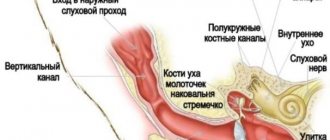
The danger of all viral infections lies in their extraordinary survivability and speed of reproduction. To avoid death if infected, veterinarians recommend vaccinating pets against the most common diseases in advance. In Russia, only one vaccination is required - it is given against rabies (hydrophobia) in cats in order to prevent further spread of the pathogenic microorganism.
What is rabies
This viral disease is highly contagious, that is, infectious, and poses a danger to all warm-blooded animals. The main enemy is the Rabies virus. It affects the central nervous system of the infected person and actively multiplies in his salivary glands.
Every year, this disease, often acute, kills several million animals. Despite the fact that Rabies is active only inside a living organism, it easily tolerates low temperatures. To destroy it, use 15-minute heating to 56 ° C or 2-minute boiling. Direct sunlight, ultraviolet radiation and some room disinfectants also have a detrimental effect.
How and from whom does infection occur?
The viral agent is released into the environment along with the saliva of an infected animal. Blood, urine, milk and other body fluids are not dangerous. Infection occurs when:
- bite or injury caused by a vector;
- getting saliva on injured areas of the skin and mucous membranes (the size of the wound is not important);
- eating a sick animal.
Within the city, the disease is spread by rodents, stray dogs and cats, and outside the city by hedgehogs, bats, raccoons, wolves and foxes. The infected person becomes dangerous even before the first symptoms appear, which makes it difficult to understand the danger of the situation after the bite.
Can cats get rabies?
Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in wild canids: foxes and wolves. Although rabies is less common in domestic cats and dogs than in stray cats, the risk of death is the same for all unvaccinated animals.
Owners of pets who do not go outside are perplexed as to how a cat can become infected with rabies in “greenhouse” conditions - and the source of infection could be a rodent that has entered the house or contaminated saliva on a shoe that your pet has licked.
About rabies
This is a very dangerous viral disease due to the fact that at first it is asymptomatic. The first signs appear already in the last stages, when treatment becomes useless. In cats, the likelihood of contracting rabies is much higher than in dogs, since they are rarely given preventive vaccination, in the belief that pets are not at risk of this pathology.
But rabies is not necessarily transmitted through a bite. A cat can become infected if it licks saliva from grass, shoes, or eats from an infected animal's unwashed bowl. The risk of infection for pets living outside the city increases even more. Rodents are often carriers of rabies. Cats are natural hunters and can become infected from the bite of a mouse, rat, or after eating them, as the virus penetrates the pet’s saliva.
All warm-blooded living organisms are susceptible to rabies. The disease is often acute and affects the central nervous system. The pathogen is released through saliva and quickly multiplies in nerve tissues. Infection occurs during a bite through wild or domestic animals. The cause is the Rabies . Cold and frost cannot destroy it. High temperatures and some disinfectants are harmful to it.
How long is the incubation period?
The infection does not make itself felt for about a week, remaining in the affected area. Next, the viral agent rushes through the nerve fibers into the cerebral cortex. He avoids the circulatory system, which makes it difficult to diagnose the disease using a clinical blood test. Once in the central nervous system, the pathogen begins to actively multiply and gradually affects all internal organs. After it penetrates the salivary glands, the infected person becomes dangerous to others. Symptoms may still be suppressed during this period.
The length of the incubation period for rabies in cats depends on the following factors:
- Amount of virus penetrated
. The less it is, the more time it will take to reproduce.
- Size and significance of the affected area
. When the lips, nose, cheeks and areas of the head located near the brain are affected, the pathogen immediately penetrates into the nerve endings.
- Age
. Signs of rabies in kittens appear within 4-7 days after infection, and in adult animals - only after 3-6 weeks.
Even a vaccinated pet has a chance of infection. This is possible if the vaccine was administered more than six months ago. By this time, the immune response has weakened and may not be able to cope with too many pathogens.
Preventive measures
You can avoid infection only by vaccinating your pet in a timely manner. Kittens are vaccinated at 3 months, provided they are healthy. It is not recommended to administer the vaccine to cats during pregnancy and lactation, weakened and sick animals, as well as kittens during the change of milk teeth. When planning this procedure, it is necessary to carry out prevention against helminths. Kittens are re-vaccinated after 8 months, then annually.
In the case when a pet is outdoors (walking on a harness or on its own), the likelihood of being infected from stray animals or rodents is quite high.
If your pet comes home with bites and scratches, you should urgently show him to a doctor. Even if the cat has no signs of rabies and has been vaccinated recently, repeated revaccination will not hurt, any veterinarian will tell you this.
First signs and main symptoms
On average, the first signs and symptoms of rabies in cats appear 1-2 weeks after infection. In rare cases, the lull lasts six months or even a year.
The infected person's behavior changes dramatically. Unsociable pets become obsessively affectionate, and those who appreciate human attention show aggression and try to stay away from other inhabitants.
Due to damage to the gastrointestinal tract, an eating disorder occurs. The animal refuses to eat, but tries to swallow inedible objects: litter, stones, sticks.
The bite site is very itchy, so the pet is constantly itching. This symptom can be easily confused with parasitosis and fungal infections, so the only way to confirm it is through laboratory diagnostics at a veterinary clinic.
More obvious signs include refusal to drink water, painful muscle contractions, excessive drooling, and sudden paralysis. They manifest themselves with serious damage to internal organs and systems. Depending on the form of the pathology, symptoms can be pronounced or blurred.
What to do if a rabid cat bites a person
Rabies is very dangerous not only for animals - if you miss the deadline when something can be done, then death cannot be avoided.
People also become infected with the virus through the bites of sick animals. The closer the bite site is to the veins, the faster the virus will reach the brain. The disease progresses especially quickly in children, so the wound is immediately washed with soap and immediately contacted by a rabiologist for treatment.
The incubation period lasts on average 1-3 months with the same stages as in cats. Self-medication at home is unacceptable, but timely anti-rabies treatment will allow a person to live healthy for many years.
Forms of manifestation
How rabies manifests itself in cats depends on the speed of its progression and the severity of the symptoms. Veterinarians distinguish 4 forms of pathology, characteristic of both kittens and adult animals. The difference in age determines only the speed of the flow. The younger the infected person, the faster he dies.
Classic (violent)
The most common form is the classic form, characterized by dramatic behavioral changes. It lasts 5-12 days and includes the following periods:
- Premonitory
. In the first days, the pet tries with all its might to attract the attention of the owner. A little later, excitement gives way to detachment and lethargy. The patient's appetite decreases or completely disappears. Instead of normal food, the animal tries to absorb inedible objects. He feels sick and diarrhea, and saliva constantly flows from his mouth. The affected area becomes inflamed or itchy. The duration of this period takes 2-4 days.
- Manic
. Symptoms worsen. Constantly dripping saliva spoils the appearance of the fur in the mouth area. The lower jaw droops, signs of hydrophobia (hydrophobia) appear. Due to spasms of the larynx, the infected person is afraid of choking and refuses water. A sick cat hides in dark corners, reacts aggressively to dark sounds and attacks its owners, aiming for the neck and face. His vision becomes cloudy, his eyes begin to squint, and his paws are paralyzed. Due to inappropriate behavior, there is a high probability of escape and attack on passers-by. The stage lasts 2-5 days.
- Depressive
. Paralysis freezes the entire body, preventing any movement. A recumbent animal develops convulsions. Death occurs within 1-3 days due to severe exhaustion or paralysis of the respiratory and cardiac organs.
The classic form is the most dangerous. An aggressive pet that has lost its mind ceases to distinguish between family members and can injure them.
Paralytic (silent)
The paralytic form is the fastest. It develops in just 3-5 days. At the very beginning, the pet obsessively fawns over its owner. As the disease progresses, apathy, fear of hydrophobia, and refusal to eat appear. The animal avoids sunlight and ignores human attention.
Complete paralysis develops already in the first days. It moves from the lower jaw to the hind limbs and torso. The last to suffer are the front paws. Due to paralysis of the larynx, the lower jaw droops and the tongue protrudes out. Excessive drooling is accompanied by coughing and difficulty breathing.
Atypical
A rare form with mild symptoms and periodic remissions. May last for several months.
The infected person suffers from gastrointestinal dysfunction. He refuses to eat and suffers from vomiting and bloody diarrhea. Due to exhaustion of the body, the cat often sleeps, becomes lethargic and depressed. Sometimes his body goes into spasms.
Abortive
The rarest and least studied form, ending in spontaneous recovery. Its symptoms are similar to the paralytic form, but the disease can also occur according to the scenario of the classical or atypical forms. The only difference is that at the moment of development of paralysis, all symptoms suddenly disappear, and the patient’s condition returns to normal.
After feeling better, a relapse is possible. It occurs within 2 weeks, develops rapidly and kills the animal in 2-4 days. The percentage of those cured is only 2%.
Prevention, vaccinations
The risk of developing rabies can be reduced through preventive vaccinations. First, the vaccine is administered to a three-month-old kitten or after the appearance of the molars - at 7-8 months, then annually. Elderly people with poor health are vaccinated every 2 years. Vaccinations do not guarantee 100% protection, but they reduce the risk of infection by 99%.
There are drugs that provide immunity only to rabies. Others are complex, preventing the development of 3-4 dangerous diseases simultaneously. The most popular drugs for vaccination are Nobivak, Leukorifelin, Rabikan, Quadriket . They have a minimal set of side effects.
Vaccination is prohibited during pregnancy, immediately after lambing, in the presence of worms, injuries, and before teeth change. A week before, deworming is carried out.
The danger of rabies in humans after a cat bite
Rabies is transmitted to all warm-blooded organisms. The incubation period most often lasts from 7 days to 1-3 months, rarely – up to six months. The disease develops especially rapidly in young children. Cases have been recorded in which rabies manifested itself after several years. But this is rather an exception. Emergency vaccination carried out in the first three days after the bite can save you. If the injections are not given on time, then the same symptoms occur as in cats, then paralysis, coma, death.
Signs of rabies in a cat for humans
Symptoms of rabies in humans after a cat bite are similar to those of infected animals. At first the wound hurts and swells. Then the following appears:
- fears, phobias, depression;
- convulsive contractions of the respiratory and swallowing muscles (which means the pathogen has already reached the muscles);
- copious amounts of saliva;
- fear of water, light, drafts;
- heat;
- hallucinations;
- dilated pupils;
- cardiopalmus;
- protrusion of the eyeballs.
A person reacts painfully to any sounds, even a whisper. Aggressive towards other people, can cause injury to himself. When the pathogen reaches the brain, paralysis, coma, and death follow.
Rabies can be prevented by routine vaccination, but there is no cure. Only a person has a chance to survive if emergency assistance is provided within three days after the bite (from 6 to 40 injections are given). However, this also does not guarantee that Rabies will be destroyed and lives saved.
Diagnosis in cases of suspicion
If hydrophobia is suspected, the cat is isolated for 10-30 days. The duration of quarantine depends on the epidemiological situation. After the specified period, the pet remains alive or dies.
The disease is diagnosed only posthumously. The virus cannot be detected in blood cells, so brain tissue is used for research. When infected, neoplasms are found in the nerve cells of the brain - Babes-Negri bodies. Other changes can be seen during autopsy of the body. The oral mucosa turns red, becomes covered with ulcers and erosive formations. Her vessels are overflowing with blood. Numerous hemorrhages are found in the cerebral convolutions and stomach. The spinal canal is filled with exudate.
Pathogenesis
Once inside the body, the virus penetrates connective and muscle tissues, then into nerve fibers. Then it enters the bloodstream, lymph, and reaches the spinal cord and brain. It accumulates in the salivary glands, where it begins to multiply rapidly. At the same time, it destroys nerve nodes and cells and moves to mucous surfaces.
Under the influence of the virus, non-purulent encephalitis develops in the brain, causing excessive excitability. Neurons begin to deteriorate, necrotic changes and paralysis appear. The cat's respiratory system fails, asphyxia and death occur.
The rate of development of the disease greatly depends on the location of the bite. The further it is from the head, the longer the incubation period. The age of the pet is also important - in kittens, elderly, sick animals, infection occurs more rapidly than in healthy ones. The duration of the incubation period is affected by the concentration of the virus, which increases with numerous bites. But the appearance of the first signs of infection always means the imminent death of the pet.
Is there a cure for rabies in cats?
There is no cure for this dangerous disease. The animal cannot be saved even after early diagnosis. If characteristic symptoms are detected, it is recommended:
- Isolate your pet in a separate room and monitor all changes that occur to it.
- Do not conduct a self-examination and contact the staff of a veterinary clinic or city emergency room.
- Prepare a veterinary passport with vaccination marks, if available.
- Avoid any contact with the infected person until doctors arrive.
The most humane solution for a stable deterioration of the patient’s condition is euthanasia, which saves the animal from the painful development of the disease. Some veterinarians believe that if this procedure is abandoned, the percentage of successful self-healing in the abortive form may increase. There is no rush to test this theory, since the chances are very small, and the owners do not intend to endure the torment of their mustachioed pet.
Vaccination is a way to protect yourself and your pet
This is the most effective method in which the body of the vaccinated mustache is able to resist the rabies virus. Protecting your pet with a vaccine means protecting yourself and your loved ones. In addition, you should limit your pet’s contact with street four-legged animals as much as possible. In a private home, it is necessary to carry out effective control of mice and rats.
Successful and safe vaccination comes down to several conditions:
- Pregnant and lactating pets cannot be vaccinated;
- First, the mustache should be freed from all cohabitants (worms, fleas and other parasites), then vaccinated;
- If your pet has a suppressed immune system due to some illness, you should first treat the mustache and then vaccinate it;
- During the period of teeth change, little fluffies are not vaccinated.
It is very important to take the problem and possible threat to life from the rabies virus seriously, understanding that the health of your four-legged friend largely depends on the owners. Vaccination, proper care, care and annual examinations by specialists will protect your beloved mustache and the whole family from danger to the maximum.
Is cat rabies dangerous for humans?
Cat rabies can be transmitted to any warm-blooded animal, including humans. The only way to protect yourself is strict isolation. Due to the high risk of infection, even doctors do not have contact with a sick cat placed in a special box. All food and water are served in protective clothing.
If you get bitten, scratched, or get saliva on your skin, immediately wash the wound with hot running water and laundry soap. After treatment, contact the emergency room.
If there is a threat of infection, it is recommended to administer rabies serum, which stimulates the immune response, or immunoglobulins containing ready-made antibodies. Doctors give 6 injections over 3 months. If you miss at least one of the announced vaccination dates, a person develops characteristic symptoms of infection. After this he will surely die.
Difficulties in making a diagnosis
An absolutely accurate diagnosis is rabies; a pet can only be diagnosed after its death. As soon as a sick mustachioer arrives at the veterinary clinic, he is placed in quarantine, where he is constantly monitored.
After a few days, the animal may feel better or symptoms may change. It is likely that the specialist will recognize another disease and possibly cure it. In this situation, the pet will return to the family, but she will first be given an anti-rabies vaccine.
In a different development of events, the symptoms are confirmed, the mustache becomes worse every day, and he dies. Only after this, specialists conduct a series of studies and confirm the diagnosis.
A dangerous source of disease for society is being disposed of.