What is bordetellosis in cats?
This disease is caused by the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica. Bordetellosis can be transmitted from animals to humans. This doesn't happen often. Infection with the bacterium mainly occurs in people with weakened immune systems.
Bordetellosis in cats is often the cause of coughing throughout the cattery, as the bacterium is released when sneezing and in saliva. A domestic cat can easily bring bordetella from the street.
Feline bordetellosis, together with viral diseases - calicivirus and herpesvirus, leads in the number of causes of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Infection occurs through contact. The source of the spread is homeless animals that hide from the cold in basements during the autumn-winter and spring periods. It is enough for one animal to get sick for the entire population in this area, which is in contact with each other, to get sick.
Bordetella is a resilient bacterium. During sneezing or expiration, it is released into the environment, where it can remain viable for 10-14 days, depending on temperature and humidity. This causes infection of domestic cats through the owner's shoes. If a person steps on the saliva or discharge of a sick animal, and his pet cat sniffs his shoes, he can become infected. This transmission route allows the bacterium to infect a large number of animals when environmental conditions suitable for survival appear.
Characteristic symptoms
Kennel cough in dogs can occur in acute and permanent, that is, chronic form. These forms differ in the nature and types of clinical manifestations.
We recommend reading: How to Cure Staphylococcus in a Dog
Acute form
As a rule, pets suffer from the disease in the first months of life. The following symptoms appear:
- general weakness of the body;
- increased body temperature;
- depressed state (the animal is constantly lying down);
- sputum production;
- coughing fits, which may worsen while moving;
- sneezing;
- decreased appetite.
Sneezing and coughing are the main signs of bordetellosis.
Incorrect or untimely treatment of bordetellosis can lead to the development of bronchitis , which eventually develops into pneumonia. Therefore, if not treated properly, the initially harmless kennel cough can be fatal.
Chronic form
If the disease becomes chronic, the animal may experience signs of conjunctivitis, runny nose or rhinitis. The dog will also continue to have a fever, coughing and sneezing attacks. During a diagnostic examination (by palpation), the doctor will notice an enlargement of the lymph nodes - this is a characteristic sign of chronic bordetellosis.
Dogs and other pets that have had kennel cough for 4-5 months become dangerous to other animals. The fact is that with prolonged exposure to pathology on the body, the pathogen begins to be released into the environment, thereby increasing the risk of infection to other dogs.
Consequences of the chronic form of bordetellosis - conjunctivitis, runny nose or rhinitis
Who can become infected with bordetellosis?
Bordetella is a bacterial disease in cats. The bacterium bordetella bronchiseptica multiplies in the upper respiratory tract. The infection, sometimes mistakenly called viral, can cause pneumonia and death of the animal.
Unlike viral diseases, which are species-specific, bordetellosis affects not only cats, but also dogs, pigs, and rabbits. In addition, people with very weakened immune systems can become infected from pets.
This zooanthroponotic disease is not severe for humans; it usually goes away in a few days and is often confused with ARVI. Some cat and dog owners even joke that they got the flu from their pets.
If in dogs borreliosis is also called kennel cough - this is caused by specific symptoms and a high degree of infectivity of animals in crowded housing, then in cats there is nasal discharge and sneezing, sometimes turning into the urge to vomit.
How to prevent the disease?
The essence of preventing bordetellosis is to organize the proper maintenance of dogs in the kennel. It is necessary to have special premises for young puppies, where microclimate regulation is possible. Newly arrived animals must be kept in quarantine for the first time. Experts also recommend adjusting the diet, because only if adequate nutrition is maintained, the animal’s body will be able to successfully fight various pathogenic microorganisms.
When animals are kept crowded, it is necessary to carry out universal immunization of vaccines. For dogs, the drug Nobivac KS is used, which is intended for intranasal administration. Initially, vaccination is carried out on small puppies less than 4 weeks old, after which the procedure is repeated every year. During the vaccination period, it is strictly not recommended to use antimicrobial drugs, as this will negatively affect the health of pets.
When animals are kept crowded, it is necessary to carry out universal immunization of vaccines
Note! After vaccination, some complications are possible, for example, the development of a mild form of conjunctivitis or sneezing. But after some time, the symptoms go away on their own.
Video - Vaccine against kennel cough
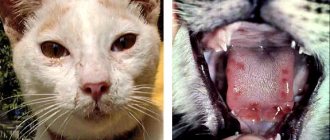
Signs and symptoms of bordetellosis in cats
The appearance of the first signs of the disease depends on the immune system. Kittens, pregnant and lactating cats with chronic diseases become infected faster and tolerate the disease much worse.
When cats become infected with the bacteria, symptoms include:
- there is a decrease in appetite and refusal to eat;
- she becomes lethargic;
- sneezes, mucus begins to come out of the nose;
- A cough occurs, which begins to intensify with any movement.
Subsequently, sneezing and watery eyes appear. Already at this stage, body temperature may increase. Wheezing and an increase in the size of the lymph nodes under the lower jaw are characteristic of the active phase of the disease. Weak cats may experience shortness of breath and bluish mucous membranes. Without adequate treatment, the animal may develop pneumonia.
The first signs appear 7-10 days after infection. It is not uncommon for cats kept together to become ill at different times. For most robust adult animals, even severe bleeds and wheezing do not cause pulmonary failure and cyanosis. The most dangerous disease is for kittens up to three months of age, pregnant and lactating females. Their risk of pneumonia is 15-20% higher.
Like most respiratory diseases, bordetellosis develops when the bacterium enters the respiratory system, where it attaches to eyelash cells. This is followed by the production of toxins that destroy local immunity. Damage to the mucous membranes makes it easier for toxins to enter the blood. Afterwards, the entire body becomes infected.
Bordetellosis is characterized by a prolonged paroxysmal cough. Presumably it is not caused by a bacterium, but by the action of its toxins on the respiratory center.
An adequate immune response avoids infection. For adult animals, it is produced through vaccination. In the first 4-5 weeks of life, young animals are protected by maternal antibodies if the mother has immunity to the disease.
During the course of the disease, the immune system of an adult animal produces enough antibodies to the bacterium, but their lifespan is variable. Even within 1 year, it is impossible to guarantee the absence of re-infection of a recovered cat.
What is bordetella
The three most common species of Bordetella are B. pertussis, B. parapertussis and B. bronchiseptica. These species are known to accumulate in the respiratory tract of mammals. It is most often seen in infants as a result of a disease known as whooping cough. The specific species that causes this disease, B. pertussis, is found only in humans.
Even after extensive research into vaccination against B. pertussis, whooping cough is still considered endemic in many countries. Due to the fact that B. pertussis is found only in humans and differs little from other Bordetella species, it is believed to have evolved in recent years from a common ancestor.
Diagnosis of bordetellosis in cats
It is difficult to identify bordetellosis yourself. To make a correct diagnosis, you need to contact a specialized institution and conduct an examination.
Cats that have a cough are considered infected with the bacteria if laboratory testing cannot be performed. To confirm the disease, the bacteriological method and PCR are used. Samples for research are pharyngeal swabs or transnasal swabs.
During the bacteriological method, the veterinarian uses sterile swabs. Bacterial seeding is carried out in a container with a suitable nutrient medium. Transportation of less than 2 hours does not reduce the number of bacteria in the wash. Longer delivery times require the use of a transport medium containing 1 percent caseic acid solution. A cool setting of 2 to 4 degrees Celsius helps preserve bacteria.
In 9 out of 10 cases, the bacteriological method will give the correct diagnosis. Violation of the conditions of transportation or taking swabs reduces the number of bacteria in the smear, increases the colony of fungi and opportunistic microflora. This may lead to a false negative result. Therefore, if it is impossible to take samples from mucous membranes in a clinic or laboratory, the PCR method is used. The polymerase chain reaction provides high sensitivity.
Often, in large clinics, other respiratory infections of cats are simultaneously examined using PCR. Serological diagnosis is almost never used: the level of possession of specific antibodies to certain antigens in cats is almost 100%.
In the absence of laboratory diagnostics, the diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture and explanations of the animal owner. The treatment prescribed for bordetellosis is identical to the use of drugs for other respiratory infections of cats.
When you notice the first symptoms, follow these steps:
- Consult a specialist at a veterinary clinic. The disease is insidious, and at home it is impossible to carry out all the necessary diagnostic measures.
- Describe to your veterinarian all the symptoms and history of the infection.
- Do a PCR test to identify respiratory diseases in the animal.
- Take a general clinical blood test.
- Undergo an X-ray examination of the chest area.
- Get additional tests if required by your veterinarian.
Bordetella and whooping cough
Whooping cough is an acute infectious disease mainly of childhood, characterized by a cyclic course and paroxysmal spasmodic cough.
The pathogen, Bordetella pertussis, was first discovered in 1900 in smears from a child’s sputum and then isolated in pure culture in 1906 by J. Bordet and O. Zhangou. The causative agent of a disease similar to whooping cough, but with a more mild course - bordetella parapertussis - was isolated and studied in 1937 by G. Eldering and P. Kendrick and, independently of them, in 1937 by W. Bradford and B. Slavin. Bordetella bronchiseptica, the causative agent of a rare pertussis-like disease in humans, was isolated in 1911 from dogs by N. Ferry, and from humans in 1926 by Brown. In 1984, a new species was isolated - Bordetella avium, the pathogenicity of which for humans has not yet been established.
Treatment of bordetellosis in cats
In order for recovery to occur as quickly as possible, treatment must be comprehensive. Only after the examination, the specialist prescribes medications and procedures.
The sooner the animal is examined by a veterinarian and receives medications, the sooner it will recover. The active phase of the disease lasts no more than 2 weeks, after which the cat can remain a carrier for several months. If kittens or immunocompromised animals become ill, veterinary care should be provided immediately.
Ready-made drugs
If the cat has no appetite, then an intravenous catheter is placed and infusion therapy is carried out. Antibiotic therapy is also carried out. The drug is selected based on determining the sensitivity of Bordetella bronchiseptica to a particular antibiotic.
It is not always possible to conduct such a test. Then the veterinarian usually prescribes a drug such as doxycycline. Additionally, mechanical cleaning of the nasal passages and eyes and removal of crusts that form from them are prescribed.
If possible, it is recommended to carry out tests to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to a particular antibiotic. This makes treatment more effective. If this is not possible, the veterinarian will select an antibiotic based on observation.
- Enrofloxacin is often used in weakened animals in the form of intramuscular injections at a dosage of 15-20 mg per kilogram of the cat’s weight. Treatment period is 10-14 days.
- Cephalosporin line often exhibit good antibacterial activity . Thus, Cephalexin suppresses not only bordetella, but also reduces the number of other pathogenic microflora of the respiratory canal.
- Amoxicillin , which is a successful drug for the treatment of respiratory diseases, is not effective for bordetellosis.
From the group of maintenance drugs, the veterinarian prescribes subcutaneous injections or infusion therapy consisting of ringer solution and glucose at a concentration of 5%. These substances are necessary for the rapid evacuation of decay products of dead cells and the maintenance of intercellular metabolism. Liquids help minimize dehydration that occurs in an animal with nasal discharge and a high fever.
Treatment methods
With timely treatment, all symptoms of the disease disappear after about 1.5-2 weeks
Provided that treatment is timely, all symptoms of the disease disappear after about 1.5-2 weeks, but the duration of bacterial carriage (carriage of infectious agents) can be from 3 to 4 months. During the treatment period, animals are separated and, providing the most comfortable living conditions, undergo restorative, symptomatic and antimicrobial treatment. Each of these methods differs in the nature of the therapeutic strategy and the drugs prescribed.
General strengthening
The doctor prescribes immunostimulating medications aimed at strengthening the protective functions of the animal’s body. The most effective general strengthening drugs include Gamavit and Ribotan. The use of Levamisole should be abandoned, since this potent drug is contraindicated for dogs with general weakness of the body.
To treat bordetellosis, the doctor prescribes immunostimulating drugs
On a note! To avoid serious complications, when treating bordetellosis, it is necessary to provide your pet with adequate nutrition. The ideal option would be to use high quality canned food.
Antisymptomatic
After the diagnosis is confirmed, the animals undergo regular examinations, and the doctor cleans the eyes and nose of dried exudate. The use of expectorants should be under the strict supervision of a specialist. All symptomatic drugs are potent, so failure to comply with the dosage or the wrong choice of medication can lead to side effects. To avoid unpleasant consequences, you must strictly follow all the veterinarian’s orders.
For the purpose of individual treatment for kennel cough in dogs, antiseptic drugs such as “Bars”, “Iris” and “Diamond Eyes”. The most effective anti-inflammatory drugs include Nazivin and Dioxidin. Also, for bordetellosis, immunomodulators can be used, for example, Thymogen, Maksidin or Anandin . All of the above products are used in the form of drops.
Antimicrobial
Among all the medications prescribed for treatment, Doxycycline stands out. Determination of antibiotic sensitivity is carried out if the pathology has become widespread, and the use of semi-synthetic antibiotics has not given the desired therapeutic effect. A mixed infection can also provoke kennel cough in dogs, which is why the attending physician may prescribe Gentamicin or fluoroquinolones (medicinal substances that have pronounced antimicrobial activity).
Solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration "Gentamicin"
Prevention of bordetellosis in cats
Since various environmental factors are to blame for the occurrence of infection in cats, it is important to comply with sanitary standards and requirements for keeping animals, as well as their transportation and quarantine conditions.
- At home, street shoes should be left on a separate shelf in the hallway, without spreading infection throughout the apartment.
- The room must be regularly ventilated and wet cleaned.
- Sick animals must be isolated immediately.
To reduce the risk of infection in cats, veterinarians recommend using disinfectants. Nurseries and shelters require disinfection mats, and the premises where animals live must be treated with any veterinary disinfectant. The bacterium is not resistant to the effects of such agents and dies quickly.