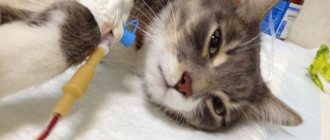
What to do if your cat has nephritis?
“Nepnritis” translated from Greek, nephritis is a severe, infectious-allergic disease that directly affects the kidneys. It can occur acutely, subacutely and chronically, and the area of localization is diffuse and focal. Depending on the stage of the disease, the symptoms and treatment of nephritis in cats vary. The kidneys act as a kind of filter, taking on all the negative consequences of infectious diseases, inflammatory processes and allergic reactions. It is important to understand that this is a dangerous disease that requires the intervention of a qualified specialist.
What is nephritis in cats
Nephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, the causes of which can be a number of factors with a possible recurrent course and the development of complications. The mechanism of disease development, depending on the type and stage of the disease, has its own clinical picture and pathomorphological specificity. Nephritis includes acute and chronic inflammatory processes of the renal glomeruli (glomerulonephritis), renal tissues and tubules (interstitial nephritis), causing proliferative or destructive processes in the kidneys.
The acute form of the disease occurs mainly after a bacterial or viral infection, less often it manifests itself as a result of poisoning, skin burns, dermatitis, including infectious and allergic etiology. Hypothermia of the animal, injury and other causes contribute to the appearance of illness.
Types of jade
Inflammation of the kidneys is distinguished by the severity of the process. It can be manifest or chronic. Depending on the tissue damage, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Glomerulonephritis. The kidney glomeruli are destroyed and gradually die.
- Pyelonephritis is a purulent inflammation of the renal pelvis.
- Interstitial. In this case, the kidney tubules become inflamed and urine filtration is impaired. It is rare in cats.
Causes
There are many causes of nephritis, but the most common signs of the disease in cats are:
- Incorrect use of medications.
- Poisoning with household chemicals.
- Poor nutrition or poisoning from poor quality food.
- Damage to the body by helminthic infestation.
- Hypothermia, injuries, etc.
Note. Most often among animals, cats are susceptible to nephritis; for example, in dogs this disease appears 3 times less often.
Causes of kidney diseases:
Often it is not possible to accurately determine the causes of the disease. The most typical are: age, genetic predisposition or congenital anomaly, ecology, infectious and systemic diseases (for example, diabetes), poisoning, trauma, unbalanced nutrition.
All animals over 7 years of age are at risk. They should be examined annually by a veterinarian, have blood tests, urine tests, ultrasounds and blood pressure checked.
Symptoms
Experts identify several types of disease; glomerulonephritis, interstitial, pyelonephritis and genetic predisposition. Please note that the symptoms of nephritis in a cat and a cat are identical. Depending on the severity of the disease, there are many pronounced symptoms. Let's look at which ones :
- General depression, sick appearance and decreased appetite in the cat.
- When you press in the kidney area with nephritis, pain appears.
- During the disease, the mucous membranes are affected, and swelling of the eyes and ears appears at their base.
- The urine becomes very dark and cloudy, and may contain pus and blood.
- A characteristic specific smell appears, the urge to urinate with nephritis increases, but the amount of urine decreases. In some cases, a cat may make plaintive sounds while urinating.
- Due to possible damage to the body by intoxication during nephritis, vomiting appears and thirst increases.
- Body temperature and blood pressure increase.
- The appearance of dry mouth, as a result of which cats often lick their lips.
- Perhaps the appearance of an ammonia odor from the animal's mouth.
- Some cats and kittens experience decreased skin elasticity and foul-smelling diarrhea.
- In rare cases, shortness of breath may occur with nephritis.
Self-medication in most cases aggravates the course of the disease, especially with infectious nephritis in a cat, and can lead to irreversible consequences. As the disease worsens, kidney failure and inflammation of the bladder may occur. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using laboratory tests of the animal’s urine, ultrasound of the kidneys and a general examination of the animal by a veterinarian. In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be ordered.
Symptoms: how does the disease manifest itself?
Nephritis in a cat has the following symptoms:
As a result of the illness, the pet develops characteristic shortness of breath.
- hyperthermia;
- frequent and scanty urine mixed with blood or cloudy sediment;
- lethargy, loss of interest in life;
- lack of appetite;
- increased thirst;
- frequent shallow breathing or shortness of breath;
- swelling of the paws, eyelids, ears;
- pain during urination;
- cyanosis or yellowness of mucous membranes;
- vomit.
Therapeutic measures
Let us immediately note that self-treatment is strictly contraindicated, especially for infectious nephritis. It is necessary to conduct research and take tests. An ultrasound examination of the affected kidneys will not hurt. All this is done to determine the exact type of pathology. This determines how to treat a sick animal. It is simply impossible to do all these manipulations at home, so immediately take your pet to a veterinary clinic. However, there are some recommendations for owners, following which you can alleviate the animal’s condition. Firstly, diet. Dry food, as well as salty, smoked, and fried foods should be excluded from the cat's diet. This is what to feed a cat with nephritis.
If the animal has been treated with something, immediately inform the veterinarian, who will decide whether to continue therapy or stop using the drug. The cat needs to be given complete rest and provided with plenty of clean, cool water. If antibiotic therapy is carried out (and this is probably the case!), then water will become especially important.
Treatment
In most cases, acute nephritis in cats is not so mild, and the pet may experience severe pain. Treatment methods are determined by the doctor after a complete examination of the animal, depending on the stage of the disease. Many of the manipulations cannot be performed at home, so it is important that they are carried out by a specialist. The main therapeutic measures include :
- During the treatment of nephritis, it is necessary to place the cat in a warm place and ensure rest. In acute cases of the disease, a 12-hour fast is prescribed.
- Diet. Doctors recommend low protein foods. The consumption of spicy, salty and dairy products is excluded.
- Corticosteroids (used for acute disease and); Prednisolone, Dexamethasone.
- Treatment with broad spectrum antibiotics; usually from the group of cephalosporins.
- Diuretics to prevent swelling and remove excess fluid during nephritis; Temisal, Furosemide, decoction of bearberry leaves, tincture of parsley leaves, Magnesium sulfate, etc.
- Iron supplements (if symptoms of anemia appear); Hemobalance, Ursoferran.
- Medicines to treat diarrhea (if any); Verakol, Hilak-Forte, Linex, Vetom 1.1.
- Laxatives (in case of constipation); Duphalac, Lactusan, vaseline oil.
- If symptoms of dehydration appear, a nutritional cocktail is prescribed; Ringer-Locke solution with glucose.
- The use of vitamin B during nephritis speeds up the healing process.
- Drugs to relieve intoxication; Enterosgel, Liarsin.
- Antiemetics; Metoclopramide, Ondansetron.
- Sedatives (in case of symptoms of heart failure); Riboxin, Cocarboxylase.
Treatment: which methods are effective?
Use of pharmaceuticals
All medications and dosage are prescribed by a doctor; self-medication leads to the death of the animal. Treatment of nephritis in cats includes a set of medications shown in the table:
| Pharmgroup | Medication |
| Antibiotics | "Amikacin" |
| "Erythromycin" | |
| "Gentamicin" | |
| "Amoxiclav" | |
| "Amoxicillin" | |
| "Vetrimoxin" | |
| Diuretics | "Furosemide" |
| "Veroshpiron" | |
| "Amiloride" | |
| "Torasemide" | |
| Potassium acetate | |
| Magnesium sulfate | |
| Vitamin complexes | "Aminosol" |
| "Fort Dodge Dufalight" | |
| "Gepavi-kel" | |
| "Tetravit" |
Medical nutrition
Among the abundance of medicinal foods, the owner can choose Purina Veterinary Diets and switch the pet to it.
If you have nephritis, you should exclude salty, smoked, fried, fatty foods from your cat’s diet, and reduce the amount of protein foods. The animal should eat fractionally, in small portions. The menu should include low-fat cottage cheese and kefir, cereal porridge, boiled vegetables and lean broth. Among feeds, preference should be given to those produced for kidney diseases. These include:
- Purina Veterinary Diets;
- Hill's Prescription Diet;
- "Advance";
- Royal Canin;
- "Farmina."
Herbal treatment
The use of herbal infusions for nephritis in cats is mandatory, since herbal remedies accelerate the penetration of antibiotics into the renal structure.
The decoction should be given to the cat through a syringe without a needle, in small portions so that the animal can swallow without choking. Inflammation of the kidneys should be treated with herbs such as bearberry, lemongrass, knotweed, dandelion, immortelle, and flax seeds. You can prepare each herb separately or make a mixture by mixing them in equal proportions. Juniper berries are effective and can be added to food. Preparation:
After brewing bearberry, the owner can give the pet this drink several times a day. Take 5 g of any plant or mixture, pour 200 ml of boiling water.- Let it brew for 20-30 minutes, cool, filter.
- Dilute the resulting broth with boiled water.
- Drink 10-15 ml 3-4 times. per day.
Useful materials:
- Cloudy eye in a cat Common causes of cloudy eyes in a cat The most common causes of cloudy eyes are glaucoma, cataracts or keratitis.…
- Cutaneous horn General description of the disease Cutaneous horn on the forehead or face (ICD 10 code - L57.0) -...
- Itching and odorless discharge Main causesBefore considering the factors that provoke the appearance of discharge that has a sour odor, it is necessary to immediately note...
- A cat’s liver How to determine that there is a malfunction in the liver All harmful substances that enter the cat’s body with ...
Prevention
It is easier to prevent a disease than to eliminate its consequences. We suggest you familiarize yourself with the basic preventive measures that will help keep your pet healthy .
- Proper nutrition . It is necessary to provide cats and kittens only with high-quality food, preferably home-cooked. If you can’t cook yourself, you can feed him dry food of at least premium class. It should also be excluded from the diet; salted, smoked, fatty, fried.
- Physical exercise . A sedentary lifestyle in cats leads to the formation of excess fat cells and metabolic disorders. This can cause kidney disease, including nephritis. Therefore, the pet must be provided with a sufficient amount of physical activity. For example, playing with a ball or using special game “fishing rods”.
- Avoid hypothermia . To prevent kidney disease, you need to keep your cat warm and avoid drafts.
- Weight control . If your pet is overweight, then it is necessary to use a health-improving diet.
- Taking vitamins . Premium and superpremium cat food contains a sufficient amount of vitamin complexes and no additional vitamin intake is required. If the diet consists only of natural products, without the use of dry food, then it is necessary to add vitamins to the food.
- Drinking water . For proper kidney function, it is necessary to provide the animal with constant access to clean, drinking water. Cleanliness of the cat's litter box. It must be regularly treated with special disinfectants.
The prognosis for the acute course of the disease is in most cases unfavorable. Therefore, the sooner a cat gets to the doctor, the greater the chance of a quick cure for nephritis without complications. If, when symptoms are detected, it is not possible to hospitalize the animal yourself, keep the pet warm and limit access to food until the doctor arrives.
Clinic
Nephritis can occur acutely, subacutely and chronically, the severity of symptoms depends on the specific form of the disease. In severe cases, the filtering ability of the kidneys is impaired, which has a serious impact on the functioning of the entire body.
Typical signs of nephritis:
- disturbance of urination - can be frequent or, on the contrary, rare, difficult;
- addiction to water - due to loss of fluid and constant dry mouth;
- increased body temperature - fever is accompanied by chills, lethargy, lethargy;
- criteria identified by the veterinarian - pain in the lumbar region, changes in blood and urine tests.
We will help you cure your pet. Call 33-94-45!
What to do first
If such a disease is detected, the pet, of course, may be prescribed medication. Both nephritis in cats, the symptoms of which were discussed above, and other diseases of the genitourinary system, with the correct selection of drugs and when used according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor, go away quite quickly.
A cat with such a pathology, of course, should first be shown to a veterinarian. In any case, after detecting symptoms, your pet should immediately be put on a starvation diet. Also, the animal must be kept warm.
A sick pet should be fed frequently. At the same time, the cat’s diet should definitely include foods that contain large amounts of potassium, calcium and carbohydrates and are low in table salt and protein. It would be a good idea to give a sick cat, for example:
- low-fat fermented milk products (kefir 1%);
- cereal and vegetable porridges;
- low-concentrated meat broths.
In case of acute nephritis in cats, fried, salted, smoked and baked foods should never be given to pets. Also, owners of such animals will have to refuse to purchase industrial feed. In case of an acute form of the cat, you can try to help by replacing the water in its drinking bowl with a decoction prepared from diuretic medicinal herbs.
Nephritis in cats
Nephritis
– from Latin nephos
-kidney and
itis
-inflammation - a term that combines various inflammatory diseases of the kidneys. In cats there are:
- Glomerulonephritis
- Pyelonephritis
- Interstitial nephritis
Nephritis in cats can occur:
Nephritis occurs both without changes in kidney function and with the development of acute and chronic renal failure.
Pyelonephritis
- inflammation involving all structures of the kidney, caused by various bacteria (most often E.coli
,
Proteus
,
Staphylococcus
). Often develops against the background of inflammation of the uterus (metritis), urocystitis (inflammation of the bladder, when the patient has not received the necessary treatment for the latter or has undergone an insufficient course for cure), predisposes to the spread of infection - cessation of urine flow when the urinary tract is blocked due to urolithiasis, as well as hematogenous by - i.e. with the bloodstream, when the source may be any source of inflammation in the body or systemic viral/bacterial infections.
Glomerulonephritis
- an autoimmune disease that affects only certain structures of the kidney - glomeruli (glomeruli).
Interstitial nephritis
- inflammation of the kidney tissue of a non-infectious nature with damage to the interstitial tissue and renal tubules. One of the causes of the last stage of kidney loss in cats (nephrosclerosis). The disease is still poorly understood, and intravital diagnosis is difficult.
Often the symptoms of nephritis in cats are nonspecific and similar to signs of other diseases:
- Decreased activity
- Decreased appetite
- Nausea
- Very rarely - shortness of breath
- Pain in the lumbar region - usually detected only during examination by a veterinarian
More characteristic of jade is:
- Increased, but not difficult and usually not painful urination
, much less often - scanty urination; - Increase fluid intake;
- Dry mouth
(in addition to the fact that the cat drinks a lot, it may lick itself frequently); - The urine may have an unpleasant odor;
- May change the color of urine, often becoming cloudy;
- Specific changes in urine analysis
(appearance of a large number of leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, renal epithelium, casts); - Increased body temperature
is relatively uncommon in cats with acute nephritis; - Very rarely in cats there is swelling of the limbs and other parts of the body.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder;
- Analysis of urine;
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- Determination of urine protein/creatinine ratio;
- In some cases, a kidney biopsy (taking a tiny piece of kidney tissue using a special needle) may be recommended to determine the exact diagnosis.
Nephritis in cats is a serious kidney disease
Kidney disease is very common among dogs and cats. But cats suffer from nephropathies much more often than dogs. Some form of kidney disease occurs in almost all older cats.
- interstitial nephritis,
- amyloidosis,
- bacterial nephritis,
- glomerulonephritis
It can be stated with reasonable confidence that pathologies of the urinary system are quite common not only in human, but also in veterinary medicine. This is due to the fact that the kidneys are responsible for removing many toxic compounds from the body, they also work as a “filter”, so that in case of any infectious, viral, parasitic disease or poisoning, they are the ones who are under attack. Because of this, nephritis often occurs: in cats, this pathology is common and severe.
What it is?
This is the name for inflammation of the kidney tissue. Since the kidneys (as we have already talked about) are responsible for removing many metabolic products from the body, the body has a very hard time with this disease. The processes of autointoxication are constantly increasing, and other manifestations of severe functional disorders are observed.
An attempt to “cure” a cat from fleas often ends with kidney damage, when almost glasses of insectoacaricidal preparations are poured onto the withers of the unfortunate animal. In general, almost all types of poisoning that can be observed in domestic cats are fraught with a similar outcome: poor nutrition (spoiled, old food), household chemicals, poisons for rats and mice... All this is extremely dangerous for cat health.
In addition, we must not forget about internal parasites, which can successfully poison an animal from the inside. As you know, helminths produce a lot of toxins. Partially they enter the blood, but their main negative effect is that the secretions of worms greatly reduce the immune status of the body. It is because of parasitic diseases that chronic nephritis often develops in cats.
Very often, kidney inflammation develops against the background of pyoderma or other generalized skin lesions. This includes burns, dermatitis, including those of infectious and allergic origin. This is due to the fact that the skin has an extensive network of blood vessels, through which a huge volume of toxins enters the blood, and from there to the liver and kidneys.
What happens?
There are acute and chronic types. There are several more types of disease:
- Glomerulonephritis, when the glomeruli are affected.
- Interstitial nephritis in cats, characterized by inflammation of the renal tubules.
- Pyelonephritis, in which purulent inflammation of the renal pelvis is often recorded. Often the prognosis for this disease is questionable, since it is very difficult.
- Hereditary pathologies, autoimmune pathological processes. Often, the appearance of this type of disease is still a mystery to scientists.
Symptoms
There are quite specific symptoms that accurately indicate damage to the kidney tissue. Firstly, the animal’s urine becomes very cloudy, mixed with pus and blood. It often has a rather unpleasant odor. When urinating, the cat hunches its back strongly, screams and meows hoarsely in pain.
If the animal has been treated with something, immediately inform the veterinarian, who will decide whether to continue therapy or stop using the drug. The cat needs to be given complete rest and provided with plenty of clean, cool water. If antibiotic therapy is carried out (and this is probably the case!), then water will become especially important.
Very often we encounter pronounced morphological lesions of the kidneys in cats, which are inadequately manifested clinically. In this regard, the kidney is an organ that begins to “scream” about its problems too late. It follows from this that recognition of the earliest stages of the pathological process (when effective etiological and pathogenetic treatment is still possible) lies in the scope of routine
laboratory diagnostics
biological fluids and intravital morphological studies of kidney tissue in cats.
Some cat breeds are predisposed to congenital pathologies. For example, Persian cats and their crosses can have polycystic kidney disease, where cysts form in the kidneys, sometimes reaching enormous sizes. This problem can be detected during a clinical examination; the kidneys are palpable and enlarged compared to a normal organ. Defeat is confirmed when
ultrasound examination
. No treatment has been developed to date. The prognosis is unfavorable and ends in kidney failure in middle-aged cats. Nephroprotectors prescribed by a veterinarian can increase the life expectancy and comfort of your pet. Congenital renal amyloidosis occurs in Abyssinians. With this pathology, a specific substance, amyloid, is deposited in many organs, including the kidneys, which leads to disruption of their functions. In susceptible animals, the process can proceed at a catastrophic pace and can lead to renal failure at a young age.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bS4VZbvGz8w
The discovery of kidney stones in cats is a rare finding. The owner may suspect a similar problem when blood is detected in the urine, pain syndrome, and sometimes kidney stones are asymptomatic. The diagnosis is made comprehensively based on ultrasound and additional diagnostic methods. The veterinarian may prescribe a special diet, antimicrobial treatment, and, if necessary, pain medications.
Most often, veterinarians have to deal with end-stage kidney disease. Owners complain of a lack of appetite in the animal, the cat begins to drink a lot, vomiting, oral ulcers, and various neurological manifestations may appear. As a rule, this is associated with prolonged kidney disease leading to functional failure; at this stage, the kidneys are destroyed by more than 50%. The diagnosis is confirmed
laboratory blood test
And
ultrasound examination
, allowing you to clarify the type of kidney pathology (kidney tumor in a cat, acute blockage of the ureter, hydronephrosis, kidney cysts, nephrosclerosis, etc.).
Unfortunately, treatment is only symptomatic:
- The water-electrolyte balance of the blood is corrected,
- a low-protein diet is prescribed,
- nephroprotectors and drugs that reduce uremia are administered.
Most likely, chronic interstitial nephritis is the cause of the above syndrome. Cats are quite hidden animals; even attentive and loving owners may not notice the first signs of illness for a long time. This is why it is so important to take your pet to the veterinarian regularly. Examination of urine and blood allows a diagnosis of kidney disease to be made in the early stages.
IN
networks of our veterinary clinics
“Cat and Dog” has all the necessary equipment to conduct any research and identify the causes of the disease; our specialists work around the clock for the benefit of the health of your pets.
Signs of disease development
Of course, all lovers of these pets should know what symptoms appear most often in cats with nephritis. Signs of this disease in acute form, in addition to problems with urination, are:
- decreased appetite and depressed state;
- pain when pressing in the kidney area;
- swelling of the eyelids, paws, base of the ears;
- jaundice.
In case of acute nephritis, a sick cat begins to go to the litter box very often. At the same time, the amount of urine she produces decreases.
Chronic nephritis in cats can be preliminarily diagnosed by the presence of symptoms such as:
- frequent “trips” to the tray with large amounts of urine;
- unpleasant ammonia odor from the animal’s mouth;
- apathy;
- vomiting and persistent diarrhea.
The body temperature of a cat with a chronic form of the disease remains normal. The urine of cats with kidney nephritis is usually cloudy and brown or reddish in color. While visiting the tray, sick animals may take unusual poses or make strange sounds.
With nephrosis in cats, among other things, immunity sharply decreases. And this, in turn, can lead to infection of the pet with fungi, viruses or bacteria. Quite often, with nephrosis, anemia is also diagnosed in a cat.
Symptoms of nephritis in cats
The initial symptoms of the disease in an animal are:
- lethargy;
- chills, increased body temperature;
- deterioration or lack of appetite;
- thirst;
- significant increase in blood pressure;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- frequent urination (pollakiuria), while the amount of urine produced decreases;
- presence of blood in the urine (hematuria) and pus;
- unpleasant smell of urine.
Also, one of the characteristic symptoms of the disease in the acute form is pain that occurs upon palpation in the kidney area, which manifests itself as anxiety in animals.
Low back pain may result in a stiff gait and a hunched position.
Acute and chronic nephritis in cats: symptoms and treatment
The kidneys play the role of a filter in our body. Kidney disease is very dangerous, but unfortunately very common in cats. In this article we will try to talk about such a disease as nephritis in cats , what its symptoms are and the necessary treatment, possible causes of its occurrence and preventive measures. All information is provided for informational purposes only.
. Never self-medicate, it is dangerous for your cat's health. If medications are used incorrectly, complications that can be fatal can occur.
Prognosis for nephritis in cats
If a sick animal with an acute form is provided with timely and correct treatment, as a rule, the animal’s condition improves after 7-10 days. Treatment of chronic nephritis takes much longer, and it will require more effort, it all depends on the degree and severity of the disease.
Similar articles
The pathology “chlamydia in cats” develops due to penetration into…
Recently, veterinarians have observed a sharp increase in pancreatic diseases...
Leave a request for treatment for your pet right now!
Characteristic signs
The symptoms of leukemia are varied. The following signs raise suspicion:
- digestive disorders;
- inflammation of the gums;
- constant illness;
- disheveled fur, oppression;
- enlargement of local lymph nodes;
- anemia;
- eye lesions;
- salivation;
- abortions;
- infertility;
- tumors.
- paresis of the limbs.
Nephritis in cats: causes
- Causes of nephritis in cats include:
- exposure to pathological microflora. Nephritis affects the kidneys, which are the body's natural filter; a very large amount of blood passes through them. If the animal’s body is affected by any infection, the amount of pathological microflora that was produced during the course of the disease will in any case pass through the kidneys with the blood. Because of this, an inflammatory reaction occurs, which in turn leads to nephritis;
- illiterate use of medications. Some owners, in pursuit of the health of their pet, often flirt and begin to stuff the cat with a variety of medications or use them incorrectly. For example, if you want to protect your pet from fleas, they use medications that need to be applied to the withers. If you overdo the dose, it can lead to kidney disease;
- food poisoning - with poor nutrition and consumption of spoiled foods, it is easy to get poisoning of the body, which provokes nephritis;
- poisoning from household chemicals;
- the activity of internal parasites - many worms secrete a huge amount of toxins while in the cat’s body. Because these toxins enter the bloodstream, the kidneys filter them and take the hit;
- epidermal lesions. Diseases that affect the skin of an animal can cause nephritis. This is due to the presence of a huge number of blood vessels in the pet’s skin. During inflammation, all bad bodies enter the bloodstream, and subsequently pass through the kidneys and genitourinary system, and therefore can damage them. Skin diseases include any kind of dermatitis, burns, ulcers, mechanical damage (abrasions, scratches, bites, wounds, etc.).
Knowing the causes of any disease gives the owner a guideline in which direction to look and what to pay attention to when keeping a cat. Thus, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of diseases that significantly reduce the quality of life of a pet, and in some situations can even end it!
Jade in cats: types
Nephritis in cats has different types of manifestations, which are listed below.
- Glomerulonephritis - this type affects the glomeruli. Treatment should be as careful as possible and be accompanied by preventive measures in the future.
- Interstitial nephritis in a cat - this type is characterized by inflammation of the channels that are located in the kidneys. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out only by a specialist, or under his supervision!
- Pyelonephritis is a complex disease that does not always occur easily. There is inflammation (usually purulent) of the renal pelvis. Treatment of pyelonephritis is not always successful.
- There are types of nephritis, or simply kidney diseases, that do not belong to any subgroup; they are hereditary. Symptoms and lesions can be different and fundamentally different from each other. This remains a mystery to scientists.
Symptoms of nephritis in cats
Diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system have pronounced symptoms.
Causes of nephrosis in cats
The reasons for the development of nephrotic syndrome in our little brothers may be of different nature and etiology. Nephrosis in cats, as a rule, develops against the background of acute, chronic viral and bacterial infections. Canine distemper, panleukopenia, salmonellosis, brucellosis, toxoplasmosis, and other highly contagious infections can trigger the development of this disease in animals.
Causes of nephrosis in cats:
- autoimmune infections;
- poisoning with potent poisons, salts of heavy metals;
- ingestion of various toxins and pesticides into the body;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- prolonged hypothermia;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body, water-salt, electrolyte metabolism;
- a sharp decrease in immune status and body resistance;
- chronic diseases of the urinary system (glomerulonephritis, nephritis).
Important! Against the background of proliferative glomerulonephritis, lipoid nephrosis can develop, which is accompanied by degeneration and replacement of organ tissue with fatty cellular structures. The pathological process is very severe and irreversible.
Long-term use of certain medications can contribute to the development of nephrosis. Various toxins and chemicals that enter the body from the outside can not only provoke severe poisoning and intoxication, but also cause circulatory problems in the renal tubules.
Nephrosis occurs in acute and chronic forms. The symptoms of the disease largely depend on the etiology, root cause, intensity of pathological processes in the kidneys, age, and general physiological condition of the animals.
Unfortunately, the chronic form is practically untreatable. The mild form, if treatment is prescribed in a timely manner, goes away in animals almost without a trace, without causing serious disruptions in the functioning of the excretory system. When choosing therapeutic therapy, it is very important to establish the etiological factor, the root cause of the disease. Treatment methods are primarily aimed at eliminating the main cause that led to the development of nephrosis in cats.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: British chinchilla - characteristics of the cat breed, care, cat food, popular colors
If poisons or toxins enter the cat's body, detoxification therapy is prescribed. Furry patients are prescribed sorbents, gastric lavage, droppers, and medications to normalize their general condition.
If nephrotic syndrome occurs due to infections, complex medical therapy is prescribed. Cats are prescribed antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic drugs, enzymes, hepatoprotectors, and immunomodulators.
To normalize metabolic processes, hormonal therapy (triiodotyranine hydrochloride, corticotropin) is used. In order to enhance diuresis, four-legged patients are prescribed mercusal, theophylline, and euphilin. To normalize the general condition, the veterinarian will select a therapeutic diet, vitamin and mineral complexes. Animals are injected with glucose with caffeine, ascorbic acid, and insulin.
To prevent the development of nephrotic syndrome in cats, it is very important to choose the right diet for your pet, monitor the state of the immune system, and prevent hypothermia. Preventive vaccinations and revaccinations will prevent your beloved cat from becoming infected with dangerous viral and bacterial infections and diseases.
Signs of chronic glomerulonephritis and methods of combating it
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years? Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Chronic glomerulonephritis is an immunoinflammatory chronic kidney disease that initially affects the renal glomeruli and tubules, subsequently spreading to other kidney tissues. Slowly progressing, damaged kidney tissue is replaced by connective tissue, sclerosis occurs, leading to chronic renal failure.
Kidneys are paired organs that perform the function of urine formation through chemical self-regulation of the body, thereby removing foreign compounds and toxic substances from the body. They take part in carbohydrate and protein metabolism and in the formation of a number of biologically active substances.
The main load during blood filtration falls on the renal glomeruli with tubules and Bowman's capsule (nephrons). At the time of birth, nephrons have already formed, but continue to mature for about 10 years. Since new glomeruli are no longer formed after birth, their loss leads to kidney failure.
Upon completion of filtration, urine is excreted through the renal tubule into the renal pelvis, from where it drains into the bladder.
First of all, with glomerulonephritis, changes occur in the nephrons:
Stages
Chronic glomerulonephritis undergoes several stages:
- Compensation stage. This is an early stage in the development of the disease. At this stage, the kidneys are functioning without visible disturbances. There is a moderate increase in blood pressure and slight swelling. A slight increase in protein in the urine, a change in its density, the presence of modified red blood cells. The concentration of urine decreases.
- Stage of decompensation. At this stage, kidney function is impaired and renal failure occurs. Blood pressure numbers are high, the body is poisoned with nitrogenous compounds, and daily urine output increases. The level of protein in the urine increases, the presence of casts and red blood cells increases, and the density of urine decreases.
- Uremia. The most difficult stage. The kidneys cannot maintain the correct composition of the blood. Intoxication with residual nitrogen, creatinine, and urea appears.
Chronic glomerulonephritis can be infectious-immune and non-infectious-immune.
Types of glomerulonephritis:
- Latent glomerulonephritis. The most common type, it accounts for 45% of the total number of patients. Symptoms are mild. Slight increase in blood pressure, mild swelling. The disease can be identified by the results of a laboratory test: protein, red blood cells and white blood cells are increased in the urine. Lasts a long time, up to several decades. Systematic outpatient monitoring of the patient is required. Working capacity is not impaired.
- Hematuric glomerulonephritis is rare, accounting for about 5% of all cases of chronic glomerulonephritis. There is an increased content of altered red blood cells in the urine, which is why the urine is red or pink. Anemia is sometimes observed. Renal failure occurs infrequently, and the course of the disease is favorable.
- Nephrotic glomerulonephritis. It affects 25% of the total number of cases of glomerulonephritis. With this type, the pressure is increased, there is severe swelling, and little urine is produced per day. There is protein in the urine, the density of the urine is increased. In a biochemical blood test, cholesterol is increased and total protein is decreased. This type of glomerulonephritis progresses moderately, but rapid progression is also possible. Kidney failure develops.
- Mixed form of the disease. Occurs in 7% of cases. Repeats the symptoms of hypertensive and nephrotic types. It is characterized by a persistently progressive course and the formation of chronic renal failure.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Signs of kidney failure in a cat, symptoms and treatment, diet and food, stages of chronic failure. Any form of the disease has two phases:
- Compensated. The kidneys are working normally.
- Decompensated. The kidneys work with impairment of their functions, chronic or renal failure progresses.
The result of chronic glomerulonephritis is the formation of chronic renal failure. The very first symptom is a decrease in the relative density of urine (isosthenuria) and an increase in the amount of urine excreted per day (polyuria). Diuresis increases at night (nocturia). Signs of uremia appear. The body is poisoned with nitrogenous substances and uremia develops.
Tubulointerstitial nephritis is a disease that is known to a small number of people. According to medical statistics, this disease in most cases affects individuals over 60-65 years of age. Only in 2% of cases is it found in the younger population.
Basic concept
Tubulointerstitial nephritis is a nonspecific disease that affects the liver. A rapidly occurring inflammatory process negatively affects the hepatic soft tissues and its canal passages. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, atrophy is possible. The etiology of this disease varies.
Inflammation of the kidneys is distinguished by the severity of the process. It can be manifest or chronic. Depending on the tissue damage, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Glomerulonephritis. The kidney glomeruli are destroyed and gradually die.
- Pyelonephritis is a purulent inflammation of the renal pelvis.
- Interstitial. In this case, the kidney tubules become inflamed and urine filtration is impaired. It is rare in cats.
Hurt
Interstitial nephritis (Tubulointerstitial nephritis)
The mechanism of development of interstitial nephritis depends on the nature and intensity of the damaging factor. Often, inflammation has an autoimmune basis and is provoked by the deposition of immune complexes circulating in the blood (during lymphoproliferative processes, systemic lupus erythematosus, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or antibodies to the basement membrane of the tubules (during antibiotic intoxication, transplant rejection).
When the process is chronic, an important role is played by the pathological activation of macrophages and T-lymphocytes, which cause proteolysis of tubular basement membranes and enhance peroxidation with the formation of free radicals. Sometimes the tubular epithelium is damaged as a result of selective accumulation and direct destructive action of a nephrotoxic substance reabsorbed from primary urine.
Local release of inflammatory mediators in response to the action of a damaging factor causes swelling of the interstitium and vascular spasm, which is aggravated by their mechanical compression. The resulting ischemia of the renal tissue potentiates dystrophic changes in cells, reduces their functionality, and in some cases provokes the development of papillary necrosis and massive hematuria.
Due to increased pressure in the tubules and a decrease in effective plasma flow, the filtering capacity of the glomerular apparatus is secondarily impaired, which leads to renal failure and an increase in serum creatinine levels. Against the background of edema of the interstitial tissue and damage to the tubular epithelium, water reabsorption decreases and urination increases.
In acute nephritis, a gradual decrease in edema of the interstitial substance is accompanied by restoration of renal plasma flow, normalization of the glomerular filtration rate and the efficiency of tubular reabsorption. The long-term presence of damaging agents in combination with persistent stromal ischemia against the background of blood flow disturbances entails irreversible changes in the epithelium and replacement of functional tissue with connective tissue fibers.
Sclerotic processes are enhanced by stimulation of fibroblast proliferation and collagenogenesis by activated lymphocytes. Hereditary predisposition plays a significant role in the occurrence of a hyperergic inflammatory reaction.
Nephritis in cats: diagnosis
After contacting a veterinary center, the disease must be diagnosed. The doctor must exclude the presence of other diseases that have a similar etiology and similar symptoms. You must tell us when you noticed the first symptoms and whether there were any prerequisites for the onset of the disease.
- Various procedures are also prescribed to determine whether cats have nephritis, for example:
Diagnosis of nephritis in cats
However, the above symptoms are not enough to make a correct diagnosis, since most of them may indicate the presence of other diseases of the animal’s genitourinary system.
In this regard, it is very important to conduct timely laboratory tests when diagnosing the disease. Urinalysis is aimed at isolating infectious microorganisms - the causative agents of the disease and determining their quantity during bacteriuria for the presence of blood, epithelial cells, protein, a significant amount of which appears at the onset of the disease (subsequently its content decreases), determining the density and pH of the urine reaction (usually , it is sour). Conducting such laboratory tests gives a complete picture of kidney function.
Within 2-3 weeks, depending on the cause of the disease and the condition of the body, if the first symptoms are ignored or as a result of unqualified treatment, the acute form may become chronic.
Unlike the acute form, chronic nephritis is manifested by frequent urination with a large volume of urine excreted (polyuria). In this regard, the animal’s thirst increases. There is pallor of the mucous membranes with a gray tint, severe swelling on the abdomen, eyelids, paws, and perineum. Anemia develops, vomiting, gastrointestinal disorders appear and, as a result, an unpleasant odor from the mouth. The kidneys are dense, however, they are little painful. Body temperature does not exceed normal.
The veterinarian's office will perform a complete blood count, including a blood chemistry profile, a complete blood count, and a urinalysis. The results of a complete blood count are usually insignificant. In severe cases, a biochemical profile may reveal abnormally low levels of the protein albumin in the blood (hypoalbuminemia) and high levels of cholesterol in the blood (hypercholesterolemia). The presence of blood proteins and other proteins in the blood can help your veterinarian make an initial diagnosis. In cats with kidney failure, urinalysis will reveal corresponding changes in the urine.
Creatinine is a waste product normally excreted by the kidneys, and its presence in urine is measured as a diagnostic indicator of kidney function. A more accurate test calculates the urine to creatinine ratio to give your veterinarian an idea of the extent of kidney damage. The degree of protein loss in urine roughly correlates with the severity of kidney disease. Thus, measuring the protein to creatinine ratio also helps in assessing response to treatment and disease progression or regression.
Quite often, nephritis is diagnosed late, only when signs of renal failure have already begun to appear.
Disease prevention
Preventing the development of nephritis in cats is quite easy. To do this you need:
- do not allow the animal to become hypothermic;
- carry out deworming on time;
- use medications correctly for various diseases;
- feed the animal only with high-quality purchased mixtures.
Of course, cat owners need to put household chemicals away as well. Also, measures to prevent nephritis include physical activity for the animal (within reasonable limits). The cat should be given more attention, for example, by playing with it.
Predictions and prevention
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and begin treatment, the disease subsides within a week. Complete recovery depends on the age of the animal, the state of the immune system, and the presence of concomitant ailments. In advanced cases, the prognosis is unfavorable, since sepsis may develop, which leads to the death of the animal.
To avoid nephritis, cats should be protected from hypothermia and drafts. Pesticides should be kept away, and when removing fleas, strictly adhere to the instructions for the product. It is recommended to treat all systemic diseases in a timely manner. To prevent helminthiasis, which can cause inflammation, it is advisable to carry out deworming once every 6 months.
Jade in cats: first aid
Providing first aid to a pet excludes the use of medications by the owner, therefore any illiterate use of medications can aggravate the problem.
situation and complicate the course of the disease. If you observe symptoms indicating nephritis or other diseases affecting the kidneys and genitourinary system, the most important thing you should do is to provide your cat with a diet until the doctor arrives. The diet consists of excluding dry food, salty foods, fried foods, and foods high in chemical additives from the diet. After diagnosis, if necessary, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment. In some situations, surgery may be required. Always follow your veterinarian's directions. Our center employs only certified specialists who are able to provide quality assistance!
Nephritis in cats: prevention
The only thing better than any treatment is its absence. To avoid the occurrence of diseases, you need to carry out a variety of preventive measures that will help strengthen the animal’s immunity.
- Here are some tips that can help avoid nephritis in cats:
Treatment regimen for nephritis in cats
A sick pet should be kept warm during therapy. In any case, it is impossible to let the animal go outside, especially in the winter season. In the acute form of the disease, veterinarians first prescribe a 12-hour fast for cats.
With nephritis, the animal usually experiences quite severe pain. Therefore, in most cases, such pets are prescribed analgesics and antispasmodics. Actually, the treatment of nephritis itself is carried out using broad-spectrum antibiotics, hormones and sulfonamides. The cat may also be prescribed iron and calcium supplements and diuretics. In some cases, nephritis may even require surgery.
Folk remedies also help cats with kidney inflammation very well. For example, you can offer your animal a warm infusion of bearberry or lingonberry leaf.
Where are the cat's kidneys located, what are their functions?
This is an important paired organ in cats, responsible for filtering metabolic products and removing toxic substances from the body. Where it is located? The kidneys are adjacent to the posterior abdominal wall at the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra. It is shaped like beans. The outside of the organ is covered with a dense capsule. Consists of the pyelocaliceal system and renal tissue. The structural unit of kidney tissue is the nephron; there are about 150,000 of them in each kidney.
The pyelocaliceal system is responsible for storing and draining urine, and the renal tissue is responsible for filtering the blood. Thus, each nephron filters blood and produces urine. As a result of the work of thousands of nephrons per day, a decent volume of urine with toxic substances dissolved in it is generated. Main functions of the kidneys:
- cleansing the body of toxins;
- removal of end products of metabolic breakdown;
- maintaining the acid level and electrolyte composition of the blood;
- regulation of blood pressure;
- participation in the synthesis of the hormone renin, necessary for osmoregulation.