What should you do if your cat falls on its side while walking?
Cats are cute creatures, inhabitants of many apartments and houses. Breeders of four-legged friends try to raise their pets healthy, strong and active. If any problems arise with the health of your ward, you should immediately look for the cause of the illness and begin treatment. The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the easier it is to prevent the development of complications. Many owners, when visiting a veterinarian, note that the cat falls on its side when walking. As a rule, this is not the only symptom. The severe condition is accompanied by loss of activity, refusal of food and water, convulsions, fever, blurred vision, twitching of the limbs. All of the above signs indicate health problems.
Treatment on an outpatient basis and at home
The consequence of damage to either the posterior columns of the spinal cord, or its roots, or peripheral nerves. Similarly, there are pathologies of the parietal lobe cortex and thalamus opticus.
Tumors and diseases of the intervertebral discs in cats also affect the development of sensitive ataxia.
The main problem is that the animal is not able to bend and straighten its limbs at the joints. The ability to consciously determine the direction of movement is lost.
There is pain in the neck and back area, movements are also painful, and the cat tries to move as little as possible. In severe cases, any movement is simply impossible.
If the brain is damaged in a small part, and treatment was prescribed as quickly as possible at an early stage, there is a chance that the animal will return to normal healthy life.
The main reasons for falling on your side
It is impossible to independently find out why a cat falls on its side when walking. Requires specialist help and hardware research. First of all, the clinic takes blood tests. Most often this is a general analysis, but in some cases a biopsy is required. Among the most common reasons for a cat’s poor health are the following factors:
- Epilepsy. A very serious disease in which the brain does not receive the required amount of oxygen. As a result, serious attacks develop. If a cat falls over on its side when walking, this may be the first sign of a serious illness. There are several types of the disease. Some occur in a milder form and do not lead to seizures with the release of foam from the mouth. In any case, the veterinarian will do an X-ray, ultrasound and MRI of the brain, as well as other parts of the body. Only after the diagnosis has been determined can adequate treatment be prescribed. As a rule, this is supported by therapy that will reduce the risk of developing epilepsy and prevent the death of the animal. The disease cannot be completely cured;
- Stroke. Another severe process in which the brain suffers, including the departments responsible for coordination and balance - the cerebellum and the middle part of the ear. The stroke condition develops in different ways. This could be a narrowing of blood vessels in the brain, or it could be a rupture or blockage. In the latter case, the disease leads to the death of the animal or paralysis. Treatment is carried out systematically, including drugs that thin the blood, dilate blood vessels, and support the functioning of the heart. It is very important during the treatment period to maintain proper feeding and undergo regular examinations by doctors;
- Dystrophy of muscle tissue. The disease manifests itself as a result of other negative processes in the body. These may be problems with the circulatory system, as a result, the leg muscles do not receive the required amount of nutrients. There may be a limb injury due to a fall. In any case, it is recommended to show the cat to a specialist. The doctor may prescribe some developmental exercises, wearing special fixing splints, as well as massage procedures;
- Paralysis or paresis. At the initial stage of development of these diseases, the cat falls on its side when walking. Treatment should begin as early as possible to avoid severe processes and complete paralysis of the torso. Recovery therapy can only be prescribed by a veterinarian based on the data obtained from tests and studies;
- Ataxia. This is a condition where there is no coordination of movements of different muscle groups in the body. Most often observed against a background of muscle tissue weakness and motor disorders.
Sudden loss of coordination in cats. Causes of coordination problems in cats
Vestibular syndrome is a pathology associated with the functioning of the inner ear and leading to impaired coordination of movements in a pet. Most often, loss of coordination in cats occurs at a fairly advanced age; animals over 12 years of age are usually susceptible to this pathology.
Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to find out exactly the reason for the loss of coordination of movement in cats, however, regardless of the provoking factors, the pathology is characterized by severe symptoms. So, most often the animal begins to throw its head to the side, stagger when walking, fall, losing its balance literally out of the blue. Such signs may be accompanied by more rare manifestations - sometimes the cat’s eyes practically run from side to side, as if she cannot concentrate her gaze on one point or is watching the rapid movement of someone invisible.
The vestibular apparatus consists of a huge number of nerve fibers stretching from the brain to the ear canal; the tasks of this conductive bundle include the orientation of the body in relation to the plane of the earth. When the apparatus is dysfunctional, a kind of “imbalance” occurs, as a result of which there is a lack of coordination when the animal moves.
Depending on the location of the damaged nerve fibers of the brain, the pathology is differentiated into 2 types: central and peripheral. Based on the type of pathology, the condition of the animal and the results of the diagnostic examination, treatment is prescribed, but more often the central vestibular syndrome can be cured, while eliminating the peripheral one is considered difficult.
The diagnostic program includes studying the pet’s medical history, as well as testing the blood for biochemical composition, but often these measures are not enough to accurately identify the cause, so skull x-rays and MRIs are prescribed.
By the way, in rare cases, insufficient functionality of the kidneys or liver can lead to a lack of coordination, so it would be useful to submit a sample of the animal’s urine for analysis according to Nechiporenko. It should also be taken into account that pathologies such as toxic poisoning and the development of a benign or malignant tumor have similar symptoms.
If the suspicion of vestibular syndrome is confirmed by diagnosis, symptomatic treatment is carried out using common pharmacological drugs. For example, Riabal, No-shpa or Cerucal will help relieve attacks of nausea that develop as a result of “seasickness”; for idiopathic syndrome of the vestibular apparatus, treatment will take a decent amount of time and medications will be selected depending on the cause; surgical intervention is not excluded.
The owner’s task is to ensure that the pet does not harm itself during this period due to the inability to control its body perfectly. Therefore, when visiting the clinic, you need to ask the veterinarian how to make the cat’s life more comfortable at this time and how to protect the animal from the danger of injury.
Often, the symptoms of vestibular syndrome disappear as suddenly as they appeared, after 1-2 weeks, however, in this case, a relapse of the pathology can occur at any time, so it is better to visit the veterinarian at the first signs of impaired coordination of movements.
The pathology is not always treatable - in Burmese and Siamese cats, vestibular syndrome is one of the genetic disorders. Treatment of a genetic disease is impossible, so the animal suffers from incoordination throughout its life or the symptoms disappear spontaneously.
If your cat moves strangely and periodically experiences the urge to vomit, you should not treat it yourself using dubious folk advice. In order not to risk the health of your beloved pet, you should immediately contact a veterinary clinic, where the animal will receive professional assistance whenever possible.
What is ataxia?
Without going into details, this is the name for a set of symptoms that imply problems with coordination of movements and body position in space. There are three types of this pathology:
- Cerebellar ataxia in cats is caused by damage to the cerebellum.
- Accordingly, vestibular occurs in cases where something is very wrong with the vestibular apparatus located in the inner ear.
- Sensitive . In some ways it is similar to the cerebellar, only in this case important nerve cords are damaged.
There are different causes of ataxia in cats. Most often, the development of the disease is due to:
- Poisoning with various poisons.
- Hereditary diseases accompanied by degenerative phenomena in the nervous tissue.
- Injuries that occur especially often in March, when loving cats fall from balconies.
- Lack of vitamin B1. This is generally typical for cats: many owners “pamper” them with fresh river fish, which contains the enzyme thiaminase. It destroys thiamine, that is, B1, resulting in ataxia. This is especially noticeable in kittens.
- If the cat is “hooked” on some plants. For example, a large dose of catnip can send a cat into “nirvana” for several minutes. At this time, the pet looks like an inveterate drunkard.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Tumor.
- Infection. In particular, feline panleukopenia is very dangerous.
- Hydrocephalus or cerebral edema.
Unfortunately, these are not all the reasons. Cerebral hypoplasia is a fairly common hereditary lesion of the cerebellum. This phenomenon develops in almost 70% of cases in kittens whose mother suffered from panleukopenia during pregnancy. In addition, it is possible that this pathology may develop with other infectious diseases that the cat picked up while in an “interesting situation.” Helminths can also help.
In very rare cases, ataxia develops due to lysosomal deficiency. There is such an intracellular organelle called a lysosome. It is needed to dispose of peroxide compounds and other nasty things. If there is something wrong with the lysosomes, all these substances begin to accumulate in the body. This pathology is extremely rare, incurable, and its prognosis is poor.
Reasons why a cat falls
Paralysis and paresis of the limbs can be associated with infectious and inflammatory lesions, impaired blood supply, spinal cord or brain injury. In this case, the animal will also experience other neurological symptoms (nystagmus, fainting, behavioral disturbances, different pupil sizes). If the spinal cord in the pelvic area is affected, the cat may have trouble urinating and defecating.
The cat's paws may begin to move apart, then the cat may fall over on its side due to tumors of the spinal cord. The same symptoms can occur with alimentary hyperparateriosis.
Muscle weakness can be caused by various myopathies (for example, caused by potassium deficiency), infectious diseases (viral infection, damage to protozoa). For example, muscle weakness is one of the earliest symptoms of botulism in a cat.
READ Complications after sterilization in a cat, a lump on the stomach, treatment methods
An animal may fall from exhaustion or as a result of heavy blood loss. Bleeding may be internal, so it is not immediately diagnosed. At the same time, the cat is lethargic, refuses food, falls asleep, its limbs are cold, the mucous membranes are bluish.
Ataxia (coordination disorders) can be congenital or acquired. There are several types of this disease in cats.
The main ones include:
- vestibular;
- cortical;
- cerebellar;
- sensitive.
With ataxia, the animal has a staggering gait, it places its paws uncertainly, as if it does not know where or how to lower the limb. Often the animal's head is tilted down or to the side. With some types of ataxia, the animal experiences tremor (minor trembling of the body during movement). Ataxia is caused by various disorders (for example, panleukopenia), poisoning (poisons and plant components), head injury and cerebral edema, group B vitamin deficiency (in particular, lack of vitamin B1), and brain tumors. Cerebellar ataxia, caused by hypoplasia of the cerebellar structures, is not uncommon in cats.
A cat may fall and have convulsions due to epilepsy. During a seizure, the animal sharply jerks its limbs, clacks its jaw, and involuntary urination may occur.
As a result of a stroke, the animal may move in a circle, meow loudly in pain, or fall on its side. The cat's behavior is disrupted. Vomiting may occur. The cat may lose consciousness.
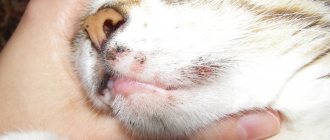
A cat may fall on its side as a result of otitis media. Inflammatory ear disease leads to disruption of the vestibular apparatus. In addition, there may be a refusal to eat, and an unpleasant odor may be felt from the auricle. Purulent discharge appears. When trying to examine or clean the ear, the cat meows, gets nervous, and may bite.
Most often the animal falls on its side. With damage to the hind limbs of any origin, stroke, otitis media, the animal’s hind legs seem to tuck under, and the cat falls to the side. With paralysis, the limbs may lie straight and the animal tries to move by moving its front paws. When he gets tired, he lies down on his side, the croup lags behind in a straight position. With myopathies and myositis of the forelimbs, the cat may fall on its front legs.
Symptoms and diagnosis
In general, the symptoms of ataxia in cats are simple. The pet looks like a drunkard, he shakes, the cat cannot walk normally, in severe cases he falls on his side with a roar, just trying to sit down. A constant tilt of the head to one side, as well as erratic circular eye movements, are very typical. Other symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause of the ataxia. For example, a cat “under mint” can walk with a wobbling gait with its head held high; from time to time, it shakes it and generously splashes saliva around. It looks terrible, but goes away quickly.
Your veterinarian will perform a complete physical examination of your cat. The information provided by the cat's owner is important. It is advisable to remember the following:
- Did the animal have access to household chemicals, poisons, or was deratization (rodent extermination) carried out in your home or area?
- Is there any information in your pet’s pedigree about any pathologies that the cat’s parents suffered from?
- Did the cat fall from the balcony, did it get hit by a bicycle, etc.
Treatment of vestibular disorder in cats
In general, vestibular disorders do not require treatment or require only minor treatment. Symptomatic, as a rule. Usually, in case of nausea in an animal with this disease, drugs such as diphenhydramine, miklesin, no-spa, riabal, cerucal, etc. are recommended. They will help your pet cope with the consequences of “seasickness”. If the basis of the disease is idiopathic, then healing will take longer (several weeks).
The most important thing in case of vestibular disorder is to exclude dangerous situations when a cat can harm itself. It is advisable to visit a veterinarian at the initial stage of the disease. He can prescribe medications that will help the animal endure the disease more comfortably, and will give you competent advice.
Treatment Basics
Be that as it may, the treatment of ataxia in cats depends purely on the reasons that caused pathological changes in the animal’s behavior. In case of poisoning, it is important to determine what exactly the animal was poisoned with. In all cases, activated carbon is prescribed, which partially absorbs the toxin, and intravenous administration of supporting compounds is practiced.
If the reasons for a cat’s somewhat inappropriate behavior lie in a “dose” of catnip or valerian , there is no need to worry: within a few minutes the effect of the substances will end and the animal will become normal again.
In case of traumatic brain injuries or even suspicions of them, you need to urgently take the cat to the veterinarian. He will assess the condition of the animal. If the brain has been damaged, there is a high probability of death, or the animal turning into a “vegetable”. In this case, euthanasia is recommended. In other cases, emergency surgery can save the cat. Similarly - in cases of back injuries, which may in one way or another threaten the integrity of the spinal cord.
Thiamine deficiency , which is detected using a biochemical blood test, can be eliminated by a balanced diet and the exclusion of foods containing thiaminase from the diet. In severe cases, vitamin B1 injections and oral multivitamin preparations may be necessary.
Cerebral hypoplasia . There is no cure for this pathology, but in some cases the disease does not progress and the cat can live with it. The quality of life, however, is “shaky” in all respects, but it is all quite acceptable. By the way, such a cat with ataxia can have offspring, and the health of the kittens will be normal (but only if the pathology is not hereditary).
Lysosomal disease... As we have already said, there is no treatment, the prognosis is unfavorable. In some cases, the animal’s condition can be maintained with diet for a relatively long time, but ultimately it all ends in the death of the cat.
Hydrocephalus. Diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed to reduce inflammation, but all these measures only slightly delay the inevitable. The prognosis, as in the previous case, is unfavorable.
With tumors, everything is also “foggy.” If the tumor is amenable to chemotherapy, or there is the possibility of its surgical removal, then everything can end well. In all other cases, sometimes it is necessary to resort to euthanasia.
Spinal injuries
Spinal cord injuries do not only occur when falling from a window.
The animal's spine may be damaged due to an unsuccessful jump on furniture or other surface. When a pet falls, it risks injuring the lumbar spine, especially if there are corners and protrusions of furniture in the way. After the incident, the animal, which has retained the ability to move, can hide. So the owner will not immediately notice the problem. But when he saw that the cat squatted on its hind legs when walking. Additional symptoms are:
- incontinence;
- paralysis of the forelimbs;
- uncertain movements;
- weakness;
- constantly drooping, limp tail.
Problems with the spinal cord also provoke congenital anomalies. Thus, Manx tailless cats have a risk of developing spina bifida in the fetus. In this case, a person can only be unaware of the cause of the problem if he picked up the animal on the street.
Having noticed changes in the pet's gait, the owner must provide him with peace. If a visit to the veterinarian is postponed, the cat is separated from other animals in the house by placing a tray and bowls of food and water next to it. But it is better that the delay does not last more than 1-2 days.
The veterinarian determines the cause of the problem based on the results of the examination, x-rays and myelogram. He may prescribe surgery to relieve pressure on the bone marrow or restore the structure of the spine. Depending on the severity of the injury, the intervention completely or partially restores the functions of the limbs.
Additionally, physiotherapy can be used for these purposes. Cats are also prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve swelling at the site of injury and surrounding tissues, painkillers and antibiotics.
If a cat falls on its side when walking, there may not be enough blood flowing to its limbs (front or back). The causes are a weakened heart or a blood clot. The latter leads to sudden paralysis and deterioration of paw function, pain and decreased temperature of the extremities. Additional symptoms of heart failure are:
- cough;
- labored breathing;
- loss of appetite and weight;
- decrease in activity.
In the case of a blood clot, problems in the limbs may appear before these signs. The veterinarian prescribes medications that thin the blood and strengthen the heart. The doctor may resort to surgery to remove the clot.
To avoid blood thickening, the owner must monitor the proportion of water in the animal’s diet. On average, an adult needs 100-120 ml of liquid per day, including intake from canned food and other products.
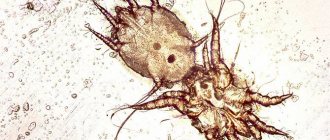
When a cat falls on its side while walking, the cause may be internal otitis. Most often it is caused by bacteria. Less common causes are yeast and other fungi. Problems with the inner ear provoke infections and injuries to the external structures of the organ. It can be:
- microscopic mites;
- foreign objects;
- wounds;
- benign polyps growing in the middle ear.
Poor balance is not the only sign of inner ear problems. Symptoms preceding or accompanying it are:
- excessive salivation;
- inability to blink;
- difficulty eating;
- differences in pupil size;
- discharge from the eyes and ears.
The veterinarian determines the cause of the disorder by taking culture samples from the ear. You may need to give your cat a sedative to do this. Based on the results of the analysis, antibiotics or antifungals are prescribed. If there are problems with balance, the pet's mobility is limited for the period of treatment.
If there is no response to treatment, fluid accumulates in the middle ear, or there is a bone infection, surgery is indicated. During the intervention, the external auditory canal can be completely removed.
Gait disturbances provoke pinching or inflammation of the sciatic nerve. Sciatica in cats occurs due to:
- injury or subsequent bone healing;
- surgical intervention;
- neoplasms;
- medical procedures, such as injections near a nerve.
Minor lesions can go away on their own; the animal just needs to be given rest. Severe injuries can tear or pull the sciatic nerve from the spinal cord. The problem is solved by surgical removal of scar tissue.
To maintain muscle performance, physiotherapy is prescribed. During the treatment period, care must be taken to ensure that the pet does not damage the affected limbs by dragging or biting them.
Balance problems occur when the brain is damaged. He suffers from infections, injuries, tumors and other diseases such as epilepsy. Treatment includes antibiotics, surgery and, in severe cases, intravenous medications to relieve the cat's suffering.
Neoplasms in the brain and spinal cord are one of the common causes of limb problems. They can put pressure on the spine, depriving the paws of mobility, or affect the functioning of the nerves.
Problems with the hind legs also arise due to diseases of the kidneys, genital organs (in particular, endometritis in females), and the gastrointestinal tract. The pet pulls them because of pain and discomfort.
Treatment, depending on the disorder, may include chemotherapy, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and other drugs.
A cat pulls its hind legs for various reasons. The simplest explanation is that the pet was pinched or crushed. But usually the problem lies in the body. The mobility of the paws is affected by the condition of the spine, brain and other organs.
If the owner notices changes in the cat’s activity, it is better to immediately consult a veterinarian. Some conditions (cancer, severe inflammatory processes), in the absence of timely treatment, lead to irreversible consequences, including death.
Causes
The most common cause of loss of coordination of movements is infectious diseases affecting the nervous system and brain. These, in most cases, include panleukopenia.
Cerebellar - often the cause of ataxia is aplasia of brain structures. This disease is congenital in nature and can arise both from a hereditary genetic predisposition and from developmental disorders in the prenatal period. Typically, sick kittens are born when the mother has panleukopenia. Also, the cause of damage to the cerebellum and the subsequent development of ataxia can be traumatic brain injury, inflammatory processes and cerebral edema.
With vestibular ataxia, there are two options for the development of the disease:
- The structure of the inner ear - the cause is its damage due to otitis media, neuritis of the craniofacial nerves, idiopathic vestibular syndrome and tumors.
- The medulla oblongata and brain stem are tumors.
Types of vestibular disorders in cats
There are two main types of vestibular disorders in cats.
. They are divided into peripheral and central disorders. The central disorder occurs in the brain, and the peripheral disorder occurs in the inner ear. Usually, the central disorder has an organic cause and when it is eliminated, the disorder stops. The main symptoms of vestibular disorder in cats:
- falls;
- loss of coordination;
- tilting the head to one side;
- movement in a circle, rocking;
- stumbling on level surfaces;
- constant and frequent movement of the eyes in different directions (nystagmus).
Symptoms
Despite the similar symptoms of all types of ataxia, there are different signs that depend on the cause of the disease.
All types of violations are characterized by:
- Staggering "drunk" gait. The cat walks with its hind legs widely spaced, raising them high.
- Changes in head position - usually it is tilted to the side or down.
When the spinal cord is damaged, pain occurs when walking, and the animal tries to move less. Very often there is no loss of coordination of the head.
Cerebellar ataxia is characterized by the presence of tremor during movement - when walking or running, the animal’s body trembles slightly, often only the back part. There may also be nystagmus, which is rapid eye movements that are independent of where the cat is looking or what the cat is observing.
If there is damage to the vestibular apparatus, then nystagmus is also observed, severe pain in the head is possible (the cat meows, sits in the corner with its forehead pressed to the wall).
Types of ataxia
Ataxia is divided into several types, depending on the affected area:
- Sensitive. Affects the cat's ability to bend and straighten its joints. Chances of cure only with the earliest possible diagnosis;
- Cerebellar. It can be static (loss of balance) or dynamic (impaired movement). It starts with small manifestations of awkwardness and maintaining balance. In the case of a genetic factor, it is incurable; in the case of a traumatic cause, the chances of recovery are real;
- Vestibular. It starts with all movements becoming slow and very careful. At later stages, the body tilt changes to the left or right, and the animal stops moving straight.
There are two main types of vestibular disorders in cats. They are divided into peripheral and central disorders. The central disorder occurs in the brain, and the peripheral disorder occurs in the inner ear. Usually, the central disorder has an organic cause and when it is eliminated, the disorder stops. The main symptoms of vestibular disorder in cats:
- falls;
- loss of coordination;
- tilting the head to one side;
- movement in a circle, rocking;
- stumbling on level surfaces;
- constant and frequent movement of the eyes in different directions (nystagmus).
Diagnostics
One of the first diagnostic methods will be a thorough history taking. It is important to know about the cat's previous injuries, infectious diseases and nutrition. If possible, family heredity and the peculiarities of pregnancy in the mother cat are determined.
The animal is examined by a neurologist to assess the functionality and disorders of the nervous system.
Determine serological reactions to dangerous feline viruses - immunodeficiency virus, panleukopenia and leukemia.
If the clinic has the opportunity, then they conduct an MRI diagnosis of the brain; tumors, aplasia of areas, hemorrhages and edema are clearly visible on it. It is also possible to use ultrasound and radiography.
The ear is examined using an otoscope.
If there is a suspicion of infection of the brain or spinal cord, cerebrospinal fluid is taken to analyze leukocytes and protein, and a bacteriological examination is also carried out.
Serious causes of dilated pupils
If one pupil is dilated and one is not, we are talking about anisocoria
In this condition, the “non-standard” large pupil has no reaction to light at all. This is a mandatory reason to visit a veterinarian/veterinary ophthalmologist. The reasons may lie directly in eye diseases or diseases of the nervous system, and, in particular, pathologies of the brain or optic nerve. This condition can lead to complete blindness if the cause is not eliminated in time (if possible, if the resulting pathology is curable).
The main causes of anisocoria lie in:
- retinal atrophy,
- posterior uveitis,
- glaucoma (angle-closure),
- dislocation of the lens,
- cerebrovascular accident,
- brain tumors (rare),
- pinching, optic nerve atrophy,
- impaired blood supply to the eye,
- increase in intracranial pressure.
If the cat has poor coordination of movement (shaky gait), dilated pupils, vomiting
The first thing to suspect is poisoning. You should pay attention to the frequency of vomiting, its contents, whether the eyes react to light at all, and take the cat to the veterinarian. Dilated pupils are usually caused by poisoning with such toxins, which cannot be independently neutralized and removed from the body. The source of intoxication can be medications, poisonous plants or poor-quality (poisoned) food.
Corneal opacities, consequences of trauma
When scarring of injuries on the cornea, opacities of its surface of varying intensity can be observed. As a result, light rays of insufficient intensity begin to enter the retina. The pupils behind the damaged cornea will reflexively dilate more to catch more light to normalize vision. There is a reaction to light, but it can be very weak, and it will seem that the eyes are constantly with dilated pupils.
If the eyes become very cloudy, have lost transparency (they have become as if covered with a white film), and the pupils are wide, like saucers, we can talk about cataracts (clouding of the lens). The disease is incurable and is followed only by blindness.
Pain syndrome
Dilated pupils in a cat can be observed when the animal feels pain. Mustached pets almost never meow, without outwardly clearly revealing the fact that they are in pain. If the cat is inactive, purrs loudly and continuously, sleeps in unnatural positions, walks with a stiff gait and at the same time dilated pupils, the cause of the condition can be determined by aching pain (renal or stomach colic, cardiac pathologies, infections, tumors).
Age
In older cats, the pupils appear more dilated than in young cats under the same lighting conditions. Also, they hardly become like narrow slits. With age, the condition of the eyes and the perception of light deteriorate, but the overall reaction to light does not decrease, i.e. in very bright light, signs of contraction persist.
Advice to owners of mustachioed pets: it’s better not to guess why the cat’s pupils are dilated. Without finding natural causes that can explain this condition from a physiological point of view, it is important to go to a veterinarian or veterinary ophthalmologist, because Many eye pathologies threaten blindness.
Author:
Grinchuk Ekaterina Andreevna veterinarian
Treatment
The tactics of the prescribed treatment depend on the causes of ataxia. B vitamins, especially B12, are mandatory. Gamavit is used to strengthen the immune system and the body as a whole.
The medicinal substance Proserin also penetrates well through the blood-brain barrier and helps restore nerve conduction.
With cerebellar ataxia, treatment of the disease is extremely difficult. After all, the basis of the disease is degenerative changes in the brain. Cerebrolysin (Cerebrolysate) is used to improve cerebral circulation and tissue regeneration.
To improve the functioning of brain tissue, glycine is used 0.25 t once a day for 2 weeks, piracetam 0.3 ml IV and caviton 0.25 t 3 times a day for a week.
In case of spinal cord damage, surgical treatment is prescribed in most cases. Physiotherapy is also used - UHF, UMI (pulse therapy), massage.
If there is an infection, then antibiotics are used - ampicillin, vancomycin. Often the cat will require anti-toxic therapy. To do this, use a drip infusion of saline solutions - saline solution with glucose. Glucocorticosteroids – prednisolone – are also administered.
If there is cerebral edema or hydrocephalus, diuretics are prescribed - furosemide, veroshpiron.
Severe tremor can be relieved by using diazepam, but in this case it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the liver and prescribe minimal doses of the drug, as it is toxic to the liver.
Owners of kittens with cerebellar ataxia should remember that after the animal reaches the age of 1 year, its condition stabilizes, and the pet can continue to live happily. Such pets have extraordinary intelligence and kindness, but they require the safest possible life and good care, and, of course, love and affection.
Now in the United States there is even a special queue where residents sign up to shelter animals with this diagnosis.
Treatment of ataxia in cats
In the case of a genetic cause, only death is possible. Most often, veterinarians offer timely care without waiting for complications to occur (constant headaches, attacks with loss of consciousness, spasms, inability to feed independently).
If the cause is traumatic or tumor, then the chances of a long life are more realistic and largely depend on early diagnosis. Most often, antispasmodic and sedative drugs and B vitamins are prescribed. Surgical intervention is possible.
It should be remembered that even in case of recovery, the cat will no longer be the same, since brain injuries never go away without a trace, and the owner needs to be prepared for the fact that the animal may be left with limited capabilities.
In general, vestibular disorders do not require treatment or require only minor treatment. Symptomatic, as a rule. Usually, in case of nausea in an animal with this disease, drugs such as diphenhydramine, miklesin, no-spa, riabal, cerucal, etc. are recommended. They will help your pet cope with the consequences of “seasickness”. If the basis of the disease is idiopathic, then healing will take longer (several weeks).
The most important thing in case of vestibular disorder is to exclude dangerous situations when a cat can harm itself. It is advisable to visit a veterinarian at the initial stage of the disease. He can prescribe medications that will help the animal endure the disease more comfortably, and will give you competent advice.
Prevention
- Mandatory vaccination against panleukopenia, rhinovirus and feline leukemia virus.
- To avoid injury to the animal as much as possible, it is advisable to limit free access to the street.
- Careful protection of the health of a pregnant cat, a ban on its communication with other animals.
- When planning a mating, be sure to check the cat for panleukopenia.
- Timely treatment of otitis and inflammatory ear diseases.
- Urgent hospitalization of a cat if a traumatic brain injury is suspected.
- Check with the breeder about genetic diseases in relatives and about the mother’s pregnancy history.