Blockage of the paraanal glands leads to extremely unpleasant consequences. Owners should be aware of the symptoms of the problem and know how to clean it. Inflammation occurs due to the accumulation of secretion in the anal sacs, and its inability to come out naturally. If it is neglected, the pet may suffer from an abscess, self-injury, baldness, and nervousness. The list of possible consequences is incomplete, so there is no need to neglect this knowledge.
What are paraanal glands
The anal glands in dogs are small sacs that are located inside the anus, just before it exits. Inside these bags, a special secret constantly accumulates, allowing dogs to differ from each other by their individual scent.
During normal emptying, feces, passing through the anus, press on these sacs, and the secretion from the sacs, along with the feces, comes out.
Thus, most dogs naturally cleanse their bodies themselves, and the owners do not even suspect the presence of any glands there. But only until you have to face this problem yourself.
Reasons for the accumulation of secretions in dogs
As mentioned above, dogs do not need brushing in their natural environment. Why is this procedure required for pets?
- Heredity. Small breeds that are prone to obesity, such as pugs, bulldogs, and dachshunds, often have problems in this area and are advised to have their glands cleaned regularly.
- Passive lifestyle. In “sofa” dogs, the release of gland secretions is difficult.
- Nutrition. The dog's body is not adapted to food from the human table, so those who cannot refuse the pleading look of their pet often encounter this problem.
- Lack of control. Many veterinarians neglect to examine the dog’s anus, so they cannot always tell the owner that secretions have begun to accumulate in the glands. At your next appointment, ask your doctor to examine the area.
Prevention is quite simple. The dog should have a full walk twice a day, because it is undesirable for the animal to endure. When walking, the animal should be active; the more the pet moves, the better its intestinal perilstatics. Sometimes you need to wash the anus area, thereby massaging it.
What causes blockage of the anal glands?
Blockage of the paraanal glands occurs because the secretion accumulates in the glands for a long time and does not come out. Problems with the anal glands are a direct consequence of problems with excretion of feces from the animal’s body.
These problems may be caused by:
- Sedentary lifestyle (the animal moves so little that problems arise not only with excretion, but also with the formation of feces).
- Poor nutrition (frequent constipation or diarrhea leads to the fact that when passing through the anus, feces have such a heterogeneous consistency that they simply do not squeeze out the secretion from the paraanal glands).
- Incorrect daily routine (the animal endures a lot and, as a result, secretions accumulate in the glands and blockage occurs).
The role of proper nutrition in treating a pet
It is extremely important when carrying out therapy to correctly formulate the dog’s diet. It consists of easily digestible foods containing fiber. Thanks to dietary fiber, the bags are naturally cleared of secretions and fluid stagnation is prevented.
To avoid causing diarrhea and constipation, your pet should be fed exclusively with high-quality, fresh foods. It is imperative to follow the regime. Overfeeding is unacceptable.
Canned, smoked, salty, fatty and spicy foods are excluded from the menu. It is strictly forbidden to give the dog food from the table. In certain situations, veterinarians recommend enriching the diet with multivitamin supplements, bran, and giving the animal mineral complexes.
How to Determine When It's Time for Your Pet to Have Anal Glands Cleaned
If the secretion accumulates in the gland for a long time, then the animal begins to experience discomfort in a certain area. The dog tries to squeeze out the contents of the bags on its own. At such moments, the pet begins to behave as its natural instincts tell it.
If the anal glands in dogs are clogged, the animal begins to behave as follows:
- Rubs her butt on the floor, especially on its fleecy surfaces. In such cases, many pet owners begin to think that their pet has worms. But they could be wrong.
- If friction on the floor fails to squeeze out the secretion, the dog tries to chew under its tail. The animal may suddenly jump up, twist towards its tail, trying to catch an invisible enemy. Sometimes it comes to the point that the animal chews out the fur under its tail.
- An unpleasant, previously unusual odor appears from the anus.
If you notice all these symptoms in your pet, then most likely he needs cleaning of the anal glands. If you are a squeamish person, or are afraid of harming your pet, then, of course, it is better to go to a veterinary clinic.
But in fact, if there is no inflammation in the anal area, and if the dog does not experience pain when pressed, then you can clean your pet’s anal glands yourself. Cleaning the glands, although not the most pleasant procedure, is quite simple.
Some information about the disease
In common parlance they are called anal sacs. Two glands are located near the anus, and the substance secreted from these sacs is very viscous and thick, with an unpleasant odor. For this reason, very often veterinarians do not offer owners to clean the animal. Most cats can independently release the glands from this substance in self-defense or when marking territory. Also, in a healthy animal, this secretion comes out during defecation. In the wild, cats easily cope with the task, but domestic pets have practically lost the ability to get rid of the harmful substance on their own. That's why owners have to help their pets.
If the animal cannot control this process, then an inflammatory reaction occurs, in which the anal sacs increase in size and cause many problems: cats cannot move normally and go to the toilet. The paraanal glands in cats cause behavior that is unusual for them: the animal begins to fidget with its butt on the floor and strongly lick the anal area.
Causes of inflammation
The following reasons for such changes are identified:
Rare, irregular walks. The pet is forced to restrain the process of defecation.- Insufficiently active lifestyle.
- Poor nutrition, such as eating too much protein or eating bones.
- Parasites.
- Frequent diarrhea.
- Damage to the anus.
- Genetic predisposition.
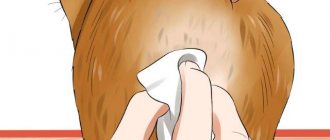
How to clean your dog's anal glands yourself
Before you begin the cleaning procedure, you must make sure that your dog has a problem with the anal glands.
To do this, you need to palpate the anus from the inside. It is best to carry out this procedure with gloves. Insert your index finger shallowly into the hole (almost at the very exit) and gently begin probing. If there are no seals, the bags are soft and practically cannot be felt, then you can be sure that everything is in order. If the dog’s paraanal glands are clogged, then even with light pressure you will immediately feel a compaction.
If you find seals, then you can safely begin the cleaning procedure.
What you will need
Prepare:
- Gloves.
- Paper napkin or clean rag.
- Basin.
- Petrolatum.
How to clean a dog's anal glands
There are two ways to clean the anal glands in dogs.
Method one
Do the following:
- Place your pet in the bathtub. If the dog is small, then you can use a simple basin.
- Ask someone from your household to hold the four-legged animal by the muzzle and body so that it does not spin or struggle.
- Put on gloves and feel the glands from the outside.
- Next, take the dog by the base of the tail and lift the tail up as far as possible, but so as not to cause pain to the animal.
- With another gloved hand or just using a napkin, use your thumb and forefinger to apply pressure to the area on the sides of the anus. If you did everything correctly, a viscous, unpleasant-smelling beige liquid should come out of the bags.
- After this, rinse everything thoroughly with water.
If after this procedure there is no result, and the paraanal glands are not freed from secretion, then under no circumstances press with double force. In this case, it is better to contact a veterinary clinic. It is possible that the glands are so clogged that home cleaning will not help and surgery will be required to remove the sacs.
Method two
Try this:
- Place your pet in the tub or basin and have someone help hold the animal.
- Wear gloves.
- Lubricate the index finger of your right hand (on top of your gloves) with Vaseline.
- With your left hand, in the same way as I described in the first method, lift the dog’s tail as much as possible.
- Carefully insert your index finger, lubricated with Vaseline, into the animal's anus. The palm should be in a position perpendicular to the floor.
- Using the index finger of your right hand, gently feel the gland.
- Next, use the index finger of your right hand (inside the anus) and the thumb of the same hand (outside the anus) to press the pouch, squeezing the secretion out.
- Rinse everything off with water.
It goes without saying that this procedure will not give your pet any pleasure. Therefore, together with your assistant, act harmoniously. The assistant must hold the four-legged firmly (but not painfully) so that he does not escape. Talk to the animal, calm it down, praise it.
As a rule, such cleaning lasts for a maximum of six months. But if you regularly carry out preventive measures, then it is quite possible that in the future you will not need to do such a procedure at all.
Prevention of blockage of the paraanal glands
So that you don’t have to find out what paraanal glands are in dogs and avoid problems with their treatment, you just need to follow the following preventive measures:
- Walk your pet more often. The less often the dog goes to the toilet, the less often the secretion is removed from the anal glands.
- Walks should be active. A sedentary lifestyle contributes to constipation and inflammation of the glands.
- Monitor the four-legged diet. It is important that the stool is well formed. This will eliminate constipation or diarrhea, which increases the risk of blockage and inflammation of the anal glands. An excess of protein foods and carbohydrates very often leads to constipation. The four-legged diet must contain fiber, which improves digestion. You can read here how to balance a dog’s diet, which foods must be present in the diet when feeding them naturally, and which should absolutely be excluded.
- Carry out hygiene procedures regularly, not forgetting to check the condition of the glands. For young animals, such a check should be carried out once a year. Elderly animals need to check the condition of their glands more often - once every six months.
Surgical methods of treatment
Note that modern veterinary medicine prefers surgical methods for treating inflammation of the paraanal sinuses.
This is due to disappointing statistics: if a dog’s glands become inflamed or clogged at least once, then there will definitely be relapses. The probability of recurrence is almost 100%.
Therefore, they resort to the following methods:
- The most common option is surgical sinus resection. The operation is called saculectomy. The procedure is extremely simple: two incisions are made (under local anesthesia), the “bags” are brought out, excised, the stump is bandaged with catgut and lubricated with an alcohol tincture of iodine.
- In some cases, cryogenic surgery is resorted to. In this case, the glands are “frozen out” with liquid nitrogen, after which they naturally atrophy and become overgrown with connective tissue. The technique has not gained much popularity due to its considerable cost.
The use of medications to treat inflammation
Sometimes cleaning is not enough to fix the problem. Drug treatment is prescribed. Treatment tactics largely depend on the degree of neglect of the situation and the condition of the pet.
Antibiotics
When a bacterial infection or severe inflammation occurs, antibiotics are prescribed. Typically, the following are used:
- Cefotaxime. Detrimental to gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. Prescribed for the treatment of purulent processes and their prevention.
- Cephalexin. A semi-synthetic antibiotic agent with a bactericidal effect.
The doctor selects the dosage individually. The veterinarian also determines the duration of therapy. Self-medication with antibiotics is strongly discouraged.
Medicines can cause side effects, if they occur, the use of the medicines should be stopped immediately.
Rectal suppositories
For inflammation of the paraanal glands, the veterinarian prescribes the use of a suppository. Rectal suppositories eliminate inflammation and accelerate the healing of affected tissues. The following drugs have the maximum effect:
- Ichthyol suppositories;
- candles with calendula;
- Methyluracil;
- Proctosedyl.
Therapy lasts from 8 to 20 days. Suppositories are used only if the anal glands are not opened. They are administered after each natural bowel movement or enema. Therapeutic suppositories are inserted into the anus with clean hands, then the dog’s tail is pressed for several minutes.
Symptoms
As mentioned above, you should identify the problem from the moment it occurs. Therefore, it is extremely important to read the information below to have a basic understanding of this disease.
Inflammation of the paraanal glands in cats shows the following symptoms:
- tenesmus;
- changing habits;
- aggression towards others;
- oppression;
- hair loss;
- refusal to eat;
- wool that is wet to the touch;
- rash;
- skin sinuses;
- pain in the tail area;
- skin ulcers;
- increased sensitivity;
- pruritus (itching);
- fever;
- hyperpigmentation.
Consequences of blockage of the anal glands
Inflammation
Inflammation of the paraanal glands occurs because the secretion accumulates inside the paraanal sacs for a long time. Having no way out, the secret begins to rot.
Characteristic signs of inflammation of the glands are: redness, rash, swelling and irritation near the anus. The fur around the hole gets wet and falls out. The dog begins to behave restlessly. She constantly rolls her butt on the floor, trying to relieve the itching and pain, gnawing under her tail.
If a dog’s paraanal glands are inflamed, then in this case there is no need to resort to self-cleaning. It is better to contact a veterinary clinic. The veterinarian will clean the inflamed glands, treat the skin and prescribe further treatment. If the owner of the animal is a careless person and does not pay any attention to the appearance of inflammation in the anal area, then irreparable consequences may occur.
Abscess
This process can be compared to a balloon bursting. The liquid inside the anal sac accumulates and accumulates and, not finding a way out, breaks through the walls of the sac.
Characteristic symptoms of an abscess: ulcers, swelling and redness around the anus. Constantly oozing foul-smelling liquid from it, dampening of the fur. The animal becomes lethargic, refuses food and water, and the temperature rises. In this case, you need to immediately run to the veterinarian, because there are often cases when abscesses lead to death.
Stages of the disease
If the paraanal glands in cats are not treated, the disease will progress and your animal will remain crippled. To make it clear what this pathology is, we will talk about its stages and how they proceed.
- First stage. Severe itching is observed, the animal behaves restlessly, and a yellowish secretion may be released in small quantities.
- The second stage - pustular rashes are observed on the animal’s body on the inner thighs, and sometimes stiffness occurs in the pelvic area. The secretion comes out thicker and in larger quantities.
- The third stage is very dangerous for the animal. The secretion begins to be released in small quantities and has a creamy consistency of a dark color.
- The fourth stage is the most dangerous. With it, the animal often stops walking due to paralysis of the pelvic girdle. The secretion is granular in nature and has the consistency of clay.
When does a fishy stench signal trouble?
If your dog suddenly begins to emit an unpleasant, pungent fishy odor, pay attention to the health and behavior of the pet. Owners should be alert to the following symptoms:
- dull, faded, brittle wool;
- the presence of foci of inflammation on the skin, ulcers, wounds;
- accumulation of wax, black plaque on the ears;
- sudden weight loss, loss of appetite;
- low activity, depressed state;
- severe itching;
- problems with chewing food;
- unstable stool, nausea, vomiting;
- unpleasant odor of urine, discoloration, frequent painful urination;
- ulcers, wounds on the oral mucosa;
- ear diseases (ear mites);
- fungal infections (mycoses);
- discharge from the nose, eyes.
Saculectomy
Sakulectomy is the removal of the paraanal glands. There are cases when the anal glands in dogs become clogged regularly. The secretion cannot come out, even with regular cleaning. Even if there is no inflammation or abscess, the cleaning procedure, although painless, is still not the most pleasant.
Wherever it goes, if the glands need to be cleaned once a year. Well, what if you need to do this constantly, almost every week. In this case, it is much more humane to perform a removal operation than to torture your pet and constantly treat and clean the inflamed gland. The operation to remove the glands is not considered difficult. The doctor makes two small incisions in the skin, approximately above the glands. Then he brings the glands out (from the anus), cuts them off and sews up the wounds. This way, neither the anus nor the rectum are damaged. To prevent the stitches from coming apart, light feeding and frequent walking are recommended after such an operation.
Today we talked about what the paraanal glands are in dogs, what role they play and how to properly care for them. I hope that you have learned a lot of new and useful information. Good luck to you!
Take care of your pets!
When to contact a veterinarian
The absence of discharge from the dog's anus due to clogging of the glands is a pathology that can be dealt with at home if its signs are seen in time. But in the case when you cannot squeeze out the mucus on your own, and the pet’s condition worsens, only the help of a veterinarian is necessary.
The dog's paraanal glands become clogged due to improper care of the pet, when it is not fed correctly, does not provide exercise, and long walks are neglected. To avoid problems with the glands, they need to be cleaned periodically. If the dog owner does not want to know what the name of the operation to remove the anal sacs should be, he must carefully monitor the pet’s health and take preventive measures.
*Prices are valid for July 2021.
Possible complications
The danger of the inflammatory process lies in the risk of complications.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner, the rectum is affected. Pathologies such as paraproctitis and proctitis develop. The worst consequence is the death of a pet, so it is very important not to ignore the problem that has arisen, but to deal with it in a timely manner.
Treatment regimen at home
The following treatment regimen at home is quite approximate; it must be adjusted based on the characteristics of a particular case of illness. In most cases, treatment is carried out as follows:
- The fur around the anus is carefully trimmed.
- Pus, dried pieces of excrement and other contaminants are washed off using either a sterile saline solution or a chlorhexidine solution. This is not a very pleasant job, but it will greatly facilitate subsequent procedures and prevent further development of the inflammatory process. Cleaning is repeated daily.
- To destroy pathogenic microflora, antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents are used in the form of injections, tablets, and rectal suppositories.
- Anti-inflammatory corticosteroids are usually prescribed.
- If necessary, antifungal agents are prescribed.
- To make the process of defecation easier for the pet, I use sedatives and painkillers.
- If the inflammation cannot be controlled, the affected glands must be removed surgically.