Relevance of the problem
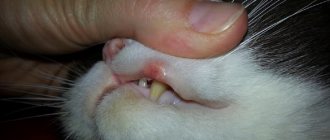
If a cat's eye becomes cloudy, it appears as if he is blind. But it is not always the case. To determine the true cause of blurred vision in a pet, you need to contact a veterinarian-ophthalmologist.
The fact is that the causes of this eye pathology can be various diseases: cataracts, keratitis, glaucoma, uveitis. They can only be recognized in a veterinary clinic using special equipment.
Cat breeds with yellow eyes
In addition to melanin, the intensity of coat and eye color is controlled by various genes, so sometimes fur melanocytes can be more active than those that determine eye color. To obtain the rich eye color that is sometimes required by the breed standard, breeders select cats with the most intense or unusual eye shade.
In some breeds, a variety of eye colors are acceptable, for example, in Persians we will find not only all shades of yellow, but also blue and green eyes. However, there are cat breeds with yellow eyes according to the standard.
Burmese cat
For these magnificent cats, which were kept at temples as sacred animals in Burma, the standard suggests an eye color ranging from yellow to gold. Green and blue eyes among Burmese are unacceptable.
Bombay cat
The Bombay cat was bred as a cross between the Burmese and the American Shorthair. Bright yellow-orange eyes perfectly complement the image of a miniature panther with glossy black fur. Green eyes are grounds for disqualification.
Abyssinian cat
This is one of the breeds popular among cat lovers, which can be seen quite often at exhibitions. The fur of Abyssinian cats has a characteristic ticked color - dark and light zones alternate in each hair. Although the breed standard allows green eyes, amber or orange eyes are much more common in Abyssinian cats and are very harmonious with the coat color.
British shorthair cat with yellow eyes
In the British breed, yellow or orange eye color is most often found, because most of these cats in Russia are blue in color, and an undefined color, for example, yellow-green, is considered a serious fault at exhibitions.
Not only blue, but all other solid, smoky, tortoiseshell colors of British cats are distinguished by orange or yellow eyes, as for most patterned ones, although green eyes are also allowed for some tabby colors. The group of chinchilla and Himalayan colors are characterized by green or blue eyes.
Similar to their British relatives, Scottish cats - Scottish Folds and Scottish Straights - are distinguished by their expressive eye color, which favorably emphasizes the color of their fur coat. Their eyes can be yellow, amber, orange, copper. The same can be said about Persian cats and exotics.
Keratitis
With this disease, vision always deteriorates or is completely lost. Keratitis is a consequence of toxic liver damage due to poisoning and intoxication, acute infectious eye diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or neurogenic pathologies.
To prevent your cat from going completely blind, immediate professional help is required.
The first symptoms of keratitis are redness of the eye and the presence of serous or purulent discharge. After some time, the cat’s eye becomes cloudy and the cornea loses its transparency. With prolonged development of the pathology, ulcers and necrosis of the cornea develop.
Jaundice in cats, necessary therapy
- Therefore, often, while awaiting the results of laboratory tests, the veterinarian will prescribe supportive measures for the cat:
- droppers to combat dehydration, correct the level of electrolytes in the blood if the animal suffers from anorexia, vomiting and diarrhea;
- drugs that lower blood sugar levels (as indicated);
- the use of drugs for anemia, hematopoietic stimulants, donor blood transfusions for severe anemia;
- course of antibiotics, antiemetic drugs.
Once the test results are in and the underlying cause of the jaundice is found, your veterinarian will decide on more targeted treatment. This can be surgical intervention (for example, if stones are found in the gall bladder or it is necessary to remove a tumor), and antiparasitic therapy, and the introduction of antidotes for poisoning with certain toxic substances. As you can see, there are many causes of jaundice in cats, so treatment protocols will vary greatly, as will the prognosis for recovery.
Therapy for jaundice will be aimed not only at eliminating its root cause (for example, infection or tumor), but also at stopping the processes that it caused. This may be pain syndrome (with obstructive jaundice), oxygen deficiency, or intoxication of the body. For these purposes, analgesics, oxygen therapy, droppers with hepatoprotective drugs, etc. will be used.
Another area of treatment is to combat symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, anemia, and dehydration.
. This will also require the introduction of intravenous drips, vitamin complexes, electrolytes, drugs against vomiting and increased stomach acidity.
Cat care
Mandatory recommendations when caring for a cat with liver failure are:
- strict adherence to veterinary prescriptions,
- a special gentle diet (consult your doctor to create a treatment menu for your cat),
- control by the veterinarian over the healing process,
- rest, peace, lack of stress for a sick animal.
Owners' fears
Sometimes cat owners, having discovered that they have jaundice, begin to worry about the health of all household members, worrying that the infection does not turn out to be contagious. In most cases, these fears are unfounded; feline hepatitis is not transmitted to humans. Of course, you must monitor the health of your pet, there are diseases that are common to us and our smaller brothers, but in the case of jaundice, you only need to worry about the health of your pet!
If you see symptoms of jaundice in a cat, call our center and you will receive a free consultation to provide first aid to your animal. At your request, the doctor will come to you at any time within 40 minutes if you need emergency help. Many medical procedures and express tests for the presence of certain infections can be done at home without wasting precious time. Remember that in this case, time should work for you, and not for the disease, since the animal often dies without timely help.
Treatment of jaundice requires an integrated approach
, therefore, on the basis of ours, you can examine your pet comprehensively, not excluding ultrasound and x-rays. Severe patients will be admitted to hospital for urgent treatment with modern drugs. After recovery, the treating veterinarian will provide advice so that the cat with jaundice can lead a healthy and active life!
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disease in cats that develops against the background of increased intraocular pressure. The cornea loses transparency during an acute attack of the disease.
Optic nerve atrophy leads to complete blindness of the animal within 2-4 days after the attack. Therefore, the animal needs urgent veterinary care.
Symptoms of an acute attack of glaucoma:
- pain when touching the eye;
- photophobia;
- corneal edema;
- high intraocular pressure.
Treatment for an acute attack of glaucoma involves urgently reducing the pressure inside the eye. Manipulations must be carried out by a veterinary specialist with monitoring of the animal’s condition.
Further treatment consists of the use of drugs that reduce intraocular pressure, diuretics and agents that help stabilize the cat's condition.
Classification of diseases
Problems of the visual organs can be divided into two large groups: inflammatory and non-inflammatory. It is also worth noting that eye disease can only be a symptom of some other animal disease .
In this case, treatment of vision alone will not bring results. According to the course of the disease, it can be divided into subacute, acute and chronic. In any case, the symptoms will never disappear on their own; they can only subside, which will soon lead to loss of vision and serious problems.
Inflammatory eye diseases in cats include both those affecting the eyeball itself and problems with the canal, tissues surrounding the eye and orbit. This includes conjunctivitis, keratitis, iritis, and various inflammations of the nasolacrimal duct.
Non-inflammatory - injuries, bruises, foreign bodies, eyelid inversions. This group also includes glaucoma, cataracts, ptosis and other less common problems.
Corneal erosions and ulcers
These corneal defects of varying depths can occur due to mechanical, chemical and thermal injuries, chlamydia, inflammatory pathologies of the eye, glaucoma and other pathologies. The eye acquires characteristic features:
- redness of the cornea of the eye;
- photophobia;
- corneal clouding.
Treatment consists of eliminating the underlying cause of the disease and symptomatic local therapy. Complex treatment includes antibacterial, corneoprotective and immunostimulating drugs.
Scar (thorn) of the cornea
A scar or cataract of the cornea causes it to become cloudy after injury, burns or ulcers. There are several types of pathology:
- peripheral cataract, it is located away from the pupil and does not have a significant harmful effect on vision;
- a total cataract that covers the pupil and cornea. Vision deteriorates significantly;
- central thorn. It is located on the pupil, covering it partially or completely. The field of view becomes limited.
Partial or complete restoration of the cornea in this pathology is possible only with timely professional treatment.
Causes of damage and clouding of the lens of the eye
The pupil of the eye does not become cloudy, as it is a hole in the iris. The transparent biolens of the eye, the lens located behind the pupil, becomes cloudy.
The main cause of lens clouding is cataracts. This disease develops for several reasons:
- age-related changes in metabolism in old individuals;
- endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism disorders;
- pupil injuries;
- infectious diseases in a pregnant cat can cause damage to the lens of the kitten’s eye;
- genetic predisposition of certain cat breeds to this pathology. These are breeds such as Persians, Siamese and Burmese.
Treatment of cataracts with medications can only temporarily slow down the course of the disease.
The definitive treatment for lens opacity is surgery to replace it. If radical treatment to replace the lens is not carried out in time, the process develops further with complications:
- uveitis - the development of an inflammatory process of the choroid of the eye, which leads to loss of vision;
- secondary glaucoma with optic nerve atrophy and the development of complete blindness;
- panophthalmitis – release of lens masses into the chambers of the eye, development of purulent inflammation, death of the eye.
Why did the cat turn yellow?
Taking into account a number of reasons
jaundice that causes this pathological manifestation is divided into only three types:
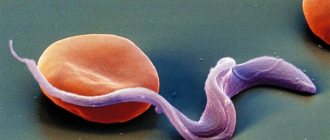
- Hemolytic or suprahepatic jaundice occurs due to increased breakdown of red blood cells. This can happen for several reasons:
- feline dirofilariasis (parasitic helminthic disease), leptospirosis,
- blood parasites (feline hemobartonellosis),
- intoxication with certain drugs and poisons (for example, as part of rodent poison), snake bites, spider bites;
- severe viral infections (leukemia, immunodeficiency virus).
2. Hepatic jaundice is a consequence of liver disease. It could be:
- poisoning with hepatoxins (mercury salts, lead, drugs - paracetamol, diazolin, insectoacaricides);
- infections of both viral and bacterial origin;
- hepatitis (liver inflammation);
- hepatosis (liver failure, metabolic disorders in the liver);
- parasitic liver diseases are leptospirosis, opisthorchiasis and echinococcosis, as well as toxoplasmosis;
- cirrhosis of the liver (degeneration of its tissue into connective tissue with disruption of all functions);
- oncological neoplasms of the liver.
Liver diseases will also be accompanied by vomiting, loss of appetite, and changes in the color of urine and feces.
3. Mechanical (subhepatic) jaundice occurs when bile stagnates in the bile ducts. This is a consequence of diseases such as:
- chronic cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder,
- pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas,
- cholelithiasis (formation of stones in the gall bladder),
- pathologies of the sphincter of Oddi (spasm, polyps, etc.).
Prevention
Preventing cloudy eyes in a cat consists of following a few simple rules for keeping the animal:
- timely vaccination against infectious diseases;
- regular examinations of the animal and timely contact with a specialist at the slightest inflammation of the pet’s eyes;
- if you suspect clouding of the eyes, urgently contact a veterinary ophthalmologist.
It should be remembered that any eye disease can lead to vision loss in a cat. Therefore, you should not ignore even the slightest eye inflammation in a cat and promptly contact a veterinary clinic.
Causes of yellowing eyes in cats
Yellowing of the sclera in a cat is not noticeable due to the large size of the iris. Even an attentive owner notices the icterus in the whites of the animal’s eyes against the background of a general deterioration in the condition of his pet, a change in his appetite or yellowing of the inner surface of the ear or the skin of the pads. Not only the sclera or the lining of the ear turns yellow, the cat’s entire skin changes color, the tongue and all visible mucous membranes become lemon-colored. This condition is called jaundice.
Jaundice, as a symptom, always indicates a high concentration of a substance such as bilirubin in the animal’s blood. It is a derivative product during the normal processing of hemoglobin from red blood cells, which the body needs to transport oxygen to every cell and organ. If hemoglobin is processed at an accelerated pace (under pathological conditions), then soon too much bilirubin will accumulate. Then yellowing of the whites of the eyes and mucous membranes occurs.
In addition to jaundice, your cat will have other signs of illness:
- indigestion;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea or vomiting;
- extreme thirst and excessive urination;
- labored breathing;
- hepatic encephalopathy;
- dark urine and light feces;
- Also, in the last stages of the disease, the animal may experience internal bleeding, and, as a result, blood in the urine and feces.
This condition is far from normal. The animal eats poorly, loses a lot of weight, may suffer from severe pain, and fall into a coma. In the absence of timely medical intervention, the pet may die.
Such a manifestation as jaundice is usually differentiated into parenchymal, mechanical or obstructive and hemolytic forms. Each form is caused by serious pathological processes in the cat’s body:
- Hepatic or parenchymal jaundice is caused by functional and organic diseases of the hepatobiliary system. Hepatitis (inflammation of the liver parenchyma), cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts) cause icterus in animal tissues.
- Severe liver diseases: cirrhosis (replacement of the organ parenchyma with connective tissue with loss of its functionality) and cancer lead to yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes. Even excessive accumulation of triglycerides (fats) by liver cells - hepatocytes - leads to yellowness of the sclera and skin.
- Baked obesity, or lipidosis. In this condition, liver cells develop into fat cells. The liver gradually loses its functions, which means the animal may die. Its causes are the cat's excess weight, diabetes, malignant tumors, and hyperthyroidism. Unfortunately, in almost half of the cases the cause of this dangerous disease cannot be established.
- The use of certain medications can lead to changes in the liver and excess bilirubin (bile pigment) in the cat's blood. It is the bile pigment that colors tissues a beautiful yellow color. These medications include: first generation antihistamines (diazolin), NSAIDs (paracetamol), antifungals (griseofulfin).
- Infectious diseases of viral etiology (viral peritonitis), protozoal infections (toxoplasmosis), bacterial pathologies and some parasitic infections cause liver pathology and the release of large amounts of bilirubin into the blood.
- Incorrect use of insectoacaricides (veterinary products intended to combat parasitic insects, in particular ticks). Many insectoacaricides have a strong toxic effect on hepatocytes. Salts of heavy metals also have a similar effect.
- Obstructive jaundice. Obstructive jaundice develops when there is an obstruction to the outflow of bile. Most often it develops due to exacerbation of cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis). If concretions (stones) block the bile duct, the animal develops biliary colic, the temperature may rise, and it is bothered by severe pain in the right hypochondrium. The mucous membranes, sclera and skin turn yellow.
- Inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts, their stenosis, pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer can lead to impaired outflow of bile and jaundice. Any tumors of the abdominal cavity that grow into the tissue of the bile ducts or mechanically compress the gallbladder and its ducts can cause large amounts of bilirubin to enter the bloodstream and cause yellowing of the animal’s tissues.
- Hemolytic jaundice. Hemolytic jaundice is caused by hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells directly in the blood vessels. This happens in some diseases (hemolytic anemia). The cause of hemolysis of erythrocytes may also be severe hypophosphatemia, aggravated by magnesium deficiency. Hemolysis can develop as a result of a cat’s body’s reaction to a blood transfusion. The entry into the blood of hemolytic poisons (zoocoumarin) and medications (warfarin) also leads to the destruction of mature red blood cells.
- Parasitic diseases: feline hemobartonellosis, feline piroplasmosis can lead to hemolysis of hemoglobin. Parasitism of certain helminths that attack vital organs can lead to hemolytic jaundice. This disease in veterinary practice is called dirofilariasis.