How does infection occur?
The causative agents of the disease enter the cat’s intestines as a result of drinking water and food contaminated with oocysts, as well as due to contact with the feces of already infected cats. Kittens under 6 months of age, as well as older and immunocompromised cats, are more susceptible to isosporosis .
Adult cats, in turn, are more resistant to the disease , but they can become carriers of the parasite, which will constitute a conditionally pathogenic microflora of their intestines, without causing any negative symptoms until the immune system weakens.
When the oocysts are in the cat's intestines, they are destroyed, releasing the parasites that are "dormant" in them. Isospores penetrate the intestinal mucosa, from where, in case of weak immunity , they can reach the liver, spleen and lymph nodes through the blood and lymphatic vessels.
Parasites live in the cat's intestines, causing watery diarrhea
The likelihood of infection is also affected by the cat's diet. Often the intermediate hosts for parasites are small rodents, which the pet can eat. Kittens are also more likely to become infected soon after birth if their mother is already a carrier of isospores.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms of isosporosis in cats appear after the incubation period, 1-2 weeks after infection. Signs of an intestinal infection may include the following:
- profuse watery diarrhea;
- the appearance of mucus and blood in the stool;
- severe dehydration and deterioration of wool quality;
- apathy and loss of appetite;
- high body temperature;
- neurological seizures in late stages.
For adult animals, isosporosis is not a big problem. As a rule, the symptoms in this case are limited to a deterioration in the condition of the coat. However, it would not be superfluous to resort to restoring the water-salt balance in infected animals, since many of them are killed by dehydration.
If alarming symptoms appear, you should bring your cat to the veterinarian
When contacting a veterinary clinic, a differential diagnosis of the disease is made in order to distinguish isosporosis from other intestinal infections, such as giardiasis and cryptosporidiosis. Most often, direct analysis of stool to detect oocysts. To simplify the process, tinting the smear can be used.
Treatment
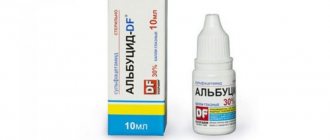
After making the correct diagnosis, the doctor explains to the owner how to treat isosporosis in a cat. In some cases, it is recommended to leave the cat in the clinic to monitor the treatment. The therapy mainly uses drugs such as Biseptol , Sulfadimethoxine , Trimethoprim / Sulfadiazine with the support of glucose injections.
Symptomatic therapy is also carried out in order to restore the water-salt balance in the animal’s body and eliminate inflammatory processes . When the animal is exhausted, the use of vitamin supplements is prescribed. If parasites develop resistance to basic drugs, Toltrazuril .
In addition, gastroprotectors may be prescribed to protect the gastrointestinal tract, as well as metronidazole to eliminate secondary pathogens in the pet's intestines.
For the purpose of prevention, you should monitor the nutrition of your pets, and also pay due attention to their hygiene. This is especially true when keeping cats in specialized nurseries. If pathogenic protists are detected in kittens, it is recommended to also begin treatment of their mother.
Source: https://101parazit.com/mikroorganizmy/protisty/koktsidioz/zabolevanie-izosporoz-u-koshek.html
Toxoplasmosis
Many animals get sick, and humans can also get sick. A dog can become infected with toxoplasmosis by eating dead birds and rodents - these are the main carriers. Taxoplasma cysts can be found in water. An animal can become infected in utero.
These parasites have one feature - only animals, the cat family, can release cysts into the environment. All other animals are intermediate hosts.
Therefore, if there is a cat in the house that has access to the street, the risk of infection to other animals and humans is much higher.
Once in the intestines, the parasites begin to actively multiply, then, with the flow of lymph, they spread throughout the body, forming foci of necrosis. It is at this moment that the risk of disease manifestation and possibly death of the animal is greatest.
The clinical picture is blurry and non-specific. In 50% of cases, there is a malfunction of the respiratory system, and in 25% the digestive and nervous systems are affected. A sick animal has a fever, has a decreased or no appetite, shortness of breath, vomiting, and diarrhea. Sometimes the animal begins to have convulsions.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of a blood test, and the immunoserological diagnostic method is also used. Feces are taken from cats for analysis.
For treatment, drugs are used that can stop the division of parasites, for example clindamycin or a combination of sulfonamides + pyrimethamine. If complications occur, symptomatic treatment is used.
Isosporosis
- a protozoal disease of dogs and cats, the main causative agents of which are canine isospora (Isospora canis) and cat isospora (I. felis), parasitizing in the small intestine of these animals.
Etiology.
Isospore oocysts are ovoid in shape, medium in size (35-45 µm in length), covered with a thin double-circuited gray shell. A mature oocyst inside contains two sporocysts, including four sporozoites, as well as a residual body, and in the cat isospora there are residual bodies in the sporocysts.
Life cycle.
- The above-mentioned isospores develop in a complex way: in the epithelial cells of the intestines of animals they go through two phases of development - schizogony (multiple reproduction) and gametogony (sexual reproduction); in the external environment, the third phase occurs - sporogony (two spores with four sporozoites are formed inside the oocyst).
- Dogs and cats become infected with isosporosis through the nutritional route (by ingesting mature oocysts).
Epizootological data.
Puppies and kittens are more often infected with isosporosis and become seriously ill. Isospore oocysts are highly resistant to chemicals (disinfectants).
Signs of illness.
The incubation period is short (5-8 days). In sick dogs and cats, depression, poor appetite, profuse diarrhea, symptoms of intoxication (clonic convulsions), and exhaustion are noted. Possible lethal outcome.
Diagnosis
The main method for diagnosing isosporosis is the study of stored samples of feces of cats and dogs according to Fulleborn. Symptoms of the disease and epidemiological data are also taken into account. First aid.
To exclude infectious diseases, the dog’s (cat’s) temperature is measured (with isospirosis it is often low), living conditions are improved (the floor and feeder are treated with hot water daily), and easily digestible food is prescribed.
Treatment is poorly developed
A satisfactory effect for isosporosis in dogs is obtained with the combined administration of sulfadimezine (0.5 per animal 3-4 times a day for 3 days in a row), and then chloramphenicol (in usually taken doses for 3-4 days in a row), after that for another 3 days - sulfadimezine (N.A. Kolabsky, P.I. Pashkin, 1974). You can use norsulfazole sodium in dogs and cats at a dose of 0.03-0.04 g/kg live weight for drinking in the form of a 0.5% aqueous solution for three days.
How to protect yourself from getting infected by parasites and insects from cats?
It is worth noting that some parasites can exist on their own for a long period of time. In this case, many larvae end up in the soil, where they live for quite a long time. That is why it is worth washing your hands after contact with soil.
Preventive measures to combat parasites:
- Wash your greens, vegetables and fruits. Since the soil may contain larvae and eggs of worms, everything that comes into contact with the soil should be washed well and doused with boiling water.
- Do not swim in prohibited areas. In the summer, in order to freshen up, people ignore warning posters and swim in ponds. The water may contain worm eggs.
- In summer, cover food with cloth or lids. Don't leave food directly on the table. Enough for a fly to sit on the product. This insect is a carrier of a huge number of ailments, including worms.
- Take care of animals. If you have a pet, don't leave it unattended. Carefully examine the feces and condition of the animal. If there is any suspicion of worms, give the animal an anthelmintic.
- Teach your child to wash their hands before and after eating. Children often dig in the sandbox, where infected cats can go to the toilet. It is enough for a child to lick his fingers for parasites to settle in the body.
- Boil and fry the meat well. Cattle also carry a large number of parasites. With insufficient heat treatment, worm eggs enter the digestive tract along with food. Infection occurs.
- Be sure to wash the trays where the animal goes to the toilet with bleach. There are also modern disinfectant liquids. With their participation, it will be possible to destroy worm eggs.
- Do not purchase products secondhand. This is especially true for dairy products and meat. High probability of infection from fruits and vegetables. Do not allow children to eat unwashed berries and fruits. Do not drink unboiled milk.
How to protect yourself from getting infected by parasites and insects from cats?
As you can see, cats are carriers of a huge number of parasites.
Not all of them are transmitted to people. But a large number of worms are still capable of living in the human body.
Treatment of protozoa
Baycox is used to treat protozoa.
This drug is for farm animals, but due to its effectiveness it is also prescribed for the treatment of dogs. Baycox is used in a dose of 5 mg of active substance per kg of body weight per day, according to different schemes from 1 to 3 days.
- Hereditary diseases of dogs
- Hereditary defects in dogs
- Coronavirus enteritis in dogs
- Death of suckling puppies from coronavirus
Source: https://naf16.narod.ru/photoalbum555.html
Babesiosis
The disease is caused by a protozoan called Babesia. The main route of transmission is from ixodid ticks, through their bites. The incubation period usually passes without symptoms. Animals with strong immune systems can survive the disease itself asymptomatically, while cats with weakened immune systems may face death. The main symptoms include darkening of urine, fever, and enlarged lymph nodes. Loss of appetite and, as a result, weight.
Coccidiosis is extremely dangerous
Coccidiosis (isosporosis) in cats is a dangerous disease, especially for kittens.
Coccidiosis (Eimeriosis, Zosporiasis) is an acute protozoal disease that occurs in cats when infected with protozoan parasites of the genus Eoimeria and Isospora.
The life cycle of coccidia has three periods: schizogony (asexual reproduction, cells divide independently without the participation of partners, and absolutely identical single-celled organisms are formed), gametogony (sexual reproduction between heterosexual cells) and sporogony (formation of oocysts - forms resistant to unfavorable environmental conditions necessary for the survival of the parasite after leaving the host’s body).
Causes and symptoms of coccidiosis
After a mature oocyst enters the body of a healthy cat, its capsule dissolves in the stomach and intestinal cells are damaged. Schizogony and gametogony occur inside the epithelial cells of the host's intestine - endogenously, and massive damage to the intestine occurs, leading to disruption of its function.
Sporogony - in the external environment, outside the host - exogenous. The source of isosporosis infection for cats are bowls, bedding, toys, trays and other objects surrounding a sick animal.
Coccidiosis is a widespread infestation of cats, but kittens are most often affected by this disease.
As well as animals with severe immunosuppression, these can be animals that are constantly exposed to stress, have severe helminthic infestation, chronic viral infections in cats, etc.
Infection occurs when an animal eats contaminated feces or an infected animal and through water.
Coccidia in a cat
- Coccidia, penetrating the epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa, destroy them and thus cause mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, which greatly reduces its absorption function.
- These affected areas of the cat's intestine are a fertile breeding ground for the uncontrolled development of opportunistic microflora (bacteria and viruses that are usually present in the intestinal lumen, but do not cause harm to a healthy animal), aggravating the course of the disease with an extensive inflammatory process.
- In the small intestine, the main type of digestion, membrane digestion, is disrupted.
- In the animal's body, dehydration and disruption of the acid-base balance in the blood occurs, which leads to dysfunction of all organs and systems. Without timely correction, this condition can lead to the death of the animal, especially if it is a kitten.
- The incubation period of coccidiosis can range from three to fifteen days or more, depending on the general condition of the animal’s body and the resistance of its immune system.
Treatment methods
Treatment of coccidiosis in cats should be comprehensive.
In addition to prescribing etiotropic therapy (treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, when treating protozoa we are talking about antibacterial drugs), the animal should also receive symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating dysfunction of organs and systems - replenishing fluid deficiency through intravenous drips. For vomiting, antiemetic drugs are prescribed, hemostatic drugs are prescribed for heavy bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, astringent drugs are prescribed for persistent diarrhea, etc.
The drugs of choice for the treatment of coccidiosis in cats are antibiotics of the sulfonamide group. For example, sulfadimethaxine is prescribed at a dosage of 50 mg/kg in the first two days, then 25 mg/kg per day for 2-3 weeks. In addition, it is necessary to observe animal hygiene measures.
To prevent coccidiosis (isosporosis) in cats, it is necessary to keep them in clean, dry, well-ventilated areas. Dishes and care items must be thoroughly and regularly washed and disinfected, and contact with stray animals must be prevented.
Source: https://rusveterinar.ru/lechenie-kokcidioza-u-koshek/
Treatment
There are many methods for treating protozoa in cats, it all depends on the type of pathogen, the severity of the disease and symptoms.
For example, drugs such as metronidazole and fenbendazole are often prescribed to treat giardiasis. In some cases, the use of one drug may be sufficient. If the disease is severe and accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, then the doctor may additionally prescribe detoxification medications.
There are also broad-spectrum drugs that are effective against all protoses. For example, veterinarians will often prescribe the drug chemical coccide. It should be given to the cat mixed in food for 3 days. Dosage 24 mgkg. Sometimes it becomes necessary to take the drug again; it will be prescribed by your doctor. You cannot prescribe treatment and select the dosage yourself. Also popular are drugs such as Baycox and Stop-coccid. They also need to be given to the cat for 3 days.
Babesiosis may sometimes require a blood transfusion, but this is rarely used in practice. Therapy usually begins with taking medications; there are good reviews for drugs such as atovaquone and imidocarb dipropionate.
Whatever protozoan causes the disease, in order to prevent it it is necessary to follow certain rules for keeping cats in the house . As they say, it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it later, especially since this is not so difficult to do.
Isosporosis (cystoisosporosis) of cats is a parasitic disease caused by protozoa (single-celled parasites) of the genus Cystoisospora (Isospora, Cystoisospora). The parasites are species-specific, that is, cat isospores are not infectious to dogs or humans, but are transmitted from cat to cat. In adult animals, infestation (infection) with isospores most often does not lead to the appearance of clinical symptoms. Isospora belongs to the family Eimeridae and is primarily an intracellular parasite of the intestinal epithelium. With minor invasion, isospores have virtually no effect on the cat’s condition; usually, immunity develops after invasion. At a high level of invasion, isospores provoke the death of the intestinal epithelium, which leads to softening of the stool, and the stool becomes unformed.
Infection occurs through ingestion of oocysts; in some cases, rodents may be reservoirs of species-specific isospores.
Common Cat Diseases
When deciding to have a pet, a person takes on a number of obligations. A kitten or an adult cat needs care; like all living beings, it can encounter diseases.
That is why in everyday life you need to pay attention to his well-being, playfulness, and appetite. There are a huge number of cat diseases in the world. If the behavior has somehow changed, then you can suspect problems.
The best solution in this case would be to contact a specialist.
If you notice the following signs, you should visit a veterinarian:
- Vomiting, excessive drooling
- Lethargy
- The desire to hide in a dark corner
- Discharge from eyes and nose, cough
- Lost appetite, weight loss
- Convulsions
Important: The normal body temperature of a cat is 37.5 - 39 degrees Celsius, moreover, in young cats and kittens it is within the upper limit, and in older cats it is within the lower limit. The breathing rate of a kitten is about 60 breaths per minute, in young individuals it is 22-24 breaths, and in adults it is 17 - 23. Normal heart rate for cats is 100 - 130 beats per minute.
How quickly you respond to a problem will directly affect your pet’s health. Therefore, try to pay attention to it when the cat’s disease is still at an early stage. So vomiting may be a sign that too much hair has accumulated in the stomach.
In this case, it is recommended to give your friend a special paste that will dissolve the fur. But regular vomiting is not a good sign; if it occurs, you need to consult a specialist. Vomiting can occur with worms, due to disruption of the intestines.
Remember that self-medicating animal diseases is quite dangerous.
Below is information about the most common diseases of cats and cats.
Among the common ailments are problems with the urinary system. Cystitis or urolithiasis may occur, which may result in your four-legged friend walking past the litter box.
There may also be a strong odor and blood in the urine. This is not a dangerous disease, but it can cause more serious negative consequences. By the way, this manifests itself due to sand in the bladder, diabetes, and lack of fluid.
A cat has white parasites on its fur: what are they?
These are lice eaters, they are not blood-sucking insects. They only parasitize the fur. They feed on hair and skin scales. Such parasites provoke dermatitis and a decrease in the amount of hair. They lay small eggs, which later develop into adults.
Signs of infection:
- The pet becomes restless and constantly rubs against something
- Scratching occurs, the skin peels, and tufts of fur fall out
- If the problem is ignored for a long time, wounds and ulcers appear, through which bacterial infections can occur.
A cat has white parasites on its fur: what are they?
Worms in cats
Helminths can be everywhere - on the grass, in warm sand, in foods such as meat or fresh, but not steamed fish, parasites are present even in the air. All you have to do is take a closer look at the nearest flower bed under a microscope and you can stay up all night. It is not uncommon for cats to have worms.
White worms can appear in a cat even if the pet is kept at home and eats only commercial food. For cats, permanent residence at home is a rarity, because they love to walk on their own. It is for this reason that parasites in cats are common.
Parasites in cats are disgusting worms that wriggle and dig into the walls of organs with their hooked protrusions, spines, and suction cups. They sit in the body and eat numerous nutrients. To protect your pet and yourself, you need to know how to identify the presence of parasites, how to properly treat them, and how effective prevention is.
Cat helminths enter the animal's body in different ways. Eggs can be swallowed while eating raw fish or meat. These animals usually immediately eat their prey immediately after catching it, so the eggs present in them immediately enter the body, which is why worms appear in kittens.
In addition, a cat may develop worms if it simply swallowed a parasite while drinking water from a puddle or river. There are also cat worms that are quickly transmitted through feces.
As you know, animals love to lick themselves, so there is always a risk that eggs stuck to their paws during a walk will be licked off. Eggs can be brought into an apartment by people on shoes. Also, a cat can simply chew grass or eat an insect.
As for the transmission of parasites to humans, this process occurs through saliva and feces.
Treatment of helminthic infestation
Worming cats is a very important undertaking, so before treating for worms, you should decide what is best to give your cat.
In most cases, sick cats are prescribed complex anthelmintic drugs. These dewormers for cats are effective against all types of helminths. But medications can be prescribed that also affect specific types of worms.
Modern medicines have virtually no side effects. However, it is very important to observe the dosage, adhere to the veterinarian’s instructions, and also take into account all contraindications.
Anthelmintics are available in the form of tablets, suspensions and drops. Among the most effective drugs are:
- piratnel;
- drontal;
- prazicide;
- vacationquantel;
- prosit;
- pratel.
To treat lungworms in cats, anthelmintics are used - Stronghold, Advocate, Milbemax.
It is worth noting that helminthic infestation can be represented by several types of parasitic worms at once. That is why it would be preferable to choose a drug with a wide spectrum of effects at any stage of infection.
All of these drugs provide effective treatment for your pet at home.
Drontal
Before using deworming medication for your pet, you should get rid of fleas and other ectoparasites. If this is not done, treatment will be useless, since the source of infection (flea) will again transmit helminth eggs to the animal.
It is noteworthy that there are universal products on sale for eliminating internal and external parasites. They are produced in the form of drops on the withers. In particular, a drug such as Stronghold has proven itself well.
It is necessary to ensure that the cat swallows the dose of medicine completely. To prevent your pet from spitting out the tablet, you can use one of the following methods:
- crush the tablet and mix it with milk, sour cream, pate or other treat that the cat likes;
- you can use a device called a piller to push the tablet into the animal’s mouth;
- crush the tablet into small pieces and dissolve in a small amount of water, and then inject the liquid into the cat’s mouth using a syringe without a needle.
For treatment to be effective, deworming is repeated after two weeks. Severe infestation requires longer anthelmintic therapy. The effectiveness of treatment is monitored through laboratory tests.
There are cases in which it is undesirable to carry out deworming:
- when the cat is severely emaciated and weakened (this condition can be caused by infectious diseases);
- during pregnancy and feeding newborn kittens;
- young age (kittens are at an age when, according to the instructions, the use of an anthelmintic drug is unacceptable);
- the cat is of advanced age (you should carefully read the instructions and consult a veterinarian).