When exposed to sunlight, chemicals or chronic inflammation, squamous cell carcinoma occurs in cats. This cancer affects the skin or oral mucosa. White-haired animals are more prone to the disease. Treatment consists of the complex use of chemistry, laser therapy and surgery. If pathology is detected early, doctors give a positive prognosis.
General description and mechanism of the disease
Squamous cell carcinoma in cats is a disease that develops from epithelial cells. The disease can develop in the mouth or on the skin.
The basis of cancer is made up of flat and round epithelial cells that have poor differentiation. Such cells are usually small in size, have a large nucleus and little cytoplasm. Sometimes they may have a large amount of cytoplasm, pericellular vacuolation and a small nucleus. In this case, they have the appearance of non-keratized angular cells.
Pathological transformations in cells occur under the influence of various factors (for example, excessive exposure to UV rays, chronic diseases).
Squamous cell carcinoma has three stages of development:
- cytological. Changes occur at the cellular level. Therefore, this stage is considered non-diagnostic. The cells may be poorly differentiated, small in size and with basophilic cytoplasm, or epithelial angular non-keratized with a high content of cytoplasm;
- dermatohistopathological. At this stage, irregular masses of keratinocytes of atypical structure are determined. The altered cells proliferate and invade the skin;
- regional. It assumes the formation of metastases in the lungs and regional lymph nodes. At this stage, diagnostic studies such as histology/cytology of lymph node tissue samples and radiography in 3 projections of the chest are effective.
This is a fairly aggressive disease that can spread quickly and form metastases. The disease occurs in 15% of pets. It is most often diagnosed in animals aged 10 years and older whose owners are active smokers.
Something else interesting: Anemia in cats - symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Why does squamous cell carcinoma appear?
In malignant oncology, a cell appears from the epithelium that is prone to uncontrolled growth. If the number of reproduction cycles of healthy epithelium is strictly limited, then in cancer cells divide quickly, which forms a tumor. Such tissue can grow into blood vessels, mucous membranes, muscles and cause severe pain. When the tumor is destroyed, daughter cells enter the blood or lymph, settle and grow in other organs.
Squamous cell carcinoma can be caused by:
- exposure to tobacco smoke;
- feeding your cat canned food, especially tuna;
- constant use of flea collars;
- local injuries with damage to the mucosa.
All these changes trigger pathogenesis and contribute to the development of cancer. If possible, it is better to exclude trigger factors and engage in prevention, taking into account the recommendations of the veterinarian.
How it manifests itself
The clinical picture of this disease depends on the type of disease. Skin cancer does not show any symptoms in the early stages of its development. As the disease progresses, the following signs appear:
- wounds on the skin heal slowly;
- abrasions and ulcers form that do not disappear for a long time. The ulcers crust over and bleed. They have convex edges. If the wounds are infected, they develop plaque and smell bad;
- non-healing purple spots of unknown etiology form on the skin. Externally, such areas of skin resemble cauliflower red cabbage;
- Hair loss occurs in damaged areas.
The symptoms described above resemble an infectious infection, which complicates the diagnosis of the disease. The fact that the diagnosis was made incorrectly is evidenced by the lack of response to treatment (the wounds continue to grow).
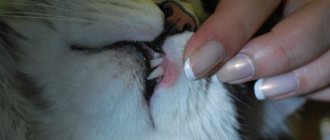
This type of cancer in the oral cavity appears as erosions and ulcers. The affected areas periodically fester. Therefore, the animal’s breath begins to stink strongly. The disease prevents the pet from eating normally, which leads to a decrease in its body weight.
Over time, a sick cat's gums begin to bleed, teeth become mobile, and profuse salivation is observed. If the cancer is localized in the upper jaw, nasal discharge may appear.
As the tumor grows, the bones become distorted, which is clearly visible from the outside. If nothing is done, there is a risk of pathological fractures.
Causes of a swollen lip in a cat
The reason that actually caused the lip swelling is not always easy to identify. In some cases, a special tool, analysis data and, of course, experience are required. Veterinarians call the main causes of this type of illness:
- Trauma;
- Eosinophilic granuloma;
- Allergies;
- A bite of an insect;
- Gingivitis and stomatitis;
- Neoplasm;
- Cyst;
- Tumor of the salivary glands;
The list of problems that can cause swelling of a cat’s lower lip is quite long. In order to help your pet as quickly as possible, you need to pay attention and study relevant literature. Below are the most common reasons why a cat has a swollen lower lip.
Injury
This reason is one of the most common. It could be caused by a bad fall, hitting a very hard object, licking a tin can, or eating fish. Treatment is symptomatic.
In some cases, simple wound treatment using an antiseptic drug is sufficient, and sometimes sutures are necessary. It all depends on the severity of the injuries received by the cat.
Eosinophilic granuloma and allergy
The first external manifestations of this disease are very similar to the manifestations of herpes on the lips, but the cause most often has an allergic origin.
You might be interested in: What causes black spots on a cat's chin?
The term is based on the name of the cells that underlie the cat's body - eosinophils. If an allergic reaction occurs, they accumulate in a lump and take the form of a solid formation.
It is difficult to independently establish this diagnosis, because its symptoms have much in common with the symptoms of fungal and bacterial diseases. The reliability of the data is guaranteed only by a laboratory analysis showing an increased number of eosinophils in the pet’s blood.
The causes of allergies are often:
- Products;
- Plant pollen;
- Household chemicals;
- Perfumery;
- Insect bites;
- Parasites;
For quality treatment, it is necessary to identify the allergen and limit the animal’s contact with it. In most cases, this is enough for the inflammation of the cat's lower lip to go away.
Stomatitis and gingivitis
Oral diseases are often accompanied by changes in the shape of the lower lip in cats. With gingivitis, the appearance of a red border around the tooth, the presence of inflammation of the gums, and bad breath are noted. The animal's appetite becomes less, as eating causes discomfort. In some cases, gingivitis is a direct indication of serious diseases: diabetes or kidney failure. If your pet is not treated, he may be left without teeth.
With stomatitis, the oral cavity is affected by fungi of the genus Candida. Clear signs indicating this are white plaques in the animal's mouth and tongue. The owner can see them on his own. Stomatitis may be caused by a malfunction of the immune system. In such cases, the root cause of the disease is first eliminated, and then complex treatment with antifungal and vitamin preparations is carried out.
Cancerous tumors and cysts
This reason is quite rare, more often in animals that are already quite old. The process develops gradually, the growth of the tumor occurs over weeks and months, until one day it becomes clearly visible. In most cases it is squamous cell carcinoma. Its symptoms:
- Increased salivation.
- Non-healing ulcers.
- Unpleasant smell.
If a cat's lower lip is swollen and the cause is a malignant neoplasm, treatment is often difficult and sometimes ineffective. If the formation is benign or is a cyst, then it is treated surgically.
You may be interested in: A cat has blood in its stool: causes, treatment and prevention
Tumor of the salivary glands
If the fact of the injury is noted, and timely assistance to the animal was not provided, then serious consequences may arise. The salivary glands are often damaged, causing their ducts to fill with thick secretions and become clogged. A cyst appears. This occurs specifically on the lower lip because the salivary glands there are located directly under the jaw. In some cases, the cyst grows and begins to cause discomfort to the animal when swallowing and breathing.
To alleviate your pet’s condition, you need to make a puncture in the area of the formation and remove the substance that has filled the cyst. If this measure does not help, the salivary gland must be removed.
Types of cancer
Today, there are two types of squamous cell carcinoma in cats: skin and oral cavity.
Skin
Squamous cell skin cancer in cats usually develops on the nose, ears, and corners of the mouth (in areas where there is little hair). Often occurs due to prolonged exposure of the animal to direct sunlight.
Something else interesting: E. coli in cats
The risk group includes cats that live in warm and hot climates. But this type of cancer also occurs in northern latitudes. Most often, animals with white fur or light spots suffer from this disease. Also, the risk of developing cancer increases as you age.
This form rarely leads to the formation of metastases. Sometimes they are found in lymph nodes located close to the site of the lesion.
Oral cavity
This form of squamous cell carcinoma in cats develops under the tongue, on its surface, in the tonsil area or on the upper palate. Doctors suggest that this disease is formed due to the habit of cats to lick their fur.
Cancer is caused by carcinogens that get on the wool when it is treated with anti-mite or anti-flea agents. Chronic inflammation of the oral cavity (for example, stomatitis) can also trigger the disease.
Methods for diagnosing tongue cancer
Doctors recommend that every person regularly examine their oral cavity using a mirror. Any strange sores, spots, or bumps should be a reason to visit a doctor. You need to have regular dental checkups.
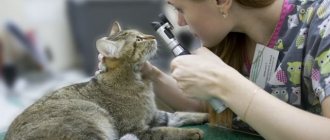
If a malignant tumor of the oral cavity and oropharynx is suspected, the examination begins with an examination by a doctor. The doctor examines the oral cavity, pharynx (pharyngoscopy), larynx (laryngoscopy), and palpates the subcutaneous lymph nodes. If formations resembling cancer are found on the tongue, a biopsy is performed: a fragment of pathologically altered tissue is obtained and sent to the laboratory for microscopic examination. It is imperative to test for human papillomavirus.
If an oncological disease is diagnosed based on a biopsy, it is necessary to assess how far the cancer has spread in the body: whether the tumor has grown into neighboring organs, whether there are foci in regional lymph nodes, or distant metastases. The following diagnostic methods help with this:
- CT scan;
- chest x-ray;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- positron emission tomography;
- X-ray contrast studies.
Features of treatment
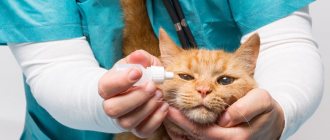
Treatment for cancer depends on its location. With timely initiation of treatment, the skin form is often completely cured. Tumors are removed surgically. Small tumors are eliminated by laser ablation. If lymph nodes or other organs are affected, chemotherapy or radiation therapy is performed.
In the oral cavity, cancer is removed through surgery. In this case, irradiation is ineffective. Treatment often involves a combination of radical resection and radiation. This reduces the risk of metastasis.
How to treat tumors in the throat?
The treatment regimen is determined by the veterinarian individually based on the etiology of the tumor; self-medication can harm the animal. If the throat is swollen due to cancer, surgery is performed. Excision of the tumor is carried out, capturing healthy tissue. A tracheostomy tube is often required to facilitate the breathing process. If metastases are detected, chemotherapy is prescribed. Cytostatic drugs are used that prevent tumor development by destroying malignant cells. However, this method has many side effects. Drug treatment includes immunomodulatory agents, vitamin-mineral complexes, antibiotics (for suppuration). Papillomas can be treated with liquid nitrogen or laser.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of squamous cell carcinoma, you need to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- minimize your pet’s exposure to the street in bright sunshine – from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m.;
- on a hot day, be in the shade with your cat;
- When the first symptoms appear, consult a veterinarian.
Squamous cell carcinoma in cats is a serious disease that requires timely and professional treatment. Otherwise, the animal will experience discomfort and may even die from related ailments.
Establishing diagnosis
The veterinarian can make a preliminary conclusion after examination, having detected signs of squamous cell carcinoma. But in order to draw final conclusions, a referral is issued to the laboratory and for scanning:
- X-rays with contrast or ultrasound are performed to assess the extent of damage to surrounding tissues;
- a biopsy will help conduct a histological examination and determine the type of cancer;
- tests will confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment is prescribed only after examination. Cancer is usually differentiated from local inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane, from some systemic pathologies and from benign oncology.
Forecast
If such a disease is detected in your pet, you should not immediately give up. Modern veterinary medicine is developing rapidly, and there are advances in the treatment of oncology in cats.
The highest percentage of cases of complete recovery occurs at the initial stage, while the disease has not yet completely started and has not spread throughout the body. The more differentiated the tumor cells are, the higher the likelihood of complete recovery.
If the lymph nodes are affected, the prognosis is less favorable and the possibility of cure is low.
Note!
Cancer is a very unpredictable disease. There have been cases when specialists refused to treat the animal, considering it hopelessly ill, but the owner continued to take good care of the cat, feed it properly, and as a result the pet completely recovered.