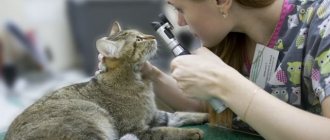
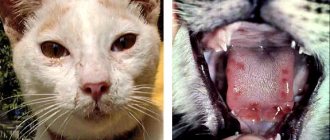
Eyes are an indicator of a cat's health. The vital organ reacts sensitively to any external and internal stimuli. Before you get a pet, you need to know what pathologies can manifest in cats throughout their lives. First of all, pay attention to the condition of the eyes. They are covered externally by the upper, lower and third eyelids. The prevalence and type of disease, intensity, and the length of time that passes before the immune response appears influence the development of dysfunction of all organs. What eye diseases do cats have? We will talk about this in our article.
Eye diseases in cats: an overview
Why do my cat's eyes hurt?
The causes of the disease may be due to external factors, breed and predisposition to any ophthalmological disease. At any age, the disease requires treatment. Otherwise, the animal may become completely blind: cell decay and protein decomposition begin.
Possible causes of the disease
- Metabolic disease.
- Problems with intraocular fluid.
- Injuries, concussions, blows, bruises of varying degrees.
- Congenital pathology, if infectious diseases were transmitted to the kitten during birth.
- Old age. With age, metabolism slows down and the eye organ becomes less protected from external influences.
Extreme sports people and mixed breeds are most susceptible to eye diseases
Extreme sports people and mestizos are the most susceptible to diseases. Less commonly, eye pathology is observed in the “British” and “Scots”. Isolated cases occur in outbred cats. The main point, from the point of view of differentiating eye diseases, is the factors that determine the presence or absence of infection:
- Conditions of detention.
- Preventive measures.
- Stress levels matter most to cats.
- The presence of a source of the pathogen and its concentration in the environment.
- Concomitant diseases that cause predisposition to the infectious process.
Taking these factors into account, we can conclude that in inadequate conditions of detention in the absence of preventive measures, when the animal is in a stressful state, there are greater risks of eye infectious diseases.
Stress can cause eye problems in cats
Types and classification of eye diseases
Eye diseases in cats are a broad and multifaceted group of diseases. Pathologies are conventionally divided into two types:
- Non-inflammatory (non-infectious) diseases.
- Inflammatory (infectious) diseases.
Table. Common eye diseases in cats
| Non-communicable diseases | Infectious diseases |
| Cataract | Keratitis |
| Mechanical damage | Glaucoma |
| Drooping of the upper eyelid | Panophthalmitis |
| Retinal disorder | Conjunctivitis |
| Eversion and non-closure of eyelids | Inflammation and ulcer of the cornea |
| Foreign body entry | Neoplasms of the conjunctiva |
The list of inflammatory eye diseases in cats includes types of keratitis: superficial, superficial vascular, deep and purulent. Some cat breeds have a fold on their cheeks that injures the cornea of the eye. Then breed keratitis occurs, which must be prevented and treated.
Video - Eye diseases in cats
Infectious diseases
Most of the troubles for cats are caused by infectious diseases that occur in severe forms. A very important and distinctive point of all infectious eye diseases is the incubation period from the moment of infection by the pathogen until the manifestation of symptoms noticeable to cat owners and veterinarians.
Viruses are capable of mass distribution between animals and can be transmitted by airborne droplets from an infected to a healthy organism. Based on the nature of the pathogens that cause eye diseases, there are several types of microorganisms:
- Viral.
- Fungal.
- Protozoans.
- Bacterial.
Most of the troubles for cats are caused by infectious diseases that are severe.
The most important are the viral and bacterial group of infections.
Clinical symptoms of inflammatory processes
The vast majority of diseases begin with exactly the same signs, when the cat’s condition worsens sharply:
- In the acute phase, an increased temperature is observed.
- Increased loss of fluid in the body.
- Complete lack of appetite.
- Lethargy and apathy.
When specific signs of pathology appear, it is most likely that there is a certain infection in the eyes. The precursors of eye diseases are the following:
- Eyelash growth inward.
- Inversions and inversions of the eyelid.
- Squinting and photophobia.
- The third eyelid extends half the eye or more.
- Swelling, redness, or clouding of the fundus of the eye.
- Lacrimation, other discharge and discharge from the eyes.
Entropion of a cat's eyelid
Symptoms are clearly visible on white fur, even if the eyes are treated with a solution. Only in the development of the process can clinical signs characteristic of each individual isolated disease be observed. If eye diseases are not treated in a timely manner, the animal’s condition worsens.
Symptoms of blepharitis in cats
Symptoms vary depending on the type of disease. In 80% of cases, veterinarians are faced with redness of the eyelid and its inflammation. Clear or purulent discharge appears in the corners. The pet is nervous and tries to scratch the inflamed area. Such actions are aimed at eliminating itching. Gradually, the size of the eyes begins to decrease, the pet is limited in the viewing angle.
Advanced blepharitis
Against the background of blepharitis, conjunctivitis often begins to develop. Depending on the expression of symptoms, you can understand how long the disease lasts.
Purulent discharge from blepharitis in cats
But, in addition to standard symptoms, there are also specific manifestations. For example, if we are talking about a fungal disease. Cat owners note that against the background of this disease they experience eyelash loss and baldness in the eye area.
If the cause of the disease is autoimmune processes, blistering formations can be found on the cat’s body. In such a situation, a biopsy is required to make a correct diagnosis.
Blistering formations in blepharitis
When inflammation is caused by infection, this is indicated by the animal's painful condition. The cat becomes lethargic, apathetic, eats and drinks practically nothing. As the disease progresses, the animal's body begins to feel feverish. In case of infection, antibacterial therapy should be started immediately.
Veterinarians often encounter scaly blepharitis. With this type, the eyelids turn red and swelling spreads. The edge of the eyelid thickens and becomes dense. Against the background of this process, the shape of the eyes narrows. Gray small scales form in the eyelash growth area, which affect eyelash loss. If the scales begin to fill with pus, then the disease develops into an ulcerative condition. This disease develops much faster. The wounds begin to scar, and the eyelid literally turns in the opposite direction.
The most common eye diseases in cats: photos
Glaucoma
Intraocular pressure increases. Poor drainage of eye fluid appears. The result is damage to the optic nerve and complete loss of vision. There are primary and secondary glaucoma. Primary begins unexpectedly due to disruption and improper outflow:
- The pupils dilate.
- No reaction to light.
- The cat begins to squint.
- Eyeballs are sunken.
- Redness of blood vessels in the whites of the eyes.
- The front of the eyes takes on a dark shade.
Glaucoma in a cat
Cataract
A fairly common occurrence in cats is when the lens of the eye becomes clouded. The lens is a natural, clean lens. Light passes through a clear lens without refraction. The image reaches the retina and is then processed by the brain.
If the natural lens becomes cloudy, the brain cells will not be able to process the image correctly. Bright, shiny eyes indicate the absence of disease. But they, like people, get sick, grow old, and lose their sight. The main symptoms of cataracts are clouding of the eye and a cloudy appearance.
Cataracts are quite common in cats.
Keratitis
Accompanied by an inflammatory process. The cornea of the eye is damaged under the influence of internal and external unfavorable factors. It occurs both as the main disease and as a concomitant with other inflammatory processes. Any impact on the cornea may cause keratitis in a cat.
Keratitis
Conjunctivitis
The membrane of the eye becomes inflamed, the process of inflammation from the inner surface spreads to the eyeball. Conjunctivitis can be acute, purulent, catarrhal. Depending on the diagnosis and form of the disease, treatment is prescribed. Primary conjunctivitis manifests itself as an independent disease. The secondary type accompanies other diseases that appear in cats.
Conjunctivitis and uveitis in a cat
Types of blepharitis
There are several varieties of this disease, depending on the form of the disease and the causes of the lesion. Highlight:
- anterior, in which only the edge of the eyelids along the growth of the eyelashes is affected;
- in the posterior case, the meibomian glands are affected;
- angular affects the mucous corners of the eyes.
Table. Main types of blepharitis
| No | View | Description |
| 1 | Simple | It is characterized by redness of the eyelid and thickening at the edges. Purulent discharge accumulates in the corners of the eye. Meibomian glands expand |
| 2 | Scaly | The eyelid is subject to severe swelling and redness. Purulent inflammation forms. White fluid accumulates in the corners of the eyes. Scales appear along the eyelash line, reminiscent of dandruff. Very often complicated by conjunctivitis |
| 3 | Ulcerative | Develops along with the purulent process. Ulcers affect the roots of the hair. The eyelids turn red and swell. Yellowish dandruff appears. When the ulcers are affected, a bleeding ulcer appears. In the absence of a proper response, the development of various pathogens is possible |
| 4 | Demodectic | The cause of this disease is tick infection. The disease is possible due to a weakened immune system. Inflammation appears in the eyelid area. This form is difficult to diagnose and difficult to treat. Most often ends with surgery |
| 5 | Allergic | Redness and swelling of the eyelids, severe itching, aversion to light, lacrimation. The cat behaves restlessly, rubbing its eyes with its paw and on the furniture. Most often occurs due to poor diet or contact with chemicals. |
| 6 | Meibomian | Settles in the meibomian glands. The eyelashes stick together and yellow pus forms on them. A thick white substance and mucus appears in the corners of the eyes |
| 7 | Phlegmonous | Unilateral form of blepharitis. Accompanied by high temperature. There is pus in the corners of the eyes. The tissue on the eyelids becomes scarred. In the absence of a proper response, necrosis occurs |
Video - First signs of eye disease in dogs and cats
How to treat eye diseases at home?
When treating the eyes, medicinal solutions, drops and ointments are used. First, the eye is washed with furatsilin or weak manganese solution. Then drops are instilled and antibiotic ointment is applied. In particularly severe cases, surgery is performed. To select a treatment method and medications, it is best to consult a veterinarian.
Medicinal solutions, drops and ointments are used to treat the eyes.
Treatment of cataracts in cats
To see the symptoms, you just need to look into your pet's eyes. If a small white spot appears instead of a pupil, most likely the first symptom of cataract has appeared. Regardless of age, it is necessary to periodically examine the cat.
Medical and surgical treatment methods are used. The medicinal method used is tissue therapy according to V.P. Filatov with the introduction of aloe extract, antibiotics, and vitamin preparations. Retrobulbar blocks are performed according to V.V. Aurorov so that the substances get behind the eyeball.
On a note! Conservative methods do not always lead to a positive effect. It is possible to slow down the development of cataracts in cats, but it is not always possible to completely cure them. The only effective method of getting rid of cataracts is surgery.
Medical and surgical treatment methods are used to treat cataracts.
Help for eyes with conjunctivitis
It is better not to torture the cat, but to immediately take it to a veterinary clinic. The disease appears as a result of an allergic reaction or a viral, less often bacterial, infection. Effective eye care for conjunctivitis:
- Before instillation, the eyes are washed with 0.05% Chlorhexidine (for external use) using a gauze pad or cotton pad.
- Eye drops for cats and dogs “Tsiprovet” are instilled into the inner corner of the affected eye - two drops each.
- After five minutes, Tobrex eye drops are instilled - two drops each.
- After another five minutes, Actipol is dripped.
- Tetracycline one percent eye ointment is used at night. Apply along the edges of the affected eyelid.
The instillation procedure is carried out six times a day for five days. If conjunctivitis does not go away, treatment continues for the next 5-9 days, reducing the dose to four times a day. During illness, especially in the cold season, it is not recommended to let your cat go outside.
Conjunctivitis is treated with drops
Help with eye pain and purulent inflammation
Purulent inflammation and lacrimation is a pathological condition when, due to the penetration of a viral infection, the eyes stick together. There are a large number of varieties of purulent inflammation. One of the most common is panophthalmitis - serious damage to the entire eye.
First aid consists of treating the eyes with Furacilin. The antibiotic “Azenil” is given orally in the form of a suspension (the powder is diluted with 9 ml of water). The medicine is used for a week. If the kitten is small, it is enough to dilute a quarter teaspoon of the suspension with one teaspoon of distilled, mineral or boiled water. Stir thoroughly until smooth.
In addition to oral administration of Azenil, the antibiotic eye ointment Terramycin or syntomycin eye ointment is used. Gently apply a cotton swab to the affected eye two to three times a day.
Drops effectively help with inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drops “Barrier” are instilled two drops 2-3 times a day for a week.
This is what panophthalmitis looks like in cats
Main symptoms and treatment methods
For timely and adequate treatment, it is necessary to know the characteristic signs of eye diseases.
Features of conjunctivitis
One of the common diseases in pets is conjunctivitis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs for the following reasons:
- injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- allergic reactions;
- infection with worms and ectoparasites;
- lack of vitamins in the body.
There are several forms of conjunctivitis: catarrhal, follicular, ulcerative and purulent. The main symptoms indicating the development of conjunctivitis are:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- the appearance of pus;
- eyelid gluing;
- photophobia;
- cloudiness.
Purulent conjunctivitis is indicated by bilateral inflammation. In addition, the owner notes the following symptoms of the disease:
- general depression of the pet. He becomes lethargic, does not want to play and frolic;
- high body temperature. Normally, the body temperature of an adult animal is 38-39°C; in children, the figure may be half a degree higher (38.5-39.5);
- poor appetite or its complete absence also indicates a painful condition;
- the cat tries to avoid inspection and palpation, this process causes him pain in the area of the eyeball;
- in advanced cases, inflammation spreads to the cornea.
Treatment steps are as follows:
- A visit to the veterinary clinic to remove a foreign object from the eye.
- Washing can be done at home every 3-4 hours. For the procedure, use a warm solution of manganese, furatsilin, chamomile or calendula decoction. Herbs help reduce inflammation, eliminate swelling and itching. In addition, natural decoctions have anti-inflammatory properties. Manganese copes well with infection, but at the same time dries out the mucous membrane. Therefore, a pale pink solution is used. It is recommended not only to thoroughly dissolve the manganese crystals, but also to filter the resulting composition through several layers of gauze. This guarantees the absence of crystals in the water, the accidental entry of which can cause a burn to the mucous membrane. Furacilin is diluted in hot water (1 g per 5 l). Used for washing while warm.
- Applying ointment. At a pharmacy or pet store you need to buy any eye ointment, for example, Tetracycline, Syntomycin or Erythromycin. The composition is placed behind the eyelid. The procedure is carried out wearing gloves. The ointment should be applied carefully with a special glass rod. Applying with fingers or cotton swabs is unacceptable. After each application of the ointment, the stick is disinfected in boiling water. This is necessary in order not to spread the infection in the future. Some people use an ointment tube to apply the ointment. This must be done extremely carefully, otherwise bacteria will settle on the spout of the tube and, during the next treatment, will again get into the eyes.
- Instillation is carried out only in washed eyes. It is necessary to instill 2-3 drops every 4 hours.
- If the disease is caused by an infection, a course of antibiotic therapy is necessary.
- A solution of novocaine and hydrocortisone (ratio 1 ml/0.2 ml) helps relieve swelling. The composition is instilled into the conjunctival sac.
- Chronic pathology is recommended to be treated with silver-based drugs.
- In a veterinary hospital, a novocaine blockade is carried out. It reduces pain and improves tissue nutrition, which leads to a speedy recovery.
- For follicular conjunctivitis, surgical intervention is performed. After the operation, ointments and antibiotics are prescribed.
Keratitis and its types
Inflammation and clouding of the cornea in cats indicate the development of keratitis. The disease is acquired and requires proper treatment. The reasons for the development of keratitis are:
- mechanical injuries of the cornea. The ingress of solid dust particles, grains of sand, blades of grass, and fibers leads to mechanical damage;
- conjunctivitis. The combination of diseases leads to the formation of keratoconjunctivitis;
- thermal or chemical burns;
- infections and viruses. Typically, keratoconjunctivitis develops against the background of a general infection of the body (herpes, adenovirus). In this case, complex treatment is required, otherwise it will not be possible to get rid of keratitis;
- allergic reactions to food, dust, pollen, household chemicals;
- inflammatory processes in the lacrimal glands, leading to drying out of the cornea;
- lack of vitamins in food;
- genetic predisposition to the disease (in British, Sphynx, Persian and Siamese cats).
The appearance of the following symptoms should alert the cat owner:
- clouding of the cornea, its dullness and roughness;
- accumulation of blood vessels on the cornea;
- the discharge causes the fur around the eye to become wet;
- accumulation of pus;
- fear of bright light;
- the appearance of scars indicates the irreversibility of the process. The animal may go blind.
Treatment is prescribed after a thorough examination and confirmation of the diagnosis. The initial stage of the disease can be treated with drugs. In advanced cases, laser correction of the cornea is used.
The following groups of drugs are used as complex therapy:
- antibacterial agents (Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Gentamicin eye ointment, Tobrex);
- antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs (Cycloferon, Gamavit).
Keratitis requires long-term treatment and special care for your pet. If the veterinarian's instructions are not followed, the animal may go blind.
Third eyelid prolapse
The nictitating membrane in cats is a kind of protection provided by nature. The third eyelid is a whitish film located in the inner corner of the eye. The prolapse of this membrane can be noticed by the following signs:
- uncontrollable trembling, closing eyelids;
- increased lacrimation;
- redness around the eye;
- copious discharge of mucus or pus.
Prolapse of the nictitating membrane is associated with the following diseases:
- conjunctivitis;
- eye damage;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- fungal pathologies;
- allergic reactions;
- helminthic infestations.
If you suspect third eyelid prolapse, you should wash your pet's eyes with a warm decoction of chamomile or calendula. If after a few hours the nictitating membrane has not returned to its place, a visit to the veterinarian is necessary. Surgery may be required.
Detection and treatment of blepharitis
There are several types of blepharitis in cats:
- simple;
- with the formation of ulcers;
- scaly;
- meibomian;
- demodectic;
- allergic.
If left untreated, simple blepharitis develops into ulcerative blepharitis. The plaque that appears along the growth of the eyelashes disappears, and ulcers appear in its place. The progression of the disease is accompanied by loss of eyelashes, further damage to the conjunctiva and eyes, and panophthalmitis develops.
The initial form of blepharitis is similar to the manifestations of conjunctivitis. The cat is worried about the following symptoms:
- lacrimation;
- itching;
- swelling and redness of the eyelids;
- reduction in eye size.
The causes of pathology include:
- viral diseases;
- tick-borne infection;
- lichen;
- injuries;
- allergic manifestations;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- endocrine and autoimmune disorders.
After the tests, long-term treatment will be required:
- the eyelids are treated with brilliant green, alcohol-ether;
- to soften the scales, use saline solution and petroleum jelly, then remove them with a cotton-gauze swab (necessarily sterile);
- Sofradex, Betnesol, Iris are prescribed for instillation;
- the conjunctival sac is filled with one of the suspensions - Gentamicin, Syntomycin, Methyluracil.
To prevent eye scratching, a protective collar is needed. You can wash your eyes with herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula, hyssop, sage, St. John's wort).
Danger of cataracts
The development of cataracts is indicated by clouding of the lens. It rarely develops in young individuals; it occurs against the background of infectious diseases. Occurs more often in older pets. Some breeds (Persians, exotics) have a genetic predisposition to the disease. Cataracts can be suspected based on the following signs:
- the animal walks carefully and very slowly;
- spatial orientation is impaired;
- in an unfamiliar environment, the cat bumps into objects and furniture.
After confirming the diagnosis, the veterinarian prescribes the necessary course of treatment. The process of clouding of the lens is irreversible; doctors can stop the rapid progression with the help of medications.
To maintain vision, use Taufon and Quinax drops. They are instilled 2 times a day, 1 drop in each eye for a month. Then they take a month's break and repeat the course. Treatment is carried out constantly, otherwise the cat may go blind.
Consequences of glaucoma and its treatment
Glaucoma is characterized by an increase in eye pressure. According to the generally accepted classification, the disease can be congenital, as well as open- and closed-angle. There are primary and secondary visual impairment. Primary glaucoma has a poor prognosis. In secondary cases, it is important to identify the cause of the pathology and eliminate it. In this case, the chances of vision restoration increase.
An important symptom to look out for is an overly dilated pupil. The eyeball hardens and enlarges, and traces of hemorrhages are noted on the conjunctiva. The open-angle form is characterized by clouded areas of the cornea. The closed-angle form is characterized by a ring-shaped closed opacification.
Pressure in the eyes reduces vision and leads to poor health. The pet needs consultation with an ophthalmologist and urgent treatment. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor conducts an examination with a slit lamp and measures eye pressure with a Maklakov tonometer.
With open-angle glaucoma, the cat needs urgent prescription of drugs that reduce intraocular pressure. The following groups of drugs are used:
- diuretics (Mannitol);
- miotics (Pilocarpine, Physostigmine, Phospholine);
- adrenergic blockers (Timolol, Betaxolol);
- hyperosmotic drugs (Glycerin).
Corticosteroids may be an additional prescription. Conservative treatment methods have little effect on the development of the disease, so many pets undergo surgical intervention:
- cyclophotocoagulation;
- cyclocryotherapy;
- cyclodiathermy.
Veterinarians also use liquid nitrogen and retrobulbar injection of alcohol in the treatment of glaucoma. If vision cannot be restored, an intraocular prosthesis is installed. Removal of the eyeball may also be suggested.
Symptoms and causes of panophthalmitis
Purulent inflammation that affects all tissues of the eye is called panophthalmitis. Registered for complex wounds of the eyeball in cats. The main causes of the pathology are pneumococci, staphylococci, and E. coli that enter the eye from the outside during injury. The main signs of the disease:
- excessive tearing;
- uncontrolled closing of the eyelids;
- avoiding bright light;
- swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva;
- clouding and swelling of the cornea;
- possible pinching of the mucous membrane of the eye.
The pet's vision sharply decreases and he is bothered by pain in the eye. As the disease progresses, other symptoms appear:
- anterior displacement of the eyeball;
- restriction of eye mobility;
- violation of the integrity of the sclera.
Treatment of panophthalmitis at home is impossible. The pet needs urgent hospitalization and surgery. The eyeball is removed and the eyelids are sutured. The sutures are removed after 24 hours, and the orbit must be lubricated with antiseptic agents for 7 days.
A dangerous complication of the disease is the transfer of purulent infection to the brain. In this case, the animal dies. Therefore, when the diagnosis of panophthalmitis is confirmed, the eye must be removed.
Combating inflammation of the nasolacrimal ducts
Excessive lacrimation and discoloration of the fur around the eyes are the main sign of an inflammatory process in the nasolacrimal ducts. The problem usually occurs in kittens, but can also affect adult animals. The causes of pathological lacrimation are:
- various eye diseases;
- blockage of tear ducts;
- foreign objects trapped in the lacrimal sac;
- inversion of the eyelids and curling of the eyelashes.
Treatment involves washing the canal or removing the lacrimal gland. If the amount of fluid released is minimal, conservative treatment is stopped. Obstruction is eliminated by rinsing through the nasal passages. Use disinfectant solutions of silver nitrate, furatsilin, boric acid, penicillin with novocaine (for pain relief).
In difficult situations, excision of the lacrimal sac or removal of the lacrimal gland is practiced. With excision, there is a possibility of the problem reoccurring due to the appearance of a scar.
Surgical intervention for entropion of the eyelid
Entropion of the eyelid occurs as a result of weakness of the ligaments that hold the skin folds. There are primary and secondary forms of pathology. The primary form refers to congenital ailments, while the secondary form occurs for a number of reasons already during the pet’s life. The main factors causing the development of the disease are:
- hereditary predisposition. Most often, the problem is identified in Persians, British, Scots, Maine Coons and Sphynxes;
- injuries;
- foreign objects in the eye;
- eye diseases accompanied by inflammation.
In rare cases, volvulus in kittens goes away on its own. But much more often, pet owners turn to specialists for help and treatment. The veterinarian performs surgical intervention, which allows you to get rid of the disease forever.
Dangerous consequences of entropion can include:
- chronic keratoconjunctivitis;
- corneal ulcer;
- ingrowth of eyelashes into the eyelid or cornea.
Characteristic signs of the disease:
- swollen, modified eyelid;
- profuse lacrimation;
- fear of light.
Causes of eyelid fusion
The anomaly can be congenital or acquired. The second form of the disease occurs against the background of head and eye injuries, eyelid burns, and also develops with chronic blepharitis. A characteristic sign of fusion is the inability to open the pet's eye, as well as the presence of scar tissue between the eyelids. Only a surgeon can help your pet.
Signs of lagophthalmos
Lagophthalmos is characterized by incomplete closure of the eyelids. The cat's palpebral fissure is visible even during sleep. Additional symptoms: lag of the lower eyelid from the eyeball, excessive production of tear fluid. The factors causing the pathology include paralysis of the facial nerve, eversion or abnormal structure of the eyelids. The only way to get rid of the problem is surgery.
Surgical treatment of ptosis
Involuntary drooping of the upper eyelid in animals indicates the development of ptosis. The cause may be muscle atrophy and facial nerve paralysis. Often, ptosis develops against the background of an inflammatory process. It cannot be done without surgical intervention.
Degenerative processes in the retina of the eye
Cats over five years of age may experience degenerative processes that affect the organ of vision. In case of dystrophy, atrophy, or detachment of the retina in especially severe cases, microsurgical operations are performed on the eyeball to restore vision and improve the health of the pet.
Cats over five years of age may have degenerative processes affecting the eyes.
What is anisocoria?
The pupil in cats is located in the center of the iris and allows light to pass through the eye into the retina. The pupil constricts or dilates according to the amount of light entering the eye, with both pupils typically dilating in dim light and constricting in bright light. Anisocoria is a condition in which a cat's pupils are different sizes, or in other words, one pupil is larger than the other. In some cases, the abnormal pupil may be the one that is smaller; in other cases, the larger pupil may be abnormal.
Trauma or foreign object in the eye
If a kitten's eyes protrude from their sockets, this indicates that the eyes are poorly protected and are at additional risk of injury. Most often occurs in the summer when dry grass appears. Especially often, young pets with damage to the visual organ are brought to see an ophthalmologist. Eye injuries vary in severity:
- Bumps and bruises.
- Concussion injuries.
- Burns of various types.
- Internal and external wounds on the cornea of the eye.
- Penetration of foreign bodies and blunt objects into the eye.
If your eyes hurt due to a mechanical injury, you will need immediate help from your doctor. As first aid, the eyes are washed with clean water at room temperature or with special ophthalmic antiseptics. It is necessary to monitor the tear flow so that the liquid flows to the nose. A light bandage using sterile gauze is applied to the injured eye. It is slightly moistened with water or an ophthalmic septic tank.
Only a veterinarian can adequately help an animal.
Some household chemicals and home renovation products can cause eye burns. By blocking access to repair work sites, your cat can be protected from various burn injuries. Regarding eye injuries, it is impossible to give advice for all situations. Hidden injuries sometimes occur when animals are contused. Only a surgeon can assess the severity. It is important to follow all subsequent doctor's recommendations.
Prevention of eye diseases in cats
To prevent your cat’s eyes from hurting and always remaining healthy, not watery or festering, preventive maintenance is carried out. Proper care begins with nutrition. It is necessary to monitor what food your cat eats and how balanced the diet is. The main prohibition is that cats should not be given sweets.
You should pay attention to the appearance of the eyes. It should look like this:
- The conjunctiva is pale pink.
- There are no additional expirations.
- Healthy eyeball, without inflammation.
- The eyes are dry, the cornea is shiny and moist.
- The eyelids are of normal size, not enlarged and without swelling.
How to treat a cat's eyes?
If the cat is not sick, the eyes are healthy and clean, you can get by with a minimal set of eye care products. For prevention purposes, special lotions and saline solutions are used. It is not recommended to use tea, especially bagged tea. Tea leaves can lead to eye inflammation. Instead of tea, it is safer to use herbal infusions. But it should be noted that allergic reactions sometimes occur to some types of herbs.
The eye wash should be at room temperature or lukewarm. The eyes are washed from once a day (at night) to three times in the morning, afternoon and evening. If discharge appears and does not stop within three to five days, it is better to immediately contact a veterinarian. Self-medication can sometimes make the situation worse.
Some cat breeds have short nasal passages and tear ducts due to their skull structure. Tears do not fall into the nose, but accumulate in the eyes. For this reason, very often, throughout the day, tears accumulate, and the cat seems to be crying. The situation is not critical, but the eyes need to be treated every day. It is better to systematically carry out prevention and proper care than to subsequently treat eye diseases.
Cats need to be vaccinated
In what cases should you not worry?
The causes of photophobia in cats are not always accompanied by pathology. Newborn kittens suffer from physiological photophobia, as their eyes continue to develop after birth.
After the first attempts to open their eyes, babies may turn away from bright light sources, trying to hide in the far and dark corner of the box. This type of photophobia is not considered by veterinarians and professional breeders as a pathology.
Another natural cause of photophobia, which should not cause concern to the owner of the animal, is the period of pregnancy by the cat. Some animals, in anticipation of replenishment, become affectionate and sociable, while others, on the contrary, try to hide away, hiding their irritation.
This behavior is determined by a natural predisposition, since in the wild cats make their nest in dark places.
Another physiologically justified cause of photophobia in a cat can be a stressful situation. Fear and emotional shock lead to the pet’s desire to retreat to a dark place, avoiding direct rays.
The most common causes of stress in an animal are:
- moving from permanent place of residence;
- long trips;
- going to the hospital;
- the arrival of a new pet in the house;
- lack of attention from the owner;
Such conditions, if properly organized, do not require the intervention of a veterinary specialist and do not lead to serious disorders in the pet’s body. You should carefully consider the reasons for the behavior and try to neutralize them.
Daily care for your pet's eyes
Pet stores have a wide selection of pet eye care products. Most often, special preparations “Ophthalmosan”, “Diamond Eyes” or a regular domestically produced eye cleaning lotion that contains succinic acid are used. They are not designed for treatment, but they help well with mild inflammation and allergic reactions. They are mainly used for eye cleansing, removal of secretions and daily treatment.
The eyes are cleaned and instilled according to the instructions, wiped with a cotton swab with movements towards the inner corner of the eye. The products are used regularly without special prescriptions, clarifications or instructions from a doctor.
- Dirt and dry discharge in the eyes are first carefully removed mechanically with clean fingers.
- Place two drops of lotion in the inner corner, where there is more discharge, or in the lower eyelid.
- Use a cotton pad to wipe the eyes towards the nose, simultaneously removing any remaining moisture.
If it doesn’t work the first time, the procedure is repeated. Your pet's eyes should be monitored regularly to avoid inflammation and wrinkles under the eyes. Inflammatory processes are especially common in smooth breed cats.
Video - How to put drops in a cat's eyes?
Treatment
Depending on the degree of development of the disease, its cause and the type of blepharitis itself, an individual treatment method is prescribed. Most often, approaches are symptomatic or complex.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at eliminating symptoms. Very often, such a regimen is prescribed if the animal has received the disease as a result of mechanical damage. If the cause is an infection, fungus, or other problems related to the pet’s health, then comprehensive treatment is prescribed. When the case is advanced, the doctor will suggest surgical intervention to preserve the animal’s vision and save it from suffering.
Depending on the degree of development of the disease, cause and type, an individual treatment method is prescribed
When a microorganism becomes the cause of the disease, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed. If a subcutaneous tick is detected in the body of an animal, three-time vaccination is prescribed with intervals of 15 days. Additionally, a fungicidal ointment is used to destroy microsporia.
You can read more about antibiotics for cats in a special article on our website.
Antibiotics are used both in the form of ointments and in the form of injections. But not all treatment can be carried out by the owner at home. Several times a month you will have to visit the veterinarian to administer antibacterial emulsions and suspensions to the affected area of blepharitis.
With the permission of a doctor, you can use traditional medicine methods. These are lotions, oil complexes, habitats, homemade drops.
With the permission of a doctor, you can use traditional medicine methods
With such an integrated approach, rest, proper nutrition and avoidance of contact with external irritants (no street walks), the animal will recover in a matter of days, and after a month it will completely forget about the illness it experienced.
Medications
In the treatment of blepharitis, veterinarians insist on the use of medications. Thanks to medications, you can achieve a quick effect without possible complications.
- To wash the eyes and remove crusts, use a mixture of petroleum jelly, soda and warm water. After mixing the ingredients in equal proportions, soak a cotton swab in the solution. Carefully treat the cat's eyes, removing crusts and scales along the way.
- Most often, veterinarians prescribe syntomycin emulsion. It relieves inflammation and prevents redness. Along with the emulsion, tetracycline and yellow-mercury ointment (one percent) have the same effect.
- Rinsing the animal's eyes with a salt solution will be an excellent remedy for ulcers.
- Iris eye drops prevent the onset of complications such as conjunctivitis. The frequency of use depends on the body weight and age of the animal.
- In the first week of treatment, veterinarians advise purchasing a special protective collar that is fixed around the neck. This will prevent your animal from scratching its eyes.
Eye drops "Iris"
Homemade eye washes
Every day, several times a day, it is necessary to clean the eye area from pus, crusts, and mucus. Not only medicinal solutions are suitable for this, but also herbal decoctions. The effectiveness of these solutions will depend on proper preparation.
- Chamomile and calendula decoction. 2 teaspoons of dried flowers should be poured with boiling water in an amount of 250 ml. Cover the container with a lid and leave for 15 minutes. The broth is filtered through multilayer gauze. Can only be used after cooling.
- Brew weak black tea. Cool the solution and strain it. Rub the animal's eyes.
- A mixture of dry sage and St. John's wort should be poured into 250 ml of boiling water. Let it brew for 15 minutes. Rinse eyes after cooling.
A decoction of chamomile and calendula is used to wash the eyes for blepharitis.
Washing procedure
In addition to the correct preparation of the product, it is important to approach the procedure itself correctly. Otherwise, you risk causing harm.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and treat with antiseptic.
- Adjust the time so that the cat is as relaxed as possible and not in a state of activity.
- Prepare the required solution in advance and cool it.
- Take a clean gauze pad. Lightly moisten it in the broth.
- Start wiping the eye area from the ear to the nose, trying to get the water into the inner part of the eyelid. You should not press, the movements should be light and pleasant.
- Wipe the treated area with dry gauze or a napkin.
Important! A new, clean cotton swab is used for each eye.
If after using the decoction you notice that the situation has worsened sharply, you should visit a veterinarian.
Use a new, clean cotton swab to wipe each eye
Correctly selected posture during the procedure will provide you with the desired result. Wrap the cat in a diaper or towel and lay it on its back. It is advisable for the animal to sit on your lap. Try to keep the light out of the cat's eyes, otherwise she will squint and the procedure will not bring the desired results.
Try not to touch the cornea of the eye, this is the most painful area with blepharitis. To consolidate the result, you can rinse your eyes with a syringe.