6775Pavel
Viral leukemia in cats is a dangerous disease that affects their hemolymphopoietic system. Characterized by malignant enlargement of myeloid tissues. The cause is an oncogenic virus called FeLV or FLV. Although it is similar to leukemia viruses in other animals, there are still significant differences in the structure of the antigens. This disease affects cats all over the world, regardless of age, but in older animals the chance of infection is noticeably lower.
Retrovirus: General information
Viral leukemia in cats is caused by an oncogenic retrovirus containing RNA that invades blood cells and destroys their genetic code. It is divided into several subgroups:
- FeLV-A. This subgroup is the main one, and the pathogenic microorganisms included in it are the “reference” leukemia viruses. They reduce immunity and are present in the blood of all animals with this disease;
- FeLV-B. This viral subgroup leads to the development of tumor processes in the body and is present in 50% of cats with this diagnosis.
- FeLV-C. Viruses of this subgroup disrupt hematopoietic processes and cause anemia. They are found in the blood of only 1% of pets with leukemia.
- FeLV-T. Viral agents infect T-lymphocyte blood cells, leading to their destruction and a decrease in the body's defenses.
Many owners are interested in the question of whether viral leukemia in cats is transmitted to humans or not? Veterinarians assure that neither humans nor other animals except cats are susceptible to it.
The leukemia virus was discovered by scientists from Glasgow in 1964. In addition to its discovery, they were able to establish a connection between leukemia and cancer of the lymphatic system in cats, with the presence of a retrovirus in the blood. The virus not only destroys the animal’s immunity, but also provokes the development of other diseases.
It begins to develop in the lymphatic system, in the tissue structures of the tonsils and nasopharynx, gradually moving into the lymph, blood and brain. The body's defenses are weakened imperceptibly, and when the virus enters the bone marrow tissue, the disease begins to develop rapidly and leads to the death of the pet. This happens because along with the blood cells produced in the bone marrow, virus cells are also produced that infect the entire body. Death often occurs due to diseases concomitant with leukemia.
More about the pathogen
Refers to oncogenic oncoviruses. Simply put, it can cause cancer. Fifteen years ago it was believed that such “qualities” of viruses were far-fetched, but now it has been precisely established that they actually have carcinogenic properties. Oddly enough, these microorganisms are divided into two large groups: endogenous and exogenous. And if everything is clear with the second category (viruses circulating in the external environment), then what about the endogenous variety (internal)? This is where the fun begins: the fact is that the normal genome of a domestic cat contains up to 100 varieties of copies of these viruses! Under the influence of some factors, they can begin to be spontaneously produced in the cat’s body itself. Some scientists believe that this is how chronic leukemia develops.
However, this happens quite rarely. In the vast majority of cases, the causative agent of the disease is exogenous viruses. When were they found? Oddly enough, this happened back in 1964. Then it was definitely determined that feline leukemia is indeed viral, and that it affects all animals, regardless of breed, physiological condition and age. It was found that it initially enters the blood, and only then into the red bone marrow. This virus is unique in many ways, as it is able to “mix” with some other pathogens. In particular, its ability to complementarily mix with the murine sarcoma virus has been proven. The “hybrid” obtained as a result of the reaction becomes aggressive towards the cells of the reticuloendothelial system of cats, but does not manifest itself in any way on mice (even if they are targeted for infection).
How is the virus transmitted?
The virus is highly contagious, so a sick animal can easily infect a healthy one. That is why the owner must know how viral leukemia is transmitted in cats.
A cat can become infected with this infectious disease through:
- contact with saliva, feces and urine of a virus carrier;
- bites;
- shared toys, beds and dishes with the carrier;
- flea bites.
The virus is also transmitted during mating and in utero. In addition, the owner can infect his pet if he came into contact with a sick animal and did not wash his hands or change his clothes.
Most often, cats living with several individuals get sick. This can be observed in shelters, nurseries and basements where homeless individuals live.
How the feline leukemia virus spreads
There are several main ways of transmitting the virus from a sick animal to a healthy one. In any case, close contact is necessary, since the virus cannot survive in the environment.
Among the most common methods of transmission of the virus:
- Saliva . The infection process will begin if a sick animal licks or bites a healthy one. The virus will penetrate the tissue and cause disease.
- Blood . To do this, it is necessary that the blood of a sick animal enters the wound of a healthy one. This happens in fights.
- Urine . Virus is also released when urinating. But it is contagious only for a short time. To infect a healthy animal, sniff the urine of a sick animal.
- Feces . Similar to urine, but this route of infection is quite rare.
- Milk and placenta . Kittens can become infected from a sick cat.
- Sexually .
- With a flea bite.
Be sure to read:
What diseases can you get from a cat: 11 infections dangerous to humans
The risk of contracting such a dangerous disease is quite high, especially among pets who come into contact with stray cats.
Risk group
Viral leukemia in cats is a rather insidious disease and some pets are at risk. The most susceptible to the disease are stray cats, mixed breeds, purebred, young and elderly pets.
The virus is unstable to external influences. It can be destroyed by treating with alcohol-containing disinfectants. It is also destroyed by the sun and sudden temperature changes.
"Note! Males, due to their lifestyle, suffer from leukemia more often than females. Therefore, veterinarians recommend that cat owners not let them roam freely and allow them to mate only with healthy females.”
What should you pay attention to?
When is the risk of infection especially high? Firstly, if your cat is constantly in contact with other animals. After all, leukemia in these animals is infectious, so such conditions are simply ideal for it. Breeders who live in urban apartment buildings may be advised not to let their pets go outside at all, and if walking is necessary, take the cat to a park or other place where the cat population is not so high. Of course, there is a high probability of infection even if several animals live in your house at once. If they are all in free-range conditions, the entire herd can contract leukemia almost instantly. Since there is no cure for this disease, all your cats may die. Don't take the risk!
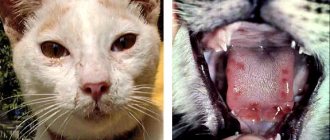
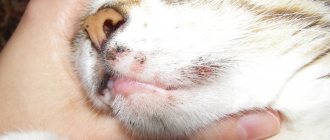
Symptoms of viral leukemia in cats
Since viral leukemia in cats is asymptomatic, it manifests itself when leukocyte counts go far beyond normal limits. In this case, the animal can no longer be helped and the only way out is euthanasia. To prevent the development of the disease and detect its signs in time, the cat should be shown to a specialist twice a year.
Symptoms of viral leukemia in cats include:
- drowsiness;
- inflammation of the bladder;
- lack of interest in games;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pallor of mucous membranes;
- frequent rises in temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- goggle-eyed;
- lethargy;
- discharge from the nose and eyes;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent colds;
- drooling.
Signs of viral leukemia in cats are not specific, so the owner will not be able to determine whether a pet has VLK on their own. Therefore, if the owner has even the slightest suspicion of leukemia, he should immediately contact a veterinarian.
Forms and types of viral leukemia in cats
A sick cat may have one or several viral strains. Depending on how strong the animal’s immunity is, leukemia can have several forms:
- transient. This is the initial form of the disease, which develops until the bone marrow is damaged. In rare cases, at this stage the pet's strong immune system may develop antibodies that will completely destroy the virus. Such a cat develops lifelong immunity to this disease and ceases to be a source of danger to other cats;
- latent. This type of disease occurs in animals with a strong immune system. The cat is a carrier of the virus, it is in its body, but the virus is not active and does not multiply;
- persistent. In this form of the disease, the virus has already infected the bone marrow and destroyed the cat's immune system. The animal begins to develop anemia and other signs of developing leukemia. The respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, skin and bladder suffer the most.
Leukemia is also differentiated by location. It happens:
- chest It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, which leads to suffocation of the pet. To make an accurate diagnosis and distinguish the symptoms of this type of leukemia from wet infectious peritonitis, a complete diagnosis of the sick cat is required;
- abdominal Leukemia is characterized by damage to the gastrointestinal tract, but at the same time it has similarities with indigestion and jaundice. Over time, the animal develops dehydration, cachexia and constipation;
- multifocal. This type of leukemia affects several systems at once and leads to rapid death due to difficulties in diagnosis.
To determine the type of disease and select a therapeutic technique, a complete diagnosis of the body should be carried out.
Why is it dangerous?
Aren't you surprised that we didn't touch on this issue in the article? It's simple - the disease is fatal and incurable. By the way, how long do cats with leukemia live? In general, the question is quite interesting. The fact is that even after infection, an animal can generally live a long and full life, being a carrier of the disease. The virus will be detected in the cat's blood, but it will not have any clinical signs. But there are also cases when a cat that contracted the leukemia virus died within a year. So everything is individual here.
Diagnostic measures
To refute or confirm the diagnosis of viral leukemia in cats, a number of tests are performed:
- general blood analysis. It allows you to determine leukocyte and erythrocyte indicators, as well as the presence of anemia;
- enzyme immunodiagnostics. With its help, you can see whether the cat’s blood contains waste products of the virus;
- polymerase chain reaction. This analysis makes it possible to assess the condition of peripheral blood.
- immunofluorescence blood test. It allows you to identify antibodies to the virus and its variety.
However, the diagnostic methods described above are rarely used, since most clinics conduct a rapid test for leukemia, which gives reliable results.
In addition to screenings, the animal undergoes ultrasound and x-rays to detect the presence of cancerous tumors and abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs.
If there are indications, the cat undergoes a biopsy, laparoscopy, colonoscopy or gastroscopy, depending on the organ damaged by the disease.
Diagnostics
Since feline leukemia is characterized by various manifestations of the disease, any chronic or periodically recurrent disease comes under suspicion.
The presence of leukemia in the blood can be determined most accurately by isolating the virus in the blood serum, as well as accurately determining the viral leukemia antigen using immunofluorescence.
If the presence of the antigen is determined by a rapid test, then a positive test must be confirmed by isolating the virus from the blood serum.
A cat is considered leukemia-free if the results of examinations carried out over a period of 12 weeks are negative.
In case of tests with positive results, the cat's condition will be determined as persistent viremia.
Once a diagnosis of viral leukemia is confirmed and there are no severe symptoms, some owners are reluctant to euthanize the animal. However, they take a deliberate risk.
Separately, it is necessary to consider such viral leukemia of cats as lymphosarcoma. It is characterized as a malignant tumor that grows into surrounding tissues and spreads its metastases to various organs. Foci of lymphosarcoma occur in the lymph nodes and follicles. Uncontrollably multiplying blood cells penetrate organs and tissues - leading to the formation of tumors that change their structure. The duration of the incubation period is usually from 60 to 80 days. But it can reach up to 6 years.
Treatment of viral leukemia in cats
Treatment of viral leukemia in cats is symptomatic. Unfortunately, it is not possible to completely cure the disease. The selected therapeutic technique will not only prevent the disease from developing, but will also prolong the animal’s life by more than one year.
The doctor selects medications depending on the pet’s condition, diagnostic results and symptoms of the disease.
If the cat’s health begins to deteriorate, the veterinarian prescribes a course of immunomodulators (AZT, Feliferon, Raltegravir and others), antibiotics, vitamins and symptomatic medications.
Blood transfusions have a good effect in treating leukemia. However, such a procedure will need to be carried out once every fourteen days. When cancer is diagnosed, chemotherapy is administered to stop the pathological process.
In addition, it will be necessary to review the cat’s diet and feed it only high-quality, heat-treated food to prevent pathogenic microflora from entering the body.
In addition to proper nutrition, the animal will have to be quarantined for life. This is especially important if there are other cats in the house. After interacting with a carrier of the virus, the owner must change clothes and wash his hands so as not to infect other pets.
"Important information! It should be remembered that euthanasia is a last resort and is used only when indicated; in other cases, properly selected therapy can prolong the animal’s life and make it full.”
Treatment
There is no medicine yet that can completely cure leukemia in cats. At the first sign of leukemia, the cat should be examined. Cancers caused by the virus cannot be cured. Even with early diagnosis, which allows early treatment, complete recovery cannot be achieved. Leukemia in cats is treated with anticancer drugs, antibiotics, vitamins, and micronutrient complexes, which helps stabilize the condition of some of them. But leukemia patients remain very dangerous to other cats because they continue to shed the virus. With further clarification of the diagnosis and confirmation of leukemia, veterinarians advise owners to euthanize the sick cat.
© shutterstock
Why does leukemia need to be treated at an early stage?
Why is it extremely important to choose a treatment regimen for viral leukemia in cats and start saving your pet as early as possible? Because in this way it will be possible to prevent the development of concomitant diseases that lead to the death of the cat.
If your pet does not receive proper treatment, this can lead to the development of:
- anemia;
- sarcomas of the lymphatic system;
- bleeding;
- breast cancer;
- frozen pregnancy;
- peritonitis;
- chronic cystitis;
- bacterial infections;
- autoimmune kidney problems;
- ascites;
- low-grade fever;
- miscarriages;
- viral diseases;
- toxoplasmosis.
If a sick cat becomes pregnant, she will give birth to infected offspring, which often do not survive due to a lack of immunity. For this reason, it is extremely important for nursery owners to monitor the health of their charges.
Prognosis for viral leukemia
What is the life expectancy of cats with viral leukemia? Everything will depend on the animal’s immunity. Typically, three to ten years pass from the moment of infection to death.
The incubation period for the disease can last from four days to eight months. Based on statistics, 90% of animals die in the fourth year of the presence of the disease. Such high mortality rates are due to the fact that symptoms begin to manifest themselves three years after infection. If the animal is properly cared for, its life with the virus will be long, but at the same time it will be dangerous for other felines.
“My last pet died of leukemia. Is it worth getting a new one?
Such questions can often be seen on “cat people” forums. It is difficult to give a definite answer. If you do not take into account moral torment, then everything depends on the thoroughness of preparing the apartment for the reception of a new “guest”. There is no point in hoping “at random”. Wash all accessible surfaces with disinfectants (regular “Whiteness” will do). All bowls, litter trays, toys and other things left over from the cat’s past must be thrown away! There is always a chance that somewhere in the distant “bins” of your favorite fur toy there will be saliva from your previous pet. In principle, with sufficiently high-quality cleaning and disinfection of the premises, the risk of infection of a new cat is very low, but it still persists. If you do the same before purchasing a new pet, but then wait a year and a half, the likelihood of the disease is reduced to almost zero.
Important! If you have a purebred cat, please refrain from purchasing a cat or kitten from a shelter as a mate. This could end badly, since practice suggests that the leukemia virus is widespread among the “pupils” of such institutions.
Preventive actions
To protect your pet from infection, he should be protected from contact with stray cats and should not be allowed to use other people’s bowls, trays, beds and toys. When moving into a new home, it must first be quartzed with a special lamp.
If a cat with leukemia died in the family, a new animal should be adopted no earlier than a year later and only after the apartment has been completely treated.
But the best way to protect an animal from infection is vaccination against viral leukemia in cats. Before an animal is vaccinated, it is tested for carrier status. Kittens can be vaccinated from two months of age, and then need to be vaccinated every year.
The vaccine does not destroy the virus, but allows you to develop immunity to it. It is for this reason that it is important to vaccinate your pet promptly.
Prevention
Every owner needs to know how to protect their cat from viral leukemia. In order to protect your animal from disease, you will need to follow a few simple rules.
- It is important to wash cat bedding periodically in high temperature water.
- After contact with other people's pets, you must wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- You will also need to place the shoes in a place inaccessible to the cat.
The vaccine against feline leukemia virus is the only way to protect the animal. The most common drug for vaccination in the Russian Federation is Leukotsel. It creates immune protection after just a few weeks. It lasts throughout the year. Then the vaccination should be repeated.