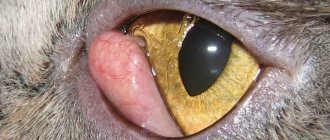
Nystagmus in a cat - why does a cat's eyes run around?
Just like humans, cats' eyes are a reflection of their health and state of mind. When your cat's eyes shift unusually, this is a sure sign that there is a problem with the nervous system. Rhythmic vibrations of the eyeballs (nystagmus) occurs in both cats and dogs. The animal's eyes twitch involuntarily, the pet is unable to control the vibrations.
Types of nystagmus in cats
There are two types of nystagmus - jerking and pendulum. Jerk (jerk) is characterized by slow eye movements in one direction, and then a sharp return to the previous state. With pendulum nystagmus, slight fluctuations of the pupils occur, in which the eyeball almost does not move. However, the jerk type is much more common in veterinary practice.
There is another classification of nystagmus - horizontal and vertical (according to the plane of eye oscillation). The vertical type occurs only with deep brain lesions and is a minor symptom. In other disorders of the nervous system, the most common is the horizontal type.
There is one more important circumstance. So-called congenital nystagmus often occurs in Siamese cats. In most cases, this is not a pathology, but a normal physiological reaction that allows you to adapt to the environment. The same can be observed in people who have overloaded their vestibular apparatus (see below).
Symptoms of nystagmus
In addition to the main symptom of “shifty” eyes, your pet may also turn its head and even spin in place.
Causes of nystagmus in cats
Most of the reasons for “shifty” eyes lie in the nervous system. Disorders of both the peripheral and central nervous systems can lead to the development of nystagmus. Shifty eyes are often associated with problems with the vestibular system, which is sensitive to the balance of the head and body.
Examples of causes of peripheral nerve diseases that lead to nystagmus include hypothyroidism, neoplastic tumors, and physical damage resulting from trauma (car accident, etc.). Diseases of the central nervous system can occur due to: thiamine deficiency (vitamin B1), tumor, viral infection (particularly feline infectious peritonitis), inflammation, heart attack, heart hemorrhage, toxin poisoning (lead and others).
Severe stress can also cause short-term nystagmus. This condition includes motion sickness in transport, as well as childbirth. Over time, the cat's vestibular system stabilizes.
Diagnosis of "shifty" eyes
Disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system can most often be diagnosed using CT (computed tomography). Sometimes a urine test is done to check for infections. If these procedures do not lead to any result, they resort to the most complex method in very prestigious clinics - analysis of cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment of nystagmus
Treatment directly depends on the disease that caused the nystagmus and its severity. Only by getting rid of the main problem can this symptom be eliminated along with it. Diseases of the central nervous system will have to be treated more intensively than lesions of the peripheral nervous system. If your cat has anorexia and vomiting, you will need to give a special fluid by mouth to prevent dehydration. However, the list of medications for each case is individual, and the veterinarian draws it up based on the diagnosis. The same goes for aftercare.
Most neurologists recommend examinations every two weeks to monitor the progress of treatment. Secondary symptoms such as vomiting and dehydration should also not be ignored. Experience shows that cats recover faster after diseases of the peripheral nervous system.
Prevention of "shifty" eyes
It is impossible to formulate a specific system of preventive measures for nystagmus, because There are many reasons, including congenitality. The only thing we can advise is to avoid poisoning your cat with lead and other toxins. In addition to Siamese cats, cats with albinism are predisposed to this disease, keep this in mind. Some kittens under one year of age may exhibit nystagmus, but this is very rare and will go away soon.
Diagnostics
One of the first diagnostic methods will be a thorough history taking. It is important to know about the cat's previous injuries, infectious diseases and nutrition. If possible, family heredity and the peculiarities of pregnancy in the mother cat are determined.
The animal is examined by a neurologist to assess the functionality and disorders of the nervous system.
Determine serological reactions to dangerous feline viruses - immunodeficiency virus, panleukopenia and leukemia.
If the clinic has the opportunity, then they conduct an MRI diagnosis of the brain; tumors, aplasia of areas, hemorrhages and edema are clearly visible on it. It is also possible to use ultrasound and radiography.
The ear is examined using an otoscope.
If there is a suspicion of infection of the brain or spinal cord, cerebrospinal fluid is taken to analyze leukocytes and protein, and a bacteriological examination is also carried out.
Often, to a professional veterinarian, ataxia is obvious upon initial examination. But to fully understand the situation, it is necessary to collect all the anamnesis data. Have there been any injuries (even several years ago), how and what does the cat eat, what severe infections has it suffered? If possible, how her mother’s pregnancy progressed. Examination of the ears with an otoscope is mandatory.
X-rays, ultrasound, or even an MRI will be needed to confirm the diagnosis and identify or rule out tumors, hemorrhage, or swelling of the brain. In some cases, if a brain or spinal cord infection is suspected, a cerebrospinal fluid test may be necessary.
Description of the pathology
Rhythmic, oscillating eye movements are called nystagmus. As a rule, they move exclusively in the horizontal plane. Vertical nystagmus is much less common... and is almost always a symptom of serious brain damage. Thus, nystagmus may be a normal physiological response or the result of pathology.
Why does it even arise, what do these erratic movements of the eyeballs mean? The eyes play a very important role in maintaining the balance of the body in space. They are directly connected to other organs of the vestibular apparatus. We can say that the brain checks the “sensor readings” by comparing information from the vestibular system with the data it receives from the eyes. Such a complexly organized system allows cats to maintain balance in any conditions. Judging by the number of comparisons between dexterous people and cats, the animal body is fully capable of this.
Unfortunately, nothing is perfect in the world, and therefore even such a system can be overloaded with information and “fooled.” You yourself could encounter this by going too far with visiting carousels. The fact is that the brain and all analyzers adapt to constant rotation, and by inertia they continue to “feel” it even after the attraction has already stopped. At this moment, if you look at the person, you can see classic nystagmus. But why does this phenomenon occur in cats? They don't ride on carousels, do they?!
Nystagmus in animals can be congenital or acquired. By the way, congenital pathology of this type is exclusively characteristic of Siamese cats. In the second case, the cause of its occurrence is some kind of injury or, possibly, a disease that has a detrimental effect on the state of the cat’s nervous system. Sometimes severe stress leads to this. For example, the birth of kittens. Childbirth in a cat with nystagmus proceeds normally, and soon the pathology disappears on its own.
Today, veterinarians clearly identify several factors that contribute to the occurrence of nystagmus in adult animals:
- Albinism. In this case, problems with retinal pigmentation are observed, which has a negative effect on visual function.
- Eye diseases. Cataracts, glaucoma, dry keratocojunctivitis and simply keratitis - all this can contribute to the development of pathology.
- Inflammation of the inner ear. Everything is clear here: if a key organ of the vestibular system fails, nothing good can be expected.
- Brain lesions.
- Some drugs used to treat neurological disorders.
Sometimes a phenomenon occurs when a kitten has a curved “swan” neck and nystagmus. As a rule, this pathology develops between four months and a year (according to age). Most often, the pathology disappears spontaneously. The causes of nystagmus in cats are still not fully understood.
Nystagmus has two subtypes, which differ in the nature of eye movements. With pendulum nystagmus, the speed of eye movement is the same in all directions. In the clonic type, there is a slow and a fast phase. The eyes move slowly in one direction and then, after a brief pause, jerk sharply in the other direction.
Causes
The main cause of the disease is the unstable functioning of the oculomotor system, which is responsible for controlling eye movements. This disease can develop due to the influence of central (general) factors or local ones.
The central (general) ones include:
Local (vestibular) factors include:
- congenital vision loss;
- acquired vision loss;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- albinism;
- astigmatism;
- farsightedness;
- myopia;
- strabismus;
- retinal dystrophy.
During a pathological process in the brain or labyrinth of the inner ear, spontaneous nystagmus occurs. The direction of vibration of the eyeball indicates the level of damage.
- Horizontal lesion is a symptom of damage to the labyrinth of the middle sections of the rhomboid fossa.
- Vertical or diagonal lesion - characteristic of damage to the upper parts of the rhomboid fossa.
- Rotational lesion - it is responsible for the unstable functioning of the lower parts of the rhomboid fossa.
An indicator of the degree of disease of the vestibular analyzer is the amplitude of eye movements during nystagmus. Such a disease can occur as a result of severe tension in the central nervous system resulting from partial disorientation.
In addition, uncontrolled eye movements may appear after a stroke. I would like to dwell on this in more detail.
Stroke is a hemorrhage in the brain. This disease leads the list of pathologies that lead to disability in more than 50% of people. After a stroke, nystagmus becomes a frequent “companion” of the patient.
It all comes out due to the fact that a disorder occurs in the vertebro-basilar system of arteries, which is expressed by:
- in oculomotor disorders;
- vestibular coordination disorders;
- encirclement of a systematic nature.
Unstable blood supply to the medulla oblongata during a stroke manifests itself in paralysis and atrophy of the tongue, visual muscles, vocal cord, and hemiplegia. Vomiting, dizziness, and nystagmus are observed.
What to do?
If nystagmus is acquired after a serious injury or illness, it can only be dulled using appropriate medications. As such, there is no cure for nystagmus in cats, as brain surgery is often required to correct the cause. It is clear that in the case of cats, no one will do this.
If the cause is a serious illness, the symptom of which may be nystagmus, then after its elimination, eye twitching “automatically” goes away. Siamese and albinos should not be “touched” at all, since their nystagmus is a physiological phenomenon and does not cause any harm to the body.
Measures to prevent eye diseases
It is easier to prevent an ophthalmic disease in an animal than to treat it. Prevention includes:
- regular vaccination;
- preventing pet hypothermia;
- examination of the animal’s visual organs after street walks;
- washing the mucous membrane and eyelids with saline solution if wounds are found on them;
- timely contact a veterinarian.
A cat squinting its eye is not necessarily due to illness. Sometimes this is a variant of the norm, for example, when the animal is sleepy or calm. It is necessary to seek veterinary help if this symptom persists for a long time and is accompanied by lacrimation, pus discharge and deterioration in the pet’s physical condition.
Eye diseases in animals. Treatment of eye diseases at the IVC MBA.
All information posted on the site is provided in accordance with the User Agreement and is not a direct instruction to action. We strongly recommend that before using any product, you must obtain a face-to-face consultation at an accredited veterinary clinic.
Nystagmus in cats
Eyes are the mirror of a cat's soul
Eyes are not only a mirror of the soul, but also an indicator of health. And an experienced cat owner can easily determine from the cat’s gaze how his pet is feeling. If your cat has a dull look, or, even worse, his eyes are running or spinning, while the cat seems to be looking into emptiness, it’s time to sound the alarm. This phenomenon is called nystagmus.
We invite you to talk about all this in our publication today about what it means, what diseases nystagmus can be a symptom of, and how to deal with it.
The magic of a look
Cat's eyes have received so many comparisons and admiration in fiction that, perhaps, it would be inappropriate to immediately start talking about them in dry language as an organ of vision.
The writer Edmond de Goncourt wrote a stunning description of cat's eyes in his diary:
“Yes, the eyes of a cat are mysterious eyes that have, so to speak, only a green reflection, not illuminated by any human tenderness, mysterious eyes with a pupil in the form of a magic letter that changes at different hours of the day, eyes in which the unknown hides, eyes alarming as they watch you and look at you searchingly.”
I think that, peering into the eyes of the cat, Goncourt was the first to look away, which struck him and made him grab his pen.
Sometimes, looking at a cat, you involuntarily catch yourself thinking that inside it sits something more than an ordinary pet.
A cat's gaze can penetrate so deeply that it seems to reach the very soul.
The intensity of the gaze is so great that sometimes you just want to run away without looking back.
This creature is able to examine you, study and observe your behavior, and do this for a long time and persistently.
Why do cats make eye contact?
A cat's eyes are a very delicate and sensitive device given to it by nature.
The eyes are the largest relative to the body among domestic animals.
The shape of the eyes depends on the breed of the cat and varies from almond-shaped to almost round.
Cats' eyes come in different colors - from pale yellow to dark blue.
It is not uncommon to find cats whose eyes are different colors.
The pupil of cats has a vertically elongated shape, expanding in the dark to cover the entire eye, and in the light shrinking into a “thread”.
Cats are straightforward animals. If they want to say something with their gaze, then they will definitely say it.
But what? And why does the cat look into the eyes?
What a cat's gaze means can be determined based on its breed.
For example, if a Siamese's light turns red, then you should be wary; most likely, the animal wants to attack a person.
This breed has the most aggressive character.
Persian cats are the most capricious, so when she looks into her owner's eyes, she is most likely demanding attention.
Curious individuals with smooth fur look at the owner simply for the sake of curiosity.
By nature, these furry pets are very curious and inquisitive.
Cats do not tolerate and are very nervous when someone looks into their eyes, but they themselves are not averse to observing the object.
Gaze-scanner
With the help of a glance at the first meeting, a cat determines who is in front of it.
Whether to expect good things for her or not. Hide, run away, defend yourself, or, on the contrary, relax and ask for something tasty.
Therefore, before starting to communicate with an object, the cat will “scan” it with its gaze.
Thus, focusing their gaze on a person or the owner in particular, small predators thoroughly study his behavior.
After a short time, the cat will have a full set of owner’s habits, his social circle, identifying signs of his friends, and habits.
Having studied its owner in detail, the cat will know his mood, how and when it is best to approach him to ask for what he wants.
Language of sight
In addition, with the help of a glance, a cat always has something to say to a person.
For example, looking at the owner for a few seconds, blinking, and then turning away from him, she shows him her recognition, but does not invite him to contact or communicate.
This is akin to a human greeting - a nod of the head. A kind of act of politeness.
A long, almost continuous, persistent gaze, both in human practice and in cat practice, is usually alarming.
Therefore, it has the meaning of a warning.
Cats can stare for a long time and express goodwill.
In this case, you can figure out the cat's intentions by reading the rest of its body language.
Look-emotion
A cat's eyes are a mirror of her emotions. Try looking into the cat's eyes, which seem irresistible.
They are so deep, their radiance is comparable only to crystals.
The fire of bright emotions constantly burns inside.
If your pet is looking straight ahead with wide eyes, it means that he is very interested in what is happening.
With blinking and flickering eyes, the cat expresses its devotion.
Half-closed eyes indicate sleepiness or remaining cautious.
A clouded gaze signifies complete calm and relaxation and is a signal of trust and friendship.
Widely open eyes and dilated pupils indicate the animal’s fear.
If a cat's pupils suddenly widen and her gaze becomes “crazy,” this indicates that she is very scared.
Aggression can mean narrow, slit-like pupils.
Slit pupils mean that the cat is alert and confident.
Staring at someone point-blank is a challenge, and at such moments it is better to keep your distance.
Who's the boss, or a staring contest?
Thus, the cat’s gaze hides its mood.
After all, wild predators that were once domesticated still remain predators “at heart.”
They just need to set up an observation post and watch the owner.
Often cats look closely and for a long time into each other's eyes to establish primacy. The same applies to humans. A cat or cat determines “who’s boss in the house.”
In addition, this is how the cat understands what mood the owner is in - whether it is possible to make contact immediately or whether it is still worth waiting for a more suitable mood and moment.
In the case when the pet is very hungry or thirsty, looking into the eyes is another method of influencing the owner.
But if a person decides to look into the eyes of a cat, then she will most likely regard this action as an expression of aggression.
It also happens that at first a cat looks into the eyes, and then can sharply press its ears, hiss, or even rush to attack, regardless of whether you are a stranger or its owner.
Why cats do this, even if there is no aggression in your gaze, is explained by the fact that among predators, a direct gaze always means obvious hostility and preparation for an attack...
Therefore, the cat may decide to get ahead of you and attack first.
Therefore, when communicating with your beloved furry, adhere to the unspoken rule - look at him casually, trying not to make eye contact for a long time.
There is no need to unnecessarily awaken animal tendencies in a little tiger cub and agitate its predatory hypostasis.
Cats' eyes are very expressive, and it's worth learning to read them...
By carefully observing your pet, you can catch his mood.
But if he himself is looking for eye contact, or looks pleadingly into your face, then why not give in to it...
In addition, almost all cats have a bewitching, almost hypnotic gaze, and if you stare at it for a long time, it pleasantly relaxes and helps you take your mind off the whole world around you.
Look-magic
Probably everyone, when looking into the eyes of a cat, caught themselves remembering various kinds of mysterious and mystical stories, inspired by an attentive and calm response look.
For centuries, people have attributed magical powers to cats and associated them with gods, witches and witchcraft.
Different nations have legends about cats and their magical abilities. In some religions, cats are considered sacred animals, bringing both happiness and misfortune.
Cats and mysticism - there is more here - you can be curious!
There are still legends that cats are connected to the astral world by an invisible thread through which they transmit and receive information from matters inaccessible to human consciousness.
Cats have something like hypnosis and are even able to instill fear in their opponents.
Cats can sometimes read the thoughts of their owners, because sometimes you don’t have time to think about the pet, and he’s already right there.
Cats always understand when their owners need help, they come to calm and support.
They completely take away all the negativity and calmly leave.
It’s a pity that you can’t consult with them, otherwise they would certainly give good advice.
A cat's gaze can change a lot. He has suggestion.
When calm, cat eyes radiate wisdom, beauty and intelligence. Capable of transmitting force.
They seem to teach their patron the laws of life.
Learning to live like cats: light and completely free is not an easy task.
It is quite difficult in our modern times not to be led by someone.
Any pet you have fills life with a certain meaning, so take care of it and protect it.
After all, the fact that he settled with you definitely means something.
&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&
For the most persistent readers - a bonus - an entertaining story:
“The war with the Cat, or how Barsik and I couldn’t share an apartment”
Sources
888 mirror
What does nystagmus mean?
I would like to note right away that if a cat owner discovers such a strange state of the eyes in his pet, when the pupil rotates as if wound up and the cat looks into emptiness, this does not bode well. This kind of phenomenon is not the norm. These rhythmic oscillatory eye movements (usually movements occur in the horizontal plane) indicate serious brain damage.
Where does nystagmus come from?
Nystagmus is an alarming symptom
Let's look at the anatomy. The eyes play a very important role, and it is impossible to imagine maintaining body balance in space without clear vision. After all, there is a close connection between the eyes and other organs of the vestibular apparatus. Thus, it can be argued that the eyes for our brain are sensors that transmit readings to the brain, and it already analyzes it and makes decisions on what to do next. But,
when a cat begins to have nystagmus, this indicates damage to the brain as the main center.
Types of nystagmus
I would like to immediately note that such a disorder can be either acquired or congenital. The latter is typical for representatives of the Siamese breed. Kittens with nystagmus are often born there.
As for acquired nystagmus, the cause may be:
- injury,
- severe stress,
- transferred disease.
And if congenital nystagmus is not treated, then acquired nystagmus can and should be fought. However, not with the symptom of spinning eyes itself, but with its root cause.
Nystagmus can also be pendulum - in this case, the speed of eye movement is the same in all directions. And also clonic - in this case, we can distinguish the slow and fast phases of pupil movement.
Definition and classification of nystagmus
A person with netsagmus cannot focus his gaze on any object; even volitional efforts to stop involuntary movements lead to nothing.
Very often this disease manifests itself in combination with a decrease in visual acuity. Although the manifestation of the disease is minimized with age, any stressful situation or severe fatigue provokes it with renewed vigor. There are cases when, due to nystagmus complicated by eye disease, people practically go blind. In general, patients feel worse, their opportunities become more difficult, their quality of life is limited and their psychological balance is lost.
If the movements of the two eyes are of the same type, then the nystagmus is considered associated, but if different, then it is considered dissociated.
Depending on the direction of vibrational movements, it can be divided into the following types:
- Horizontal - when the eye shake occurs along the horizontal axis;
- Vertical - the eye “runs” up and down;
- Diagonal - movement occurs diagonally;
- Converging is rapid movement of the eyeballs towards each other;
- Rotatory - the eye performs rotational actions around the sagittal axis.
The nature of the movements is as follows:
- Pendulum-shaped nystagmus. Uniform punitive movements of the eyeballs occur from one side to the other;
- Jerky nystagmus of the eyes. Manifests itself as a slow movement of the eyes in one direction and a very rapid return to its original position;
- Mixed type. It is characterized by the presence of symptoms of both pendulum-shaped and jerk-like nystagmus.
Root causes of nystagmus
Veterinarians have been able to identify the most common root causes of nystagmus in cats. These are the following manifestations:
- Albinism – in this case, the cat has a problematic pattern of retinal pigmentation, visual function deteriorates, and the animal may lose vision.
- Eye diseases - nystagmus may develop against the background of cataracts, glaucoma, dry keratitis or conjunctivitis.
- Inflammatory processes of the inner ear - when the main organ of the vestibular system fails, vision also suffers.
- Taking medications – in particular drugs to treat neurological problems in cats.
- Physiological pathologies - some cats develop swan neck syndrome between 4 months and 12 months. The cat walks with its head tilted to one side and its pupil is spinning.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a person experiences oscillatory movements of the eyeballs, then it is necessary to be examined by the following specialists:
- ophthalmologist;
- neurologist;
- ENT doctor;
- neurosurgeon.
During the examination, the ophthalmologist examines visual functions and checks the condition of the optic nerve, fundus and retina. To determine the severity of nystagmus, you can apply the following criteria, which are used to make a simpler and more convenient diagnosis. The criteria have 3 main stages:
- 1 tbsp. - appears only when looking to the side.
- 2st. – if symptoms appear when looking directly.
- 3st. – appears when looking to the side.
In addition, it is necessary to identify the patient’s disease, which provoked the pathological process.
The following methods are used for identification:
- MRI of the brain;
- electronystagmography, it allows you to record the amplitude and direction of eye movements;
- assessment of visual acuity;
- electroretinography - examination of the retina.
Treatment methods for nystagmus are as follows:
- Optical vision correction. The doctor selects appropriate glasses or contact lenses for the patient. If the patient has atrophy or changes in the retina, the ophthalmologist recommends glasses with density filters that can provide optimal visual acuity.
- Treatment of pleoptic type. The retina of the eye is stimulated and specially designed eye exercises are performed.
- Drug therapy. This treatment is more supportive in nature, it helps to relax the muscles of the eye.
- Surgical intervention. An extreme method of therapy, used in cases where the above methods are powerless.
How to cure nystagmus
Nystagmus occurs with ear diseases
In the case of congenital nystagmus, the prognosis is not good. You can try to correct the situation on the operating table. But where can you find such a good veterinarian who will agree to perform a complex operation on a cat’s brain, without any guarantees of the result?
In the case of acquired nystagmus, it is important to establish the root cause of the disease and direct all efforts to eliminate it. However, I would like to note that you should be careful with albinos and Siamese - their nystagmus cannot be treated. Moreover, some veterinarians talk about animals adapting to this condition. Is it so? It’s difficult to say, but veterinary medicine does not undertake to correct the situation in their case.
Video about nystagmus in cats
Today we talked about a phenomenon in cats called nystagmus. About the causes of a running pupil, types of nystagmus and how to cure such a disorder. We hope our article will be useful to you. If you have experienced nystagmus in your cat, be sure to share your experience and story with us.
We are waiting for your feedback and comments, join our VKontakte group!
Phenomenological description of the forms of nystagmus
Congenital nystagmus occurs along with the following visual diseases:
- refractive error;
- color vision impairment;
- cataract;
- hemeralopia;
- albinism.
In most people suffering from the congenital form of the disease, the retina is not damaged. Ophthalmologists claim that the cause of congenital nystagmus is a violation of oculomotor function in the brain stem.
Free nystagmus is caused by tension in the extraocular muscles during fixation or convergence. Oscillation frequency is 10-17 per second. With this form of the disease, differential diagnosis should be carried out. This form of nystagmus is also called hysterical or eye tremor.
Nystagmus is constantly present in people who are blind from birth. It is caused by insufficiency of light stimuli and lack of visual control over the eyes.
Latent is a form of congenital fixation nystagmus. It can be detected by interference with binocular fixation.
Undulating is a special form of nystagmus (congenital). It appears at the age of 1.5 years and has a favorable course lasting about 12 months. This ailment occurs when efforts are made to fixate the gaze or when looking in a certain direction.
Almost everyone knows that the eyes can accurately determine the health status of an animal. If they are clean and clear, then the cat is probably fine. But what if your pet’s eyes periodically twitch from side to side, although he doesn’t seem to be looking anywhere? This phenomenon is called nystagmus. In a cat, its appearance sometimes indicates the presence of some pathologies, but in some cases this phenomenon does not pose a danger.
Vestibular syndrome in cats
Author: Karulin Petr Konstantinovich
Content
Symptoms
Feline vestibular syndrome is any process that leads to disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus in the head of an animal.
Anatomically, it is located in the inner ear, in close proximity to the brain. Therefore, the symptoms of its damage may be associated with pathologies in the structures of the latter.
If there are disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, the animal experiences uncoordination of movements, the cat often cannot stand normally, it drifts to the sides when walking, and may fall forward or backward. There is a throwing back, and more often a tilt of the head or walking in a circle - mainly in the direction of the lesion. You can also observe nystagmus - the cat's eyes move non-stop in a horizontal, vertical direction or in a circle. In some cats, disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus may be accompanied by vomiting, as in people with motion sickness in transport.
Causes
Vestibular syndrome in cats can usually be caused by several types of diseases.
First of all, these are ear diseases. Any pathologies associated with damage to both the external auditory canal and the middle and inner ear can cause the symptoms described above. Such diseases mainly include long-term otitis media of a bacterial or fungal nature, or caused by ectoparasites. In the absence of proper treatment for a long time, inflammation from the external auditory canal can spread to the middle ear. Also, various neoplasms can be found in the ears, which can also be accompanied by inflammation of surrounding structures.
Sometimes damage to the vestibular apparatus is provoked by the owners themselves, injuring the ear canal by cleaning the ears too intensively or using inappropriate medications during treatment.
The next series of pathologies leading to vestibular syndrome in cats are brain tumors. Affecting certain parts of the structures and accompanied by edema and inflammation, tumors, in addition to vestibular symptoms, can also lead to seizures, so special attention should be paid to this group of diseases. Inflammatory processes (meningoencephalitis and encephalitis) can also affect brain structures, but in cats they are not as common.
Infectious diseases can also lead to typical symptoms of vestibular syndrome. These diseases include viral peritonitis, toxoplasmosis, viral immunodeficiency and feline leukemia virus. Unfortunately, not all of them are treatable, but nevertheless, diagnosing them is very important.
And finally, a rare, but nevertheless common disease is the so-called idiopathic vestibular syndrome - a lesion of the vestibular apparatus of unknown origin. As a rule, with this disease there are no structural, inflammatory or any other lesions in the brain and ear canals. It is more common in older cats and goes away on its own without any therapy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing vestibular syndrome in cats is not so difficult; it is enough to evaluate the primary symptoms. It is more difficult to identify the root cause. Otitis of the external auditory canal is clearly visible during external examination and otoscopy. To evaluate the middle and inner ear, brain structures, and identify inflammation and neoplasms in these areas, it is recommended to resort to MRI diagnostics. To diagnose infectious diseases, a blood or cerebrospinal fluid test is required.
As for the diagnosis of idiopathic vestibular syndrome, it is made on the basis that all differential diagnoses have been excluded.
Treatment of vestibular syndrome in cats also comes down to eliminating the root cause. Neoplasms, if possible, undergo surgical removal and/or chemotherapy. Most infections and inflammation require long-term drug therapy using antibiotics, corticosteroids and specific drugs.
The article was prepared by Karulin P.K., veterinary neurologist at MEDVET © 2017 SEC MEDVET
General symptoms
Despite the similar symptoms of all types of ataxia, there are different signs that depend on the cause of the disease.
All types of violations are characterized by:
- Staggering "drunk" gait. The cat walks with its hind legs widely spaced, raising them high.
- Changes in head position - usually it is tilted to the side or down.
When the spinal cord is damaged, pain occurs when walking, and the animal tries to move less. Very often there is no loss of coordination of the head.
Cerebellar ataxia is characterized by the presence of tremor during movement - when walking or running, the animal’s body trembles slightly, often only the back part. There may also be nystagmus, which is rapid eye movements that are independent of where the cat is looking or what the cat is observing.
If there is damage to the vestibular apparatus, then nystagmus is also observed, severe pain in the head is possible (the cat meows, sits in the corner with its forehead pressed to the wall).
In addition to individual signs of the disease, characteristic only of one of its forms, there are several general symptoms by which ataxia can be identified:
- The cat has a wobbling gait with drifts to the side.
- When walking, the paws are widely spaced; The animal seems to be constantly afraid of falling.
- Often falls while walking or running.
- Rarely holds head straight; more often - with an inclination to the side or down.
- Does not control her body: even with fairly confident walking, she is not able to jump, go down/ascend, or turn around a turn.
- In severe cases, he cannot consistently perform the simplest movements. Remains in one place, but wobbles a lot and falls.
- Partially or completely not oriented in space. Bumps into objects and does not know how to calculate real distance.
The disease has species-typical and generally similar symptoms. The different symptoms depend on the causes. All types of pathology are characterized by:
- the cat holds its head atypically, it can tilt it to the side or lower it down;
- a staggering gait is observed, the animal loses coordination, the cat can walk, raising its hind legs high.
If the animal's spinal cord is damaged, it will experience pain when walking. Such cats try to hide in a quiet place and move less.
Attention! In severe forms, paralysis of the hind limbs can develop in cats.
With cerebellar ataxia, tremor occurs when running or walking. The kitten will often tremble, and most often the trembling is noticeable only in the back of the body. The cat also has dilated pupils and poor coordination.
If the vestibular apparatus is affected, the cat will suffer from severe headaches. Such animals constantly meow, hide in the corner, pressing their foreheads against the wall.
Hind limb paralysis