try to establish which allergen caused it.
Fungal infection
Fungal infections rarely lead to serious damage to the mucous membranes. Most often, mycoses can be observed on the animal’s body. However, candidiasis of the oral and lip mucosa can be associated with skin maceration - the process of moisturizing and swelling of the epidermis due to prolonged contact with liquid. The presence of Candida yeast fungi on the lips is most often associated with immune disorders or long-term and unjustified use of glucocorticosteroids.
Swelling on the lower lip
Infection with fungi of the genus Candida is often called fungal stomatitis and its symptoms are white plaques in the mouth and on the tongue of the animal. Treatment of fungal infections requires complex treatment; it is necessary to eliminate their root cause, for example, immune depression. And use local antifungal drugs.
Tumor
Tumors in the mouth are rare in cats. Alas, if they do occur, they are more likely to be malignant.
Benign formations include gingival fibroma and epulis. Both formations grow on the gum, only the fibroma is larger in size. Fibroma may have the color of the gum itself or be paler, it is insensitive, and feels firm to the touch. Treatment is surgical removal. You can see what a cat looks like after a tumor in his mouth has been removed in the video below.
The most common malignant tumor in the oral cavity is squamous cell carcinoma. The tumor grows from the cells of the mouth and throat, accompanied by the appearance of non-healing ulcers, salivation and an unpleasant odor. It quickly spreads through neighboring tissues and lymph nodes, causing severe swelling. It is difficult to treat, surgical removal and radiation therapy do not always lead to positive results, and the mortality rate from carcinoma is high and painful.
Feline acne as a reason why the face of cats becomes swollen
The sebaceous glands are connected directly to the hair follicles and serve to produce sebum secretion, which is intended for the waterproofness of the hair and the elasticity of the skin.
It is on the chin, lips, eyelids, foreskin and scrotum that colonies of larger sebaceous glands are located.
More severe cases of the disease are treated with an ointment or gel containing benzoyl peroxide (such as OxyDex) or chlorhexidine.
But in cases of secondary infection (fungal infections) with the formation of comedones and edema, additional antibiotic therapy is necessary.
How to cure a pet?
Of course, treatment does not need to begin until a final diagnosis is made. Each of the described conditions requires an individual treatment regimen. The drug Dexamethasone is often used to treat conditions that cause swollen lips and lesions in the mouth. Dexamethasone has the active ingredient dexamethasone disodium and is available in the form of injection ampoules. Dexamethasone has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and anti-shock effects.
In case of infectious lesions, Dexamethasone complements antibiotics. Dexamethasone should be given in the dosages specified in the instructions for use. Another drug that has a detrimental effect on a number of pathogenic microorganisms is Sinulox. Sinulox is available in the form of a suspension or tablets. Sinulox is effective for infectious lesions of soft tissues and mucous membranes. Sinulox is often prescribed for gingivitis. Sinulox should be given strictly according to the instructions for use. There is a tablet form of Sinulox.
Snake bites as a reason why the face of cats becomes swollen
Do not apply a tourniquet to the affected limb - it does not prevent the spread of poison through the bloodstream.
Do not cauterize the wound - this will provoke inflammation, but will not reduce the absorption of the poison.
- Infusion therapy to reduce toxicity and maintain kidney function.
- Diuretics to relieve swelling and accelerate the removal of poison from the body.
- Preparations for optimizing the functioning of coagulation systems.
- If necessary, surgical treatment of the wound.
Video “Brushing pets’ teeth”
To avoid many of the problems described above, it is enough to monitor your pet’s oral hygiene. The video below will tell you how to brush your pets' teeth at home and in the clinic.
Sorry, there are no surveys available at this time.
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the usefulness of the article: Rate the author ( 15 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
Injuries
Cats are very curious: even a pet that has no chance of getting outside can find adventure in its face while exploring the apartment. A small wound (for example, when trying to bite a cactus - this happens!) will most likely heal quickly. However, for some time a small sore or ulcer will be noticeable in its place.
An animal may become interested in the stove or heater that has just been turned off, and get burned: the burn also leaves a mark in the form of a sore.
You might be interested in: A cat scratches its skin until it bleeds: how to help your pet?
Symptoms of oropharyngeal diseases in cats.
There are many signs that indicate that your cat has problems with the oral cavity or pharynx, including:
- Loss of appetite. The cat stops being interested in food, or goes to the saucer, but refuses to eat;
- Dysphagia. Swallowing disorder indicates difficulty eating or swallowing food—the cat eats with apparent caution, shows signs of discomfort, may drop food from its mouth, or has difficulty swallowing;
- Ptyalism is excessive salivation or drooling from the mouth (sometimes with bleeding);
- Halitosis is an unpleasant odor from a cat’s mouth;
- The cat scratches or rubs its mouth with its paws, sometimes shaking its head;
- Weight loss - usually due to lack of appetite;
Diagnostics
The absence of anxiety in an animal when an ulcer appears on the upper lip is the main symptom of the disease. A biopsy will help confirm the assumption. The veterinarian takes a microscopic piece of skin from the affected and healthy areas. If the analysis shows eosinophilic proliferation, then this is a reason to diagnose Jacobs disease.
Attention! In a blood test, the number of eosinophils may be normal, therefore, in case of non-healing red spots on a cat’s lip, only a biopsy is considered reliable.
If the animal has a history of viral leukemia or the cat has recently been ill, then a veterinarian who discovers a spot on his patient’s lip should immediately check the diagnosis.
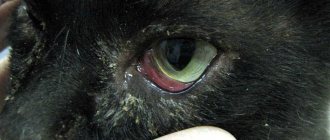
Inflammation of the lips of cats
Symptoms of this disease occur as a result of periodontitis, when the periosteum of the tooth root is inflamed or in the case of an infectious disease in the cat’s oral cavity. Injections or cuts from weeds while walking can cause irritation and the lips will begin to peel. Treatment for inflammation of the lips consists of washing the affected areas with an antiseptic solution and lubricating them with an ointment containing an antibiotic twice a day. If a cat develops periodontitis, the cat's teeth need to be treated.
Abscess as a reason why the face of cats swells
- With a fully developed abscess, a clearly defined subcutaneous swelling or swelling appears at the site of infection, filled with pus and hot to the touch.
- The site of inflammation is often painful, so the cat may resist stroking in this area. Lameness may also occur if the abscess is located on the paw.
- A bald spot in the tumor area is possible. There may also be a scab or small puncture wound in this area.
- Leakage of blood or pus from the wound.
- The abscess may have a strong, unpleasant odor.
- The animal may show symptoms of fever, including lethargy and lack of appetite.
- Abscesses are painful and significantly impair the well-being of animals.
- The infection can spread deep into the body, such as the joints and ears.
- Cats suffering from combat abscess are at risk of contracting the immunodeficiency virus.
- Blood and pus released from the wound can spread infection throughout the house, as well as contaminate furniture and floors.
In case of illness, antibiotics of the penicillin, cephalosporin group or clindamycin are prescribed for oral use.