The development of veterinary medicine for small animals in our country began relatively recently. Just 30-40 years ago, most people would not even think about investing in pet care. Productive and economically useful animals were treated. And while dogs could still be classified in this group with a stretch, cats did not fall into this category. The lack of demand for the treatment of domestic cats has prevented the development of veterinary medicine in this area. The lack of knowledge among veterinarians and the general population has led to the birth of myths about the impeccable health of cats: “cats practically do not get sick, and if they do get sick, it is incurable.” Unfortunately, the stereotype that has developed in this way still prevents many cat owners from being attentive to the health of their little friends and preventing their diseases. This article will introduce you to the most common diseases of cats.
Signs of all diseases can be divided into specific and nonspecific. Nonspecific signs are manifested by the poor condition of the animal as a whole and are observed to varying degrees in almost all pathologies. These include: increased body temperature (above 39 °C), decreased appetite, apathy, and decreased social activity. Specific signs of diseases directly indicate the area of a possible problem.
Diseases of the genitourinary system
The concept of the genitourinary system means the totality of organs that form the urinary and reproductive systems: kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, ovaries, testes, uterus, prostate gland.
Diseases of these organs are usually manifested by a violation of their function and a demonstration of anxiety in the animal. The main specific signs of such pathologies include:
- disturbance of normal urination (from frequent to complete absence);
- pain when urinating;
- hematuria (appearance of red blood cells in the urine);
- the presence of mucus and blood on the genitals;
- frequent licking of the genitals;
- increased thirst;
- abdominal pain (pain in the abdomen).
Among the most common diseases that can manifest themselves in this way, it is worth noting kidney disease (acute and chronic renal failure), urolithiasis, inflammation of the bladder (idiopathic and infectious cystitis), inflammation of the urethra, inflammation of the uterus - endometritis.
If the above symptoms are detected, you should contact a veterinarian as soon as possible to receive qualified advice, carry out the necessary diagnostics (ultrasound, blood and urine tests) and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Controlling the animal’s fluid intake in this situation can be considered not only prevention, but also, to a certain extent, treatment. Sufficient saturation of the body with water helps to improve urine production and reduce symptoms. To maintain a cat's sufficient fluid intake, a combined type of feeding is best, which involves the daily use of dry and wet food. The use of wet food in this case helps to increase the level of moisture consumed.
The most effective ways to prevent diseases of the genitourinary system also include compliance with feeding standards. Thus, the diet must be balanced with macro- and microelements and contain sufficient amounts of vitamins and essential amino acids. These standards are fully met by Purina® PRO PLAN® cat food. Feeding cats complete Purina® PRO PLAN® diets has been proven to help maintain normal urine acidity and prevent the formation of urolithiasis. If you feed your animal non-commercial food and prepare it yourself, you should seek the advice of a professional veterinary nutritionist.
What to do at home?
If your cat's cold is mild, it can be treated at home. Before treating with medications, it is worth observing the animal and trying to relieve the symptoms of a cold. If there is no improvement within 24 hours, then you should urgently consult a veterinarian, he will prescribe antibiotics that will help cure the animal. If the cat’s condition stabilizes, then most likely he will cope on his own. The most common home remedies to help treat your pet are:
- If your cat has a cold, then first of all you need to give it rest.
- The pet needs a warm and dry room; under no circumstances should it be in a draft.
- A sick animal needs an increased drinking regime. You can give him warm milk.
- You can make warming compresses and heating pads; at this time, the cat’s blood flow increases, so it will warm up faster. In this case, recovery will take much less time.
- The nasal passages need to be cleared by cleansing measures. Why roll a cotton pad into a tube and clean your pet’s nose with it. If the cat does not have an allergic reaction, then instead of boiled water, you can use a decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage.
- If a cat has a cold and its nose is not breathing, then you can drip a few drops of eucalyptus onto the bedding on which the animal sleeps. This will make it easier for him to breathe.
- It is good to treat an animal with a massage; it has a warming effect.
- If your pet is sneezing and has a runny nose, you can blow pre-poured streptocide into his nostrils.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
The organs of the gastrointestinal tract include not only the digestive tube itself, represented by the esophagus, stomach and intestines, but also the organs involved in the digestion of food (liver, gall bladder, pancreas).
The main diseases for this group of diseases include:
- pathologies of the liver (hepatopathy) and biliary tract: fatty liver, inflammation of the gallbladder and its ducts;
- pathologies of the pancreas: pancreatitis;
- Pathologies of the digestive tube include diseases of inflammatory origin: gastritis, enteritis, colitis, and non-inflammatory origin: tumors, helminthiases, protozoonoses.
Often, during play, cats swallow inedible objects, which can cause serious disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Specific symptoms of the above diseases are vomiting, diarrhea or, conversely, constipation, the appearance of blood and/or mucus in the stool, change in the color of feces, and increased salivation.
When the first signs of diseases of the digestive system appear, it is necessary to contact a veterinarian as soon as possible. If this is not possible, it is recommended to limit the animal’s food intake - remove food for 10–15 hours, feed an adsorbent (for example, activated carbon or smectite) and provide access to fresh, clean water.
To prevent diseases of the digestive tract and maintain its health, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- choose a complete, balanced diet with high digestibility. For example, one of the Purina® PRO PLAN® diets. For animals with a tendency to diseases of the digestive system, it is recommended to use the easily digestible food Purina® PRO PLAN® Delicate, the main source of protein in which is turkey meat;
- avoid spontaneous sudden changes in feed;
- carry out regular scheduled deworming (at least 2 times a year);
- do not give food from your table;
- monitor the cleanliness, freshness and quality of the water your cat drinks;
- remove from the cat's field of vision all small objects that could be swallowed during play.
Colds in cats - symptoms
You should not try to figure out on your own how to treat a cat for a cold at home. If you suspect a disease, you should take your pet to a qualified veterinarian. Treatment of a pet requires a thorough differential diagnosis, on the basis of which a specialist will be able to understand how best to treat a cat for a cold. However, for the treatment to be effective, it is necessary to create a comfortable environment for the sick pet. To do this, the following measures must be taken:
- Create peace and quiet for the cat;
- Place the animal in a dry and well-heated room;
- Provide the cat with a warm drink (water or milk);
- In the absence of elevated body temperature, you can apply warm compresses or heating pads;
- A good effect is created by a massage that will increase blood circulation and help the cat warm up faster after hypothermia.
Symptomatic treatment is usually used as the main therapy. For a runny nose and other symptoms of a cold, use special drops, expectorants and antipyretics prescribed by a veterinarian. Under no circumstances should you give your cat medications intended for human use.
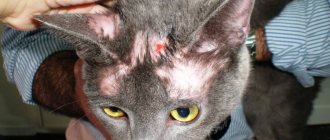
Diseases of the skin and coat. Allergic reactions
The skin and fur of cats are a natural barrier that protects the body from the negative effects of environmental factors. In addition to protective, the skin performs thermoregulatory, excretory, and receptor functions. Many metabolic processes take place in the skin, which in one way or another affect the functioning of all body systems. It is not surprising that general ill health and metabolic imbalances often manifest themselves in the form of deterioration in the quality of the skin. The main symptoms of skin and coat pathologies are:
- itching The animal becomes restless and constantly scratches itself;
- changes in the appearance of certain areas of the skin, rashes, formation of redness, weeping spots, swelling, etc.;
- the appearance of a large amount of dandruff and/or sebum;
- excessive shedding;
- complete loss of hair in certain areas (focal baldness).
These signs can be both symptoms of severe systemic diseases (for example, allergies) and true skin problems, for example, flea or tick infestation, fungal skin infections, injuries and burns.
The treatment that a veterinarian can prescribe for a cat will be mainly aimed at eliminating the root cause of the pathology and relieving symptoms.
Prevention of skin diseases includes regular treatment of the animal for parasites, preventing the cat from coming into contact with caustic substances and dangerous objects, and providing balanced feeding.
Diets suitable for cats with problem skin should have the following characteristics:
- sufficient vitamin A and zinc content - promotes better skin regeneration, necessary for collagen synthesis;
- high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega-3 and omega-6) – reduces skin inflammation and improves coat quality;
- high content of antioxidants (vit. E and vitamin C) – enhances the protection of skin cells from the harmful effects of free radicals;
- high protein content to ensure regenerative processes.
The Purina® PRO PLAN® Cat® line of foods are perfectly balanced to provide all body functions, including healthy skin. For animals with problem skin, the Purina® PRO PLAN® Derma Plus® specialized diet is especially suitable. It contains salmon meat as a source of protein, which ensures excellent taste of the food and additionally saturates the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids. A limited amount of protein sources in the diet reduces its potential allergenicity, which has a beneficial effect on the health of cats with sensitive skin. It has been proven that animals that consume Purina® PRO PLAN® Derma Plus® on an ongoing basis significantly improve the quality of their skin and normalize the molting process.
It is worth noting that manifestations of allergic reactions include not only diseases of the skin and its integument, but also diseases of a variety of organ systems, for example, respiratory, digestive. This means that allergies can also manifest themselves in the form of conjunctivitis, sneezing, coughing, vomiting and diarrhea. A veterinarian will help you identify an allergic disease in a timely manner and prescribe qualified therapy.
Causes
As a rule, colds in cats develop against the background of hypothermia. As a result of prolonged exposure to low temperatures on the animal's body, its general condition worsens. The course of a cold is largely determined by the duration of hypothermia, as well as the level of perfection of the cat’s thermoregulation mechanism.
Weakened and exhausted pets, as well as those who have suffered severe bleeding and severe illness, are at greatest risk of contracting a cold. But before you treat a cat for a cold, you should determine the cause of its occurrence. This data will help limit the impact of the provoking factor, which will not interfere with further treatment of the animal. The following reasons can trigger cold symptoms:
- Violation of feeding regime. Without receiving enough nutrients and vitamins, the cat’s body is weakened and cannot resist viruses from the outside;
- Infections. The presence of infectious diseases seriously undermines the pet’s immunity, opening access to other pathogenic bacteria and viruses;
- Incorrect care. Keeping a cat in a cold and damp room causes hypothermia and, as a result, a cold in the animal;
- Staying in a draft. This can happen to a cat immediately after bathing. Therefore, to avoid a cold in your pet, after water treatments, do not open the windows in the room and dry the cat with a terry towel.
Hypothermia can happen to a cat not only at home, but also on the street. In this regard, try not to walk your pet in windy and rainy weather.
Dental diseases
The most common dental pathologies in cats include:
- periodontal disease is a non-inflammatory disease characterized by the occurrence of degenerative processes in the tissues surrounding the tooth, exposure of the tooth root and increased mobility;
- Tartar deposits;
- resorptive dental disease - a disease manifested by the appearance of pockets of cavities in the tooth structure;
- juvenile gingivitis - inflammation of the gums that occurs during the process of changing teeth and is protracted;
- dental injuries: fractures, enamel chips, thermal burns.
Most often, an animal owner may suspect oral diseases by the appearance of bad breath, increased salivation, and bleeding gums.
Treatment of the animal is prescribed by a veterinary dentist after a thorough examination of the oral cavity (most often under anesthesia). Often, therapeutic and diagnostic procedures involve radiography and ultrasonic teeth cleaning.
To prevent oral pathologies, regular brushing of teeth with specialized toothpaste, as well as the use of professional foods that help remove plaque, are recommended. Cats predisposed to plaque formation are recommended to use specialized diets from Purina® PRO PLAN® Dental Plus®. Their unique formula helps prevent the appearance of tartar and reduce plaque formation by up to 40%.
Obesity
Often, owners, in pursuit of providing their pet with a better quality of life, offer excessive amounts of food. The result of this is the accumulation of excess fat mass and even clinical obesity of the animal.
And although excess body weight in itself is not so terrible, it can significantly complicate the life of a pet. The fact is that the growth of adipose tissue gradually leads to changes in hormonal levels, increased stress on joints and ligaments, the cardiovascular system, and a decrease in physical endurance. Obese cats have an increased risk of developing diabetes.
In addition to the above, in overweight cats, in the event of sudden starvation (more than 2 days), the risk of developing liver lipidosis, a serious disease that can be fatal, increases many times over.
Treatment and prevention of this pathology in cats consists mainly of providing the animal with a balanced diet, the calorie content not exceeding its daily needs. Among Purina® PRO PLAN® daily foods, diets with the Optilight® complex are used to prevent the development of obesity, with reduced calorie content, but at the same time a fully balanced composition, rich in protein and fiber.
Causes of eye infection in cats
Cats' eyes can fester for various reasons, and here are the most common ones:
- Conjunctivitis is the most common cause of eye infection in animals. This disease is very easy to cure; the most important thing is not to let it get worse.
- Trauma to the mucous membrane can also cause suppuration of the eye. Small wounds on the animal heal on their own, but larger ones should be treated.
- Blepharitis is a dangerous eye disease in cats that can occur as a result of a chemical burn or injury.
- Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea that leads to suppuration of the eye.
- Due to poor health and low immunity, the animal's eyes may fester.
- Also, cats' eyes can fester due to poor nutrition.
- As a result of a “dirty nest”, the cat’s eyes may fester.
- If the kitten is hypothermic, it may develop purulent discharge from the eyes.
- Heredity.
Infectious diseases of cats
The most common infectious diseases of cats are panleukopenia, rhinotracheitis, and calcivirosis. One of the diseases that affects other animals is rabies.
Infectious panleukopenia
This is one of the most contagious diseases of viral origin, which is also called “feline distemper”. Characterized by high mortality (90%). In a sick animal, gastrointestinal symptoms are primarily observed: diarrhea, vomiting. Most often, body temperature rises. The disease affects all organs and is terrible for its complications. Without treatment, the animal can die in 4–5 days. If the illness drags on for up to 9 days or more, cats usually survive, acquiring lifelong immunity, but remaining virus carriers, so the mother who has recovered from the disease can infect her offspring.
Infectious rhinotracheitis
Infectious rhinotracheitis is a contagious disease that occurs in cats at any age. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Incubation period: 2–4 days. The mouth, nose, eyes and respiratory organs are affected. The disease can be complicated by keratoconjunctivitis and pneumonia. Among kittens under 6 months of age, mortality reaches 30%. Most recovered animals remain virus carriers. Symptoms include cough, discharge from the nose and eyes, inflammation of the oral mucosa, and fever.
Calcivirus infection (calcivirosis)
An acute viral disease accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature and damage to the respiratory tract. Infection occurs by contact and airborne droplets. Kittens and young animals are most often affected. Incubation period: 1–4 days. Symptoms: fever, inflammation and ulceration of the tongue, lips and oral mucosa (stomatitis), rhinitis, conjunctivitis.
Rabies
A well-known viral disease, although it is rarely encountered in veterinary practice. Infection occurs through contact, after the bite of a rabid animal. After the first symptoms appear, therapy is impossible, the animal is doomed. Transmission of the pathogen occurs through the bite of a sick animal. Symptoms occur in two types: violent and quiet. In the first case, the cat becomes extremely aggressive and attacks all people and other animals. Please note that all this happens in complete silence; the rabid pet does not make a sound. He begins to be terrified of water and eating inedible objects, and reacts sharply to loud sounds and bright light. In a quiet form, everything looks much more harmless. The cat, even if in the recent past was very aggressive and characterful, becomes very affectionate. Saliva in such animals, as a rule, is also secreted, albeit in smaller volumes. Cats infected with a silent form of rabies easily “gain trust” in people and bite them. Often a person finds out about his illness only when nothing can be done to help him. Just like a sick cat. All rabid animals are euthanized and their bodies are disposed of by burning. Fortunately, rabies is easy to prevent with timely vaccination, which should never be neglected.
Treatment
Treatment of infectious diseases is a set of measures aimed at suppressing symptoms and stimulating the animal’s immunity. If you notice the first symptoms, immediately limit your cat's contact with other animals (quarantine) and contact your veterinarian. You should not self-medicate – it could cost your pet’s life.
Cat diseases
Feline distemper or panleukopenia
Most often, kittens suffer from this disease. Manifests itself in the form of an appetite disorder and refusal to suck the cat. Panleukopenia rarely occurs in adults, as their immunity easily suppresses it. You can rid a sick animal of distemper using antiviral drugs.
They must be given at least three times a day. It is important to improve the functioning of the immune system and immunomodulators are used for this purpose. If a sick pet begins to exhibit anemia and vomiting, the veterinarian gives subcutaneous injections. It is possible to get rid of feline distemper in about a week with the right approach.
Respiratory diseases
Respiratory diseases are transmitted through airborne droplets. Infections penetrate into the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, eyes and respiratory organs in a short period of time. Before the disease manifests itself, it goes through an incubation period that lasts about 15 days.
The main symptoms of respiratory diseases are sneezing and swelling of the mucous membranes of various organs. The disease is treated by intramuscular injections of antibiotics.
Leukemia
The most insidious disease that cats can get is leukemia. For a long time it does not remind of itself, and thus the owners miss the moment when they could rid the pet of it quickly and without consequences. Leukemia affects the circulatory system and manifests itself in the form of anemia and low mobility.
A cat may give birth to still kittens if it suffers from this disease. Alas, it is almost impossible to get rid of leukemia when it has entered the second and subsequent stages. The veterinarian can only alleviate the animal’s suffering by prescribing immunomodulators. The duration of illness in a cat with leukemia does not exceed 5 years.
Third eyelid
The nictitating membrane or third eyelid in cats is not visible during wakefulness. If it becomes visible, then this indicates the appearance of an adenoma of the eyelid. Its removal is possible only surgically. In the postoperative period, the animal should be given anti-inflammatory medications. A removed third eyelid will not impair your pet's vision.
Chlamydia
Until recently, it was believed that chlamydia was a disease that only humans could suffer from. In fact, it also appears among representatives of the cat family. Symptoms of chlamydia are expressed in the form of a pet refusing food and water. Less common are a runny nose, wheezing and ocular conjunctivitis. If you need to cure chlamydia, then the first step is to limit the animal's movement.
Under no circumstances should you let him go outside. Give your sick pet tetracycline and apply special ointments to the eyes as prescribed by your veterinarian. Complete recovery from chlamydia occurs within 15 to 60 days.
Mycoplasmosis
If a cat experiences baldness in the area of the ribs, and also begins to cough and pus appears, then we can safely say that the causative agents of mycoplasmosis have entered its body. Only a veterinarian can make a final diagnosis. Mycoplasmosis is treated with vitamins, disinfecting drops, antibiotics and saline solutions.
The appearance of parasites
Ticks, fleas and lice eaters are not averse to living at the expense of a cat. If the owner begins to notice that the animal is constantly itching, then, most likely, certain parasites have chosen it as a comfortable place to live. Getting rid of fleas, ticks and lice is quite simple.
Pet stores and veterinary pharmacies sell drops that successfully combat parasites. By the way, it is recommended to use them to prevent their occurrence. If your cat spends most of the day outside, then put a special collar on it. She may also develop parasites such as worms in cats. The panacea for them is tablets, which can be purchased at any veterinary pharmacy.
Endocrine system disease
If nutrients cannot penetrate the cells for a long time, this causes the endocrine system to fail. Diabetes appears instantly. The cat becomes lethargic, loses interest in life, and the smell of acetone appears from the mouth.
It is impossible to get rid of problems with the endocrine system. Diet will help improve the situation. Your veterinarian may prescribe insulin injections as well as medications to help lower blood sugar levels.
Nervous system disease
One cat out of several thousand may develop epilepsy. Moreover, you should not think that the cause of the disease is an infection. An animal's epilepsy is due to the presence of pathology in its genetic code. The disease manifests itself in different ways. From twitching of limbs to complete paralysis.
The treatment of epilepsy should be carried out by a neurologist, who will be difficult to find in an ordinary veterinary clinic. Alas, the disease can only be transferred into a state of remission. Modern science cannot completely rid either animals or people of epilepsy.
Rectal prolapse
A healthy cat's diet should include both liquid and dry food. The predominance of only dry food can cause constipation, which, in turn, can lead to rectal prolapse. Treatment in this case is as follows:
- make an appointment with a veterinarian as soon as possible;
- a specialist will examine the intestine. If there are no dead areas of tissue, then it is set back;
- part of the intestine will be removed if necrosis is detected. In such a situation, surgery is required.
After surgery, the cat should eat only liquid food for a long time to avoid relapses.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis refers to the development of inflammation in the pancreas, in which the animal becomes drowsy, its hair falls out, vomiting and ulcers on the tongue occur. Pancreatitis can be cured only with an integrated approach. The veterinarian prescribes a lot of medications that are designed to destroy bacteria that contribute to the development of the disease. After this, insulin injections are given.
Brain diseases
Appears in adult cats. The animal may begin to lose its balance, fall when walking, and also become disoriented in space. Brain diseases develop quickly and it is important to quickly begin to cure them. It is best to give your cat injections prescribed by your veterinarian. They will dull the pain and prevent the disease from developing. If the disease has subsided, then long-term physical therapy is required to bring physical abilities back to normal.
Osteochondrodysplasia
If there is a Scottish cat in the family, then you should know that there is a high probability that the animal will develop this disease. It is characterized by deformation of the limbs and problems with movement. It is almost impossible to get rid of osteochondrosplasia. Veterinarians practice surgical removal of deformities, but this is not always possible. The disease is accompanied by severe pain, which can be dulled by painkillers.
Asthma
The cat began to breathe heavily and began to cough - these are the main symptoms of asthma. It appears exclusively as a result of infection entering the body through the respiratory tract. The mucous membrane takes on a bluish-gray color. Treatment of asthma begins with identifying the culprit of the disease, and only after that it is necessary to give the pet anti-inflammatory drugs.
Cats are unique animals by nature. Their intuition is so developed that they anticipate unfavorable events and try to get rid of the risk of their occurrence.
The cat carefully protects its health:
- does not eat low-quality food;
- does not drink dirty water;
- avoids noisy and unfamiliar places and people;
- does not enter into direct conflict with a potential enemy until the last moment;
- agility and flexible musculoskeletal system allows these animals to fall even from great heights without damaging vital organs.
All this allows cats to be maximally protected from diseases and injuries.