- What causes acne?
- How does acne appear?
- Modern approaches to acne treatment
The appearance of black dots on a cat's chin does not cause concern to every pet owner. This approach to the condition of a pet’s skin is easily explained by the fact that blackheads or acne, it would seem, do not in any way affect the cat’s health and do not affect its general well-being. In fact, acne in cats, the treatment of which must be comprehensive, indicates not only health problems in the pet. In cases of bacterial infection, inflammation may develop with the formation of purulent foci, subcutaneous abscesses, phlegmon, and the like.
Nature of the disease
The structure of the skin of the cat family is very similar to the structure of human skin.
These similarities suggest that many cats experience the same dermatological conditions as humans. The most common skin disease is acne. The location of the rash blisters on the surface of the skin depends on the location of the sebaceous glands. Most often, symptoms characteristic of acne are observed in cats in the area of the ears, abdomen and ribs. The appearance of a small cluster of pimples in the chin area is the most common occurrence. This problem does not pose a risk to the health of the pet. In most cases, such symptoms are only temporary and do not in any way affect the functioning of internal organs.
Among the negative consequences of acne, one should highlight the loss of aesthetic appeal due to disturbances in the process of sebaceous secretion production. The main danger of this problem is the high risk of developing dermatitis. With this disease, small ulcers form on the surface of the skin. If the cat begins to scratch the lesions, the situation may be complicated by the addition of a secondary infection.
How does acne appear in cats?
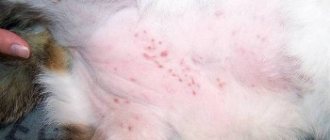
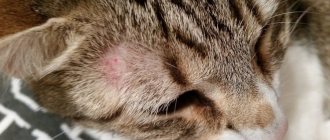
Black spots on a cat's chin, the treatment of which can be a very labor-intensive and lengthy process, in practice manifest themselves in a set of symptoms characteristic of this skin disease. In the early stages of development, black comedones in cats may look like normal skin debris. Later, redness and swelling of the affected areas of the skin appear.
Objectively, small acne eruptions with black, or less often white, cone-shaped tips are determined on the skin of the chin. Over time, simple acne becomes infected, becomes inflamed, and increases in size. The skin in the affected area begins to hurt, and itching also occurs. Therefore, the cat tries to scratch it, and wounds are formed on which purulent and bloody crusts form.
The addition of a secondary infection is accompanied by the formation of purulent nodes with alopecia at the sites of hair follicles. This condition is very dangerous for the animal, as it can provoke generalization of the inflammatory process and disruption of the pet’s general condition.
Most often, this pathology appears on the cat’s lips and chin. It looks like a large accumulation of black dots (comedones) in one place, similar to poppy seeds. Often they do not bother the animal for a long time, but over time they can turn into small purulent inflammations, which, after opening, form crusts.
In the event of additional infection of the affected area or as a result of a general weakening of the body of a sick animal, the cat may experience itching at the site where acne appears, hair falls out, and the affected area becomes swollen.
If you scratch the itchy area vigorously, there is a risk of secondary bacterial infection.
The disease under discussion can appear in domestic cats of any breed, gender and age. True, some of them experience acne only once in their life, while for some it is a constant problem that requires attention and care from the owners.
By the way, it has been noticed that acne occurs in sterilized individuals much less frequently than in their counterparts ready for reproduction.
For Persian cats, this pathology can be especially serious, as it has a negative impact on their skin folds.
Varieties
| Type of ulcers | Peculiarities |
| Surface | Are the result of scratches or shallow bites |
| The skin becomes reddish and a white dot appears on it | |
| Mostly the abscess opens on its own and does not require any treatment. | |
| Deep | Manifest against the background of bites with damage to the deep layers of the epidermis |
| The damaged surface of the skin is very painful, but in appearance it is not very different from healthy | |
| When palpating, a compacted area is noticed | |
| Spicy or hot | The inflammatory response develops quickly |
| There is a red wound, in place of which a crust appears | |
| Cold | Accompanied by a deep abscess, which has a chronic course |
| Such ulcers are permanent and may not go away for several years. | |
| Often recur | |
| Benign | Purulent discharge contains many living leukocytes |
| The cat's immune system rejects the affected areas, resulting in thick, white pus that does not have a strong odor appear on the chin. | |
| Malignant | White blood cells in the exudate die off or are very weak, while the cancer cells are strong |
| If purulent spots are not eliminated in a timely manner, phlegmon develops. |
READ Personal website - all about the Rhodesian Ridgeback, Ridgeback standard, feeding, history of the breed || Feeding the Rhodesian Ridgeback
External manifestation of the disease
The appearance of the rash and the nature of the lesion depend on the form and location of the inflammation. The rash blisters may have a reddish base and a white top. At certain stages of the development of the disease, purulent exudate may form inside the blisters.
It is not recommended to try to squeeze out such rashes. You need to wait until the acne opens up on its own. In order to speed up this process, you can use special ointments with a drying effect.
We suggest you read: Miscarriage in a cat: causes and help. If a cat suddenly miscarries, what should the owners do? Cats miscarried what to do Acne occurs due to inflammation of the sebaceous glands on the skin
Importance of diagnosis
Under no circumstances should you conduct a diagnostic examination of your pet yourself. It is best to entrust this matter to veterinarians. The clinical picture characteristic of acne is similar to diseases such as dermatomycosis, scabies mites and allergic reactions.
If carefully examined, pimples on the chin may turn out to be dirt or insect bites. To determine the causes of acne, it is necessary to scrape the lesions. Microscopic examination of the material allows you to accurately determine the causes of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment.
What you can do at home
There are a number of specific rules for self-treatment of skin diseases in pets. When the first symptoms of acne appear, you should pay increased attention to your pet. In order to reduce the severity of itching, it is necessary to use special shampoos while bathing. In order to dry the rash blisters, you can use tar soap or a three percent solution of hydrogen peroxide.
In order to facilitate the application of medications to areas of inflammation, you need to carefully shave the hair on the affected areas of the body. In the presence of keratinized tissue, special keratolytic compounds are used. Salicylic acid can be used for this purpose. In combination with this medication, experts recommend using various local drugs, the action of which is aimed at regenerating damaged tissues and normalizing intercellular metabolism.
When talking about how to treat cat chin acne at home, it is important to mention that human scrubs and lotions should not be used to treat blackheads. It is also prohibited to treat acne in pets with antibacterial drugs. Antibiotics are used only in cases of severe forms of the disease, when the rash spreads throughout the pet's body.
Even taking into account that the diagnosis made independently will be correct, the use of many medications can negatively affect the animal’s well-being. In addition, in the absence of the necessary knowledge, it is very difficult to choose the right dosage.
Treatment of sores on the chin
The first thing you need to do if any symptoms appear is to consult a specialist. In addition to examining the affected area, the doctor will prescribe tests to rule out possible other diseases associated with sores on the chin. If the diagnosis is confirmed, complex treatment is prescribed:
- tar soap and shampoo;
- medicated shampoos;
- anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents;
- Percutan;
- boosting immunity with vitamins;
- Avoid fatty foods and plastic utensils.
| Medication group | Name |
| Antiseptic drugs | "Chlorhexidine" |
| "Miramistin" | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | |
| Shampoos for cat hygiene | "Bifar" |
| "Hartz" | |
| "Doctor" | |
| "Lactoderm" | |
| Medicines against ulcers in the form of ointments and gels | "Flucinar" |
| "Synthomycin liniment" | |
| Sulfuric ointment |
READ Imunofan drug for stimulating cat immunity
The affected area is washed with a decoction.
If crusts or spots have formed in the fur, it is possible to get rid of them by using iodine. Medicines based on natural ingredients are also effective for purulent wounds in cats. Some medications can be prepared at home. A decoction made from calendula or chamomile inflorescence helps well with ulcers on cat skin. Dip a cotton swab into the resulting solution and fix it on the problem area of the chin. In a similar way, you can treat a cat using celandine.
What causes acne?
Unfortunately, it has not yet been possible to establish the exact reason why acne develops on a cat’s chin and lips.
The following factors are known to contribute to the development of skin disease:
- genetic predisposition;
- defects in the development of sebaceous glands and hair follicles in cats;
- frequent stressful situations that provoke a change in the quality of the secretion of the sebaceous glands, making it more viscous and thick;
- violation of hygiene standards;
- hormonal imbalance;
- allergic reactions;
- immunodeficiency states;
- skin diseases (demodex, malassezia, trichophytosis, dermatophytosis, fungal infections);
- using plastic bowls, especially if they are rarely washed.
The choice of treatment tactics for acne in cats depends on the factors that provoked the development of the disease, on the state of the animal’s immune system, the presence of chronic diseases of the visceral organs, allergies to medications, as well as the individual characteristics of the body. This is why you should not treat your cat’s acne on your own. It is better to entrust this process to an experienced veterinarian.
The main cause of acne is inflammation of the hair follicles as a result of dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. However, the cause of such violations has not yet been identified. Experts from the field of veterinary medicine say that there are more than two dozen different reasons for the development of such a pathology. Let's take a look at the most common causes of acne in cats:
- Physiological predisposition. According to statistics, certain cat breeds are more susceptible to acne. Hairless cat breeds suffer from acne much more often than other members of the cat family.
- Incorrect care. Frequent bathing, little attention to hygiene, and the use of hygiene products not intended for cats are often the causes of acne.
- Incorrectly formulated diet. A lack of vitamins and beneficial microelements causes not only the appearance of acne on the surface of the skin of pets, but also other more complex diseases.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Chondroprotectors for dogs and cats. The need to use vitamins for dogs for joints.
All cats are susceptible to pimples, regardless of the breed, age or gender of the animal.
The appearance of acne can be caused by dermatitis, hormonal disorders, metabolic disorders, as well as pathologies associated with the rate of intercellular nutrient metabolism. Acne can be a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems. In addition, problems with the functionality of the sebaceous glands can be caused by prolonged stress due to moving, climate change and other various factors.
Clinical symptoms
Acne in cats is characterized by symptoms such as the appearance of blackheads and red blisters, a rash on the chin, ears, tail and back. At the initial stages of the development of the disease, symptoms such as redness, swelling and swelling of the affected areas are observed. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of boils and medium-sized pustules. The formation of rashes can be accompanied by itching and pain, causing severe discomfort in the pet.
Failure to take timely measures can lead to hair loss. Due to the severity of the itching, the pet may be irritated and show aggression. However, there is no significant change in the cats' behavior. The disease in question does not affect those processes that play an important role in the life of domestic animals.
Possible ways to get rid of cat acne using folk remedies
To get rid of acne in cats, home treatment is prescribed. Folk remedies should be used only after consulting a doctor. Particularly popular are:
- A decoction of calendula and chamomile is mixed with furatsilin, then a compress is applied to the affected areas.
- Rub your neck with a piece of pumpkin for 5 minutes a couple of times a day. Use only a fresh piece of vegetable.
- A decoction of celandine is applied as a compress 2 times a day.
- A decoction of yarrow leaves is applied to the affected area using gauze or a cotton swab.
- Apply a thin layer of clotrimazole or sulfur ointment to pimples.
Modern approaches to acne treatment
Let's look at how to treat acne in cats on the chin and other parts of the body. One of the most common remedies for acne is chlorhexidine solution. However, the use of this remedy may not bring the desired result if the root cause of the disturbances in the sebaceous glands is not eliminated.
Iodine can be used in combination with chlorhexidine. Thanks to its drying effect, iodine accelerates the spontaneous opening of acne. Before using iodine, the affected tissues should be thoroughly treated with chlorhexidine. To treat acne in pets, only a weakly concentrated iodine solution is used.
Along with the above medications, you can use hydrogen peroxide and calendula tincture. The use of these medications will reduce the severity of symptoms characteristic of acne. But in order to achieve a guaranteed and lasting effect, it is very important to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the four-legged pet’s body.
To reduce the severity of inflammation, tetracycline or salicylic ointment should be used. It is enough to treat the affected areas of the body with these medications once a day. When using products for external application, care should be taken to ensure that the cat does not have the opportunity to wash the composition off the skin.
We suggest you read: How do flea drops for cats work?
In rare cases, for acne, systemic antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Among the variety of similar drugs used in the treatment of pets, Enrofloxacin and Amoxicillin should be highlighted due to their effective effects. Along with them, syntomycin and tetracycline ointments are used to treat affected areas of the body. The dosage and regimen are prescribed based on the individual characteristics of the animal.
One of the symptoms of acne is itching in the chin area.
How to treat acne on a cat's chin? This question can often be found on forums on the Internet. It is important to remember that before treating sores of unknown origin on a cat’s chin, you should understand their nature and the reason for their appearance, otherwise you can harm the animal and provoke the development of serious complications in it.
As a rule, for uncomplicated forms of the disease, veterinarians recommend local treatment of acne in cats at home, aimed at treating the affected areas of the animal’s skin with antiseptic and antiseborrheic agents: shampoos, tar soap, iodine, chlorhexidine, salicylic alcohol and the like. These methods of therapy should be carried out with great caution and under the supervision of a specialist.
The most effective means of local therapy for acne in cats are considered to be:
- cleansing shampoos with a high content of sulfur and salicylic acid;
- products that inhibit the formation of secretions from the sebaceous glands (Baziron gel for the treatment of acne in cats, Peroxiderm shampoo);
- antifungal creams and gels (Clotrimazole);
- antibacterial drugs for external use.
In cases where pathogenic microorganisms are attached to acne with the development of purulent inflammatory processes of the skin, the veterinarian may decide on the advisability of prescribing broad-spectrum antibiotics orally and steroid hormones. To regulate metabolic processes in the skin and improve its condition, the cat is prescribed complexes of essential fatty acids - omega-3 or omega-6.
Black spots on your cat's chin?
Feline acne is a skin condition that causes clogged pores primarily in the lip and chin area. Cats of all breeds are susceptible to the disease, and in hairless breeds: sphinxes, elves, lefties, bambinos and others, comedones (blackheads, blackheads) can be located throughout the body. There is no breed or gender predisposition; both young and older animals can suffer.
Reasons for the formation of comedones
Black spots are formed due to impaired desquamation of the skin epithelium and dysfunction of the sebaceous glands or excessive secretion. Predisposing factors:
- Allergic reactions. The protective function of the skin is impaired
- Parasitic diseases, as well as long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs, viral leukemia and immunodeficiency of cats, cancer
- Secondary bacterial and fungal infection
- Bowls for drinking water and food made of low-quality or long-used plastic
- Not washing bowls frequently or thoroughly enough
- Unbalanced or unsuitable food for the cat
- Disturbance of keratinization and functioning of the sebaceous glands
- Lack of hygiene
- Poor living conditions
- Genetic predisposition
- Stress
Acne symptoms
Often owners complain about dirt and dark bumps on the chin that cannot be washed off. And, more often than not, these are the owners of light-colored cats. However, the disease occurs with equal frequency in animals of all colors. This problem may not bother the cat at all and may only be a cosmetic defect. However, with concomitant diseases and skin inflammation, the following symptoms may occur:
- Itching in the muzzle area
- Hypotrichosis (sparse hair) or complete absence of hair
- Black dots
- Swelling, enlargement of lips and chin
- Skin redness, crusts and black scales
- The appearance of pustules with pus or papules (dense nodules)
It is worth distinguishing this disease from flea allergic dermatitis, notoedrosis, aphanipterosis, demodicosis, eosinophilic granuloma, facial dermatitis of Persian cats, and many other dermatological pathologies of cats.
Usually acne is characterized by several stages:
- The first stage of the disease is expressed by increased secretion of the sebaceous glands. The attention of the owner of a cat with light fur may be attracted by the persistent presence of fatty yellow spots on the pet’s chin, but in most cases the course is unnoticeable.
- In the second stage, comedones are formed. This happens because increased secretion of the sebaceous glands is accompanied by increased keratinization - the production of keratin protein, the main structural component of skin and wool. Protein masses prevent the normal emptying of the sebaceous gland, and as a result, the hair follicle into which the sebaceous gland duct flows becomes blocked by a mixture of glandular contents and protein. A comedon looks like a black dot, slightly protruding above the surface of the skin, and is often mistaken for pollution. Comedones are usually located on the chin, and somewhat less commonly on the skin of the lower lip. Typically, similar changes, if you part the fur, can be found at the base of the cat's tail.
- The third stage is characterized by inflammatory changes in the affected hair follicles, which are caused by bacterial flora. Folliculitis develops: first a red papule (bump) at the base of the hair, then a pustule (abscess) - the hair follicle dies and the hair will never grow again. After opening and drying of the pustules, crusts form. Experiencing pain and itching, the cat scratches the affected area, aggravating its infection. When the cat recovers, there are traces of superficial scarring in the affected area and areas of thinning of the coat.
Complications
A complication of acne can be deep or superficial pyoderma, pyotraumatic dermatitis. The cat may experience severe itching and pain, scratching the skin until it bleeds with the risk of infection of the wounds and a more serious inflammatory process. With severe blockage, atheromas can form - cysts of the sebaceous glands. They may need to be removed surgically under general anesthesia. If acne is detected, we recommend contacting a veterinary dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures must be carried out to exclude concomitant diseases and confirm the diagnosis:
● Superficial and deep skin scrapings. ● Microscopy of wool. ● Cytological examination of the skin, contents of pustules. ● If demodicosis is detected, general blood tests and research are performed to exclude leukemia and immunodeficiency.
Treatment
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure a cat for acne.
You can only relieve inflammation, eliminate predisposing factors and prevent relapses. If itching occurs, you will need to wear a protective collar. You should not squeeze out blackheads and pustules, as there is a high risk of infection and causing deeper inflammation. Periodically wipe problem areas with Chlorhexidine and lubricate with the ointment specified by the veterinarian. If the cat allows itself to be washed, then you can use Doctor shampoo with benzoyl peroxide once or twice a week. Avoid prolonged use of alcohol-based drying products as this can increase the secretion of the sebaceous glands, which can cause new blockages and further spread of acne. If a cat tries to lick the cream from its chin, then you need to distract the cat for 15-20 minutes and after this time, blot the remaining cream with a napkin. Your cat's diet may also need to be adjusted. When treating acne, you need to be patient. Unfortunately, improvements do not come as quickly as we would like. Treatments must be regular. Be sure to follow all doctor's orders. If you have any doubts, there is no effect or there is a deterioration in the picture, be sure to contact your doctor to adjust the therapy.
Preventing cat acne
For prevention purposes, it is recommended:
- Use glass, ceramic or metal bowls. Keep them clean.
- Change the water in the drinking bowl twice a day.
- Keep your chin well-groomed. If the cat does not wash itself, then you will have to help it with this.
- Keep your cat's resting areas, houses and beds clean.
- The cat's diet should not include food from the common table, since excess fat content of food activates the sebaceous glands; do not overfeed the cat.
- Follow your veterinarian's recommendations.
This disease has practically no cure. Fortunately, if hygienic care is taken and secondary infection is contained, it is only a cosmetic problem and does not affect the cat’s quality of life.
Diet
A properly formulated diet can not only strengthen the cat’s immune system, but also prevent the appearance of acne. Daily food should contain a large amount of vitamins and micronutrients. The diet of cats should contain foods rich in tocopherol, ascorbic acid and vitamin A. The listed elements help protect pets from various infectious and dermatological diseases.
In order to normalize metabolism and the functioning of the sebaceous glands, it is necessary to feed cats porridge. Slow carbohydrates contained in cereals speed up metabolism and improve local immunity. It is not recommended to feed animals fatty foods, canned food and sausage. These products negatively affect the condition of the liver and the production of subcutaneous fat.
Preventive measures
An advanced form of the disease can lead to serious complications. Based on this, it is very important to start treatment of the disease in a timely manner. In order to reduce the risk of acne formation, preventive measures should be taken carefully.
In order to prevent recurrence of acne, you should wash the dishes from which the animal eats as often as possible. The water in the bowl should be changed at least twice during the day. After your pet eats, you need to wipe the chin with a napkin soaked in warm water. In order to normalize the functioning of the sebaceous glands, you should remove all fatty foods from your diet. In order to strengthen your pet's immune system, you should feed it healthy food rich in vitamins.
Causes and mechanism of disease development
The reason for the failure of the keratinization process of epidermal cells in cats has not been established. Therefore, experts identify several factors that contribute to this phenomenon and lead to the appearance of black spots on the fur of cats. These include:
- increased secretion from the sebaceous glands of the epidermis;
- sticking of food debris to the beard or skin on the cat’s chin;
- decreased immunity after severe infectious diseases, as well as during the rehabilitation period after injuries or operations;
- dysfunction of the endocrine glands;
- intoxication phenomena caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas;
- allergic reactions;
- skin pathologies;
- dermatophytoses;
- demodicosis;
- improper care of the animal's skin and fur;
- some infectious and parasitic diseases;
- severe or prolonged stress.
Important! Owners must carefully monitor the cleanliness and integrity of the dishes from which the animal eats and drinks. Pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in chips, scratches and cracks, then enter the pet’s skin and can easily provoke inflammation and cause sores on the chin of cats.
The mechanism of comedones formation in cats occurs in 5 stages:
- Increased secretion from the sebaceous glands (sebum).
- Blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands with a mixture of sebum and dead epithelial cells.
- Formation of open cysts (comedones) at the mouth of the hair follicle.
- Oxidation of the contents of comedones in the presence of oxygen. Visually, this is marked by the appearance of black dots on the cat’s skin.
- Opening of comedones.