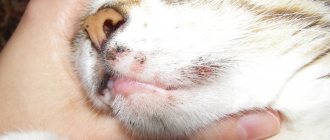
What it is?
A common “folk” name, by which several varieties of such diseases are best known, is “ringworm.” As the name suggests, one of the most specific features of this pathology is the formation of hairless areas on the skin. In some cases, numerous patches of baldness appear throughout the cat's body, which subsequently merge into one hairless area. In the photo, such animals leave a very pitiful impression.
How and what to treat lichen in cats
Treatment of dermatophytosis with extensive lesions is long-term and labor-intensive. It includes oral administration of antifungals, local treatments (washing with shampoos, external antifungal agents), as well as environmental treatment. All animals that are in close contact with the patient must be treated. As a rule, in uncomplicated cases and for asymptomatic animals, local treatments (washing with shampoos) are sufficient. The end of treatment is determined by two negative cultures at an interval of one month.
It is very important to carry out both sowings before stopping treatments. One can understand the owners who find it difficult to constantly treat all their pets and their apartment with special products when there are no longer any traces of lichen on the cat. However, its spores are very resistant, and if you stop treatment and surface treatment ahead of time, there will be a relapse quite quickly. Moreover, symptoms may reoccur not in the cat, but in children or elderly relatives.
The Vakderm vaccine, which, unfortunately, is widely used by both owners and some doctors, has no proven effectiveness, and even in some cases causes an increase in clinical signs. Common cases of recovery after the use of “vaccines against lichen” are associated with spontaneous self-healing, which is a common and described phenomenon for this group of diseases.
The use of immunostimulants in the treatment of lichen in randomized trials also did not show any results.
Pathogen, characteristics
Most often, the disease is caused by Microsporum fungi, less often by Trichophyton or Achoreon. Like many pathogenic fungi, they are characterized by impressive resistance to environmental influences. Thus, hairs and skin flakes affected by spores can remain dangerous for cats for six years at once (sometimes up to ten) provided they are kept indoors. If we talk about the street, then the spores there remain active and viable for about three to four months, which is also a lot.
Diagnosis of ringworm
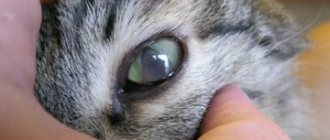
In most cases, ringworm in cats, caused by the fungus M. canis, will glow yellow-green fluorescent when the skin and fur are examined in a dark room under a special ultraviolet lamp called a Wood's lamp.
This is how lichen glows under a Wood's lamp
However, clear fluorescence is not observed in all cases, and some other dermatophyte species do not fluoresce under a Wood's lamp. Therefore, additional diagnostics may be required to confirm the presence of ringworm fungi. Some skin ointments and other materials also fluoresce and may give a false positive result.
The most accurate method for diagnosing ringworm in cats is to culture dermatophytes in the laboratory. To do this, samples are taken from hair and skin scrapings. Positive test results can sometimes be confirmed within a few days. But in some cases, fungal spores can grow slowly and culture results can take up to four weeks, meaning a suspected case may not be called negative for at least a month.
There are many causes of hair loss and hair loss in cats. Before making a diagnosis of ringworm, your veterinarian dermatologist may recommend additional testing to rule out some of these causes.
Who is most susceptible?
In most cases, young animals and kittens become ill. However, pathogenic fungi of any of the genera mentioned above are very virulent, so they infect adult cats with almost equal success. Cases of dermatomycosis are recorded throughout the year. Their manifestation is especially frequent in the autumn, which is facilitated by increased air humidity, since in such conditions the mushrooms are most comfortable. In areas where there is an increased number of rats and mice, cases of the disease occur especially often, since rodents actively participate in the spread of fungal spores.
Treatment of dermatophytosis in dogs
Diagnosis of dermatophytosis begins with examining the animal's fur under a Wood's lamp. Under its influence, the lesions glow yellow-green. But since not all fungi fluoresce, and the glow may disappear due to medications that the owner has already given to the dog, the veterinarian’s second step will be to examine the hairs from the borders of the hairless area under a microscope. A skin scraping examination will also be performed.
Some dermatophyte fungi grow very slowly. To confirm or refute their presence, the suspicious hair is placed in a special environment for germination. This process can take up to four weeks, so dermatophytosis is not always confirmed on the same day you go to the vet.
If a dog is suspected of having ringworm, then treatment should be started immediately to avoid the spread of infection among households, as well as in children's institutions if the child visits them. Your veterinarian will recommend the specific treatment method for your pet. Therapy depends on the condition of the animal, the severity of the infection and other factors.
For the treatment of dermatophytosis use:
- creams;
- ointments;
- shampoos.
Find out the causes, symptoms and treatment of eczema in dogs.
The surrounding environment (room, enclosure, etc.) must be disinfected. This is necessary so that fungal spores cannot infect anyone again.
The following antifungal drugs are commonly used:
- "Itraconazole" in a dosage of 5 mg/kg, release form - tablets.
- "Terbinafine" - 30 mg/kg 1 time per day. Available in the form of tablets, ointments and sprays.
- "Griseofulvin" - 10 mg/kg 1 time per day. Release form: tablets and ointment.
At an early stage
If the animal is completely healthy, but you are going to travel with it to the country or to a vacation spot, then it is advisable to vaccinate your pet. For this purpose, the Polivak-TM vaccine has been developed. It is intended for the prevention of dermatomycosis in domestic and farm animals. Dosage - 1–1.5 cm³ - depending on the age of the dog or cat. The injection is administered intramuscularly at intervals of 10–14 days.
Important! The vaccine will begin to be fully effective within a month from the moment of the first injection. This must be taken into account so that the animal is fully protected by the time of the trip.
When the form is running
Local therapy is sometimes used alone to treat dermatophytoses, including ringworm, but more often it is used in combination with oral medications. Creams and ointments are intended for application to affected areas. Considering that the fur around this area is infected, it is advisable to cut it off. The doctor may also recommend washing your dog with an antifungal medicated shampoo. This should be done 2 times a week. After bathing, all surfaces that have come into contact with water are disinfected with an aqueous solution of bleach.
As for medications, they are recommended in the following sequence: purchase Itraconazole, if it is not in the pharmacy, then Terbinafine (or its analogue, Lamisil), but if it is not available either, then choose Griseofulvin. Medicines are listed according to the likelihood of side effects from their use. Each dog's body reacts individually, which can shorten or lengthen the course of treatment. Follow your doctor's instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. The moment when it is considered that treatment is completed are two wool examinations with an interval of several weeks, during which no fungal spores are detected.
How to treat the dog and the premises
Infected fur is full of spores. Therefore, it must be removed from the premises in a timely manner. It is also advisable to minimize the number of rooms that a sick pet visits. This will make cleaning easier.
It is also necessary to exclude contact of others with the dog during treatment. The infected animal must be quarantined for three weeks after starting antifungal medications. Further isolation times should be checked with your veterinarian.
Important! Tablets are given by mixing with fatty foods. This improves absorption and promotes the absorption of the medicine into the body.
Cleaning should consist of thoroughly vacuuming the floors, followed by washing with a solution containing bleach or bleach. The vacuum cleaner will not disinfect surfaces. But it allows you to remove large debris and wool. The concentration of the disinfectant solution used is 1:10, i.e. There should be ten parts water to one part bleach. The room must be cleaned daily.
Treatment of the affected area of skin involves applying an antifungal ointment. For this:
- Carefully trim the hair around the infected area with scissors. The instrument should be wiped with ethyl alcohol before and after the procedure. The cut wool should be burned.
- Wipe the skin with an antiseptic. Use Chlorhexidine or another drug.
- Apply ointment.
Predisposing factors
We have already indicated one of them - youth. But it is even easier for fungi to take root on the skin of an animal that has been treated with glucocorticoid drugs for a long time, since they significantly weaken the body’s immunity. The same can be said about any other hormonal drug, by the way. As you might guess, if the cat was already sick (infection, virus) at the time of contact with the fungal spores, then the process of introducing the fungus is greatly simplified. Worm infestations also widely “open the gates” for dermatomycosis, since the toxins secreted by parasites have a bad effect on the overall resistance of the cat’s body.
Important! In recent years, it has been definitively proven that dermatomycosis can be transmitted by blood-sucking insects, so a cat may well get sick, even if it lives in a city apartment and never goes outside (just like a person).
What distinguishes lichen from other infectious diseases?
Ringworm (dermatophytosis) is highly contagious but not life-threatening. Ringworm is controllable and treatable and is zoonotic and transmitted through direct contact. From a dermatological point of view, the same can be said about infestations with fleas, ticks, Cheyletiellosis, Sarcoptic mange (itching) and otodectosis.
Dermatophytosis is not only highly contagious, but also infectious. Therefore, it shares many aspects with other infectious diseases. So what makes this disease different from other diseases?
- The first and most important aspect is that it is an infectious skin disease of public health concern.
- Second, routine oral or primary care procedures (eg, vaccination, flea control) do not protect other animals or animal populations from the disease.
- Thirdly, this disease is very common in kittens, which are very popular among people. What makes it especially important for accurate and quick diagnosis, as well as making an appropriate decision among breeders or catteries
Clinical signs
The tricky thing about ringworm is that its symptoms do not appear immediately. According to various experts, the incubation period is about 8-36 days. All this time, the animal already poses a serious danger to surrounding cats and people, but symptoms have not yet appeared.
Important! If at this moment the cat is nursing kittens, they are almost guaranteed to become infected. It should be remembered that signs of the disease may generally appear by three weeks of age!
Signs of the disease and diagnosis
Poor living and feeding conditions for cats, the presence of injuries on their skin in the form of abrasions, scratches or scratches, uncontrolled walking of pets and their contact with sick individuals are the main causes of infection. Stray infected cats pose a particular danger in the spread of the disease.
The incubation period can last 3-4 weeks. Lesions can be focal or spread throughout the animal's body.
With “ringworm” ( microsporia ), the clinical symptoms of the disease are superficial:
- limited scaly patches;
- crusts form on the skin;
- hair in the affected areas is sparse;
- wool breaks easily.
A specialist can tell you whether this mushroom is dangerous for people after examining the animal.
Attention. In adults, a latent form is often observed, in which there is no massive formation of crusts, scales and hair loss. The disease can only be diagnosed using a fluorescent examination.
Trichophytosis is characterized by:
- formation of areas of inflamed skin;
- flaky scaly surface in places where the pathogen is localized;
- sharply defined lesions with broken hair.
The diagnosis is made by specialists based on the results of microscopic and luminescent studies, as well as a set of characteristic clinical signs.
What to do?
First of all, no amateur performances! Any “treatment” at home will only lead to the fact that you, your family and the cat will all itch and become dangerous spreaders of the disease. Not a pleasant prospect? Then quickly take your tailed friend to the veterinary clinic! And it would be a good idea for your household to boil (all that is possible) bedding, toys, and wash the floor with a saturated solution of regular bleach. It is advisable to “fry” everything else for a day or two in direct sunlight.
In general, the treatment of dermatomycosis in cats is unique for two reasons: firstly, a vaccine is used for this. Secondly, this is the only fungal disease for which antibiotics are used. Not all kinds, of course, but only griseofulvin. A drug that has no analogues (yes, the expression is tired, but it is true) in the world, which at one time was developed by Soviet scientists. Its disadvantage is severe toxicity. The modern analogue, clindesine, has much more gentle properties, but is also much more expensive.
How does a cat become infected with dermatophytosis?
The concept of dermatophytosis means not one disease, but several, provoked by various fungal microflora. The difference in dermatophytosis lies in the manifestations of the pathology, as well as in the methods of treatment. In veterinary clinical practice, cats are diagnosed with several types of dermatophytoses:
- ringworm;
- favus or scab;
- trichophytosis;
- microsporia.
A dangerous property of ringworm is its ability to be transmitted from sick animals to clinically healthy ones. Not only dogs, but also rodents can become a source of infection for a domestic cat.
The infectious agent has the ability to form a huge number of spores and scatter them into the environment. Infection can occur even if the cat lies on the litter where an infected animal previously lay.
With good functioning of the body's immune system, dermatophytosis goes away on its own, without the intervention of a doctor or the use of medications. Otherwise, lichen affects the pet’s body gradually, starting from a small area of skin, covering new healthy areas. Among the factors that can serve as a kind of trigger for the development of dermatophytosis in a cat are the following:
- a sharp decrease in the cat’s body’s defenses;
- high air humidity indoors or outdoors;
- disturbance in the animal’s diet, deficiency of vitamin and mineral complexes;
- violation of cat hygiene rules (frequent or too infrequent washing);
- use of animal hair and skin care products that do not have the correct chemical composition.
The risk group for infection with dermatophytosis includes elderly cats, sick animals and animals weakened after surgical interventions. Females bearing and nursing offspring are also at risk.
Adults, and especially young children, are susceptible to infection with ringworm.
Danger to humans
We found that ringworm from cats is freely transmitted to humans.
Children and the elderly are susceptible to fungal skin diseases. Treatment of a person is a long process. A mild form of dermatophytosis can develop into a chronic form and negatively affect the entire functional activity of the body.
Over time, the infection weakens the immune system and becomes a conduit for many other diseases. A person can become infected through contact with a cat, even during the incubation period. Spores found on hairs can enter the human body when touched. Therefore, it is necessary to treat in the early stages, as quickly as possible, in order to prevent the spread of fungi.
Prevention
Preventing lichen is easier than treating it. Be sure to visit the veterinary clinic at least once a year. Examine your cat after every walk or contact with another animal. Protect from the street. Do not allow someone else's pet to eat from a bowl or lie on the pet's bedding. When visiting exhibitions, avoid contact with other pets. Take care of nutrition and increase your pet's immunity.
Have you ever encountered ringworm? Leave questions in the comments to the article