Hair care
Roundworms
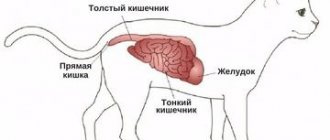
The most common worms in cats are roundworms, of which there are many varieties. The most common “guests” in cats’ bodies are roundworms. Their appearance resembles spaghetti; the length of the worms can reach 5 centimeters or more (the photo shows what worms look like in cats). Kittens become infected with ascariasis through their mother's milk, while an adult cat introduces worms into her body by eating rats, raw meat, and also through contact with animals.
Worms form clusters in the intestines, clog the bile ducts, and damage the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. They have a strong toxic effect on the body.
Cestodes are long and flatworms that can reach a length of 70 centimeters. The bodies of cestodes consist of numerous segments, each producing larvae (the photo shows a cestode body consisting of segments). A cat can become infected with tapeworms if its food consists of raw meat or raw fish; this also includes meat and fish that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment. Invasion is also possible through the carriers of cestodes - fleas.
Trematodes are white thread-like worms whose bodies are equipped with suckers. With the help of suction cups, they attach to the walls of the intestine, causing mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, and also have a toxic effect. Trematodes are much less common than the two previous types of helminths, but it is the worms of this species that pose a mortal danger to cats.
You can detect helminthic disease in a kitten or adult cat by its characteristic symptoms. As a rule, the most important signs of all helminthiases are similar. So, what could be the symptoms of the disease in a cat:
- Stool disorders, a characteristic symptom will be both diarrhea and constipation, and there is also a possibility of alternating diarrhea with constipation.
- Attacks of vomiting; in severe cases, worms or blood impurities will be present in the vomit.
- Segments of worms can be seen in the animal's feces and on its fur.
- Kittens and adult cats begin to ride on the fifth point, which is caused by severe itching of the anus.
- There may be mucus and blood in the stool.
- Swollen and rounded belly.
- Unreasonable weight loss.
- Lack of appetite or increased appetite.
- Cough.
- Labored breathing.
- Developmental delay.
- Hair loss, exhausted appearance, fatigue.
- Yellowness of the mucous membranes.
- Convulsions and paralysis of limbs in severe cases.
If such symptoms are detected, it is necessary to immediately show the animal to a veterinarian and undergo diagnostic tests prescribed by him (usually a stool test). After making a diagnosis, the veterinarian will prescribe the necessary treatment for your furry pet.
Types of worms
In veterinary medicine, helminthiasis is a fairly well-known disease that is often found in pets. Helminths (worms) that infect a cat’s body come in several varieties. The most common types of worms in cats:
- Round nematodes or white worms are the most common parasites. There are mature worms reaching 10 centimeters in length. The most common nematodes are hookworms. They are usually less than 2 centimeters in size and are found in the small intestine. Roundworms feed on the blood of an infected animal and can cause life-threatening anemia.
Roundworms (nematodes)
- Flat , these include trematodes or flukes, they infect the lungs and liver. When infected with this type of worm, sometimes pets do not show signs of illness at all. The worms that cause paragonimiasis migrate to the lungs and destroy lung tissue. In this case, the animal has a cough. Opisthorchiasis larvae parasitize the liver, disrupting its full functioning. They can also colonize the pancreas and gallbladder.
- Tapeworms usually reach up to 70 centimeters and consist of multiple segments. The cat's body in this case is usually used as a temporary host. Animals usually get sick from eating a sick animal. Tapeworms can be detected when examining your pet. Small segments of a parasite that looks like rice are sometimes found on the fur near the cat's anus.
Tapeworms (cestodes)
Roundworms are usually small in size, but can cause serious harm to the animal, since they are found in the body in large quantities and affect not only the intestines, but also the liver and esophagus.
Find medications for parasites
This service is a small help in finding cures for parasites. To start using it, select the type of parasite. If you don’t know what kind of parasite you are infected with, this parasite identification tool will help you by symptoms.
How to understand that a cat or kitten has worms
If your cat experiences changes in appetite, its behavior is alarming, or typical symptoms of the development of parasites in the body have already appeared, you should consult a veterinary clinic. It can be difficult to understand on your own that a cat is infected, especially in the initial stages. After the doctor examines the animal, special tests will be prescribed to accurately diagnose the animal’s condition and determine the types of worms.
The following studies are practiced in veterinary medicine for cats:
- Helminthoovoscopic methods. Analysis of excrement or smear for the presence of parasitic eggs;
- Helmintholarvoscopic methods. They are divided into separate types (studies of samples of feces, tissues and organs), help to detect helminth larvae and the parasites themselves;
The main material for testing is animal excrement, a smear, but other tissues, secretions of internal organs, and saliva can be examined. Tests make it possible to accurately diagnose the presence of infestation and identify the type of worms. If diseases of the internal organs are suspected, including those caused by helminths, an ultrasound and blood test are prescribed.
How to identify worms yourself
There are obvious signs of worms multiplying in the animal’s body, and you can try to diagnose the problem yourself. So how can you tell if your cat is infected with worms?
We recommend paying attention to symptoms such as:
- Developmental delay , which is typical for kittens, they grow poorly and do not develop enough;
- Wool quality. If it is dull, or there is loss of it, then you need to reconsider your diet, add vitamins, and conduct diagnostics, including for the presence of parasites;
- Problems with bowel movements , stools are too loose, frequent, or there is prolonged constipation;
- Despite the cleanliness of cats, constant licking of the anus should alert you;
- Impurities form in the eyes ; if they are removed, they form again in a short period;
- The gums and mucous membranes become whitish. This is a sign of anemia caused by parasites;
- Frequent vomiting. If the cat vomited once, then perhaps this process was provoked by fur or a fragment of food, but frequent reactions are symptoms of a developing pathology or worms;
- Unnatural abdominal shape, barrel-shaped bloating;
- Structure of feces. Blood, mucus, or the worms themselves appear in the stool.
If you find worms in your cat, you need to contact the clinic to select the optimal anthelmintic drug. Since there are different types of worms, there are differences in their treatment.
At home, it is difficult to accurately determine which parasites an animal needs to be rid of. In addition, many diseases of internal organs, pathologies affecting the immune system, and improper care and nutrition of the cat have similar symptoms.
Main long worms in cats
Roundworms
In most cases, cats are diagnosed with infection with nematodes such as hookworms and toxocaras.
- Hookworms are small worms up to 1 cm in size. They feed on the host’s blood, leading to anemia and making many wounds in the intestinal walls with sharp teeth. Several dozen of these helminths can lead to the death of a small cat in a matter of days;
- Toxocaras are the causative agents of toxocariasis, white, thin worms reaching a maximum length of 20 cm. They take away useful substances from the cat, causing vitamin deficiency and exhaustion. With severe invasion, they can completely block the intestinal lumen. In young animals whose intestines are too small for such parasites, the intestines may rupture.
Toxocara
Tapeworms (cestodes)
Cestodes are long flatworms, the length of which can reach up to 70 cm. The bodies of cestodes consist of numerous segments, each producing larvae. Tapeworms parasitize the walls of the small intestine.
Detection of diseases caused by tapeworms is much easier, since segments that secrete helminths can often be found near the anus.
- The causative agent of alveococcosis is alveococcus. Small worms, their length does not exceed 1-4 millimeters. They parasitize the intestines.
- Cucumber tapeworms that cause dipylidia reach 20-30 cm in length. They parasitize the intestines.
Flatworms (flukes)
Flatworms in cats are quite rare. Trematodes are often called flukes due to the suckers that are located on their bodies.
Trematodes are white thread-like worms that attach to the intestinal walls using suction cups, causing mechanical damage to the mucous membrane and also have a toxic effect.
Trematodes are much less common than the two previous types of helminths, but it is worms of this species that pose a mortal danger to cats, as they are capable of destroying internal organs and tissues. They parasitize not only the intestines, but also the liver, bladder, and lungs.
- The pulmonary fluke causes paragonimiasis. It reaches 0.3-1 cm in length. It parasitizes the animal’s lungs, forming cysts and destroying lung cells.
- The liver fluke (cat fluke) up to 5 mm long causes opisthorchiasis - a dangerous disease that affects the liver and gall bladder.
What to do if your cat has white worms in his stool?
› Veterinary
Science has proven that 30 types of different helminths can parasitize a cat’s body. Some individuals spend their entire lives inside the animal, while others are forced to leave the body to complete their development process. Usually, with a small number of parasites, the pet does not experience discomfort; problems appear when they migrate or actively reproduce.
Let's find out what types of worms can be found in a cat's feces and how to properly carry out deworming.
What types of white worms can be found in a cat’s feces?
While cleaning a cat's litter box, owners sometimes find white worms (living or motionless) in their feces. These are worms. They are flat (cestodes) and round (nematodes). It is quite easy to distinguish them from each other.
Cestodes (found in stool) look like cucumber seeds or grains of rice and only move for a few minutes. But nematodes look like spaghetti and are able to move for quite a long time.
Cestodes (white flat worms)
Cestodes or flatworms are a large group of parasites that are found in different animals. In cats, the most common are Dipylidia, Alveococcus, Diphyllobothria and Echinococcus. In feces, two types of worms can most often be found, which cause Diphyllobothriasis and Dipilidiosis.
They look like small (5-10 mm) white oblong inclusions that move along the surface of the feces. People mistakenly believe that these are adult worms, and if they have left the intestines, then nothing needs to be done to the cat. This is the main mistake.
The appearance of white worms in a cat’s feces means that a parasite up to 70 cm long has settled in the animal’s intestines.
It has reached puberty, actively reproduces and secretes lower segments with fertilized eggs (in parasitology they are called “segments”). Moreover, he does not need a second individual, these worms are bisexual.
Hermaphroditism (the simultaneous presence of male and female reproductive organs) is a distinctive feature of cestodes.
You can find white flat worms in a cat not only in the feces, but also around the anus, stuck to the fur, or when segments accidentally fall out of the animal’s anus.
Important! Worms that are in the cat’s body secrete special proteins that reduce the activity of the enzyme (trypsin) in the cat’s digestive juices. This way the helminths are protected from digestion and can live from several months to 1 year.
Types of white worms (Dipylidium, Echinococcus, Alveococcus, Diphyllobothrium) in cats
- Dipylidium, or cucumber tapeworm, enters the cat's intestines when an infected flea is accidentally ingested. When an insect is digested, a worm larva emerges, which attaches to the wall of the stomach and actively grows.
She absorbs nutrients from food throughout her body. After the helminth reaches maturity, the process of formation of cocoons with eggs begins, which are located in the lower parts of the worm’s body. Then the white filled segments bud off and come out with feces.Next, the eggs are eaten by flea larvae and the process is repeated.
The disease in cats caused by the cucumber tapeworm is called dipylidia.
There is a danger to humans only if an infectious flea is swallowed (in adults this is practically impossible, but in small children with close contact the risk of contracting dipylidia is much higher).
- Diphyllobothrium is a parasitic worm that is acquired by cats when they eat raw fish. During the digestion process, a white worm larva emerges from the fish and attaches to the wall of the animal’s small intestine. She lives there for 3-4 weeks and grows up to 1.5 m. During the period of its life, the long helminth secretes cocoons of eggs, which are released with the cat’s feces. After a month, the parasite completely leaves the body during vomiting or defecation.
Diphyllobothrium is also dangerous to humans and other carnivores. Their worm grows up to 10 meters with a lifespan of up to several years.
- Alveococcus is a small parasite, infection occurs by eating infected rodents. The worm larva penetrates the small intestine of the cat and grows for 3 months, reaching up to 5 mm in length, then forms segments with eggs, which break off as they mature and come out with the animal’s feces. In the environment, alveococcal eggs are preserved due to the formation of fine bubble foam, which attracts rodents. If a person accidentally eats grass with invasive foam, then tumor-like infiltrates (a vesicle with the head of a worm) are formed in the liver with the possibility of metastasis to the brain, lungs, and other organs. Infection leads to various disorders in the body, including death.
- Echinococcus is a small white worm, the size of which in the mature state does not exceed . A cat can become infected in two ways: by eating an invasive rodent (with an egg hatching into a worm larva inside) or by ingesting worm eggs from the grass. Depending on this, there are two options for the development of the disease. In the case of eating a rodent, the mechanism will be similar to alveococcosis. If a cat swallows Echinococcus eggs from the grass, then bubbles with worm heads will form in the internal organs of the animal, which will remain underdeveloped, but will bring a lot of painful sensations to the pet. In humans, infection proceeds similarly.
Appearance of worms in cat feces
All feline cestodes are united by external similarity in body structure. These are long, segmented white helminths with suckers that differ only in size.
What do segments of white flatworms look like in a cat’s feces:
Name of the parasiteSize of an adult wormSize of a segment with eggsAppearance of a segment with eggsVisualization of worms in feces
| Dipylidium | 30-70 cm | 1-1.5 cm | Oval (like a grain of rice) | Naked eye |
| Diphyllobothrium | 100-150 cm | 1-1.5 cm | Short, rectangular | Naked eye |
| Alveococcus sexually mature | 0.5 cm | less than 1 mm | Oval | Under a microscope |
| Echinococcus sexually mature | 0.5-0.7 cm | less than 1 mm | Oval | Under a microscope |
A distinctive feature of feline cestodes is the short time period of motor activity of individual segments that were found in the feces.
Usually, after a few minutes, the energy reserve of the white segment runs out and it stops moving. However, the parasite eggs inside remain viable for a long time.
Symptoms of the disease
External clinical manifestations of cestodiasis in the early stages are usually absent. As the worms grow and develop, they release toxic substances that are absorbed into the cat’s blood and lead to increasing intoxication of the body.
Vomiting appears, uneven stools with an admixture of white worms in the feces, taste perversions, the feeling of hunger increases, and the body is depleted. Sometimes toxins affect the cat's nervous system, leading to seizures.
Treatment and prevention
To successfully cure worms, it is necessary to deworm the cat with veterinary drugs based on praziquantel. This active substance is included in the preparations:
- "Milprazon" (meat tablets for kittens and cats);
- "Milbemax" (chewable tablets for large and small cats);
- "Kanikvantel" (1 tablet with meat flavor, designed for 10 kg);
- “Cestal cat” (liver-flavored tablet – 4 kg);
- "Drontal cat" (4 kg tablet);
- “Profender” (drops on the withers);
- “Dironet (tablets, suspension and drops on the withers);
- "Prasitel" (tablets);
- "Fenpraz" (tablets with royal jelly).
For intestinal cestodias, a double dose of the drug with an interval of 10-14 days is usually sufficient. For greater effectiveness, medications are given in the morning, before feeding the cat.
After the animal recovers, the course of anthelmintic therapy will need to be repeated every 3 months to prevent re-infestation.
Important! If an animal has been diagnosed with cystic echinococcosis (bubbles in the internal organs), then the doctor prescribes complex treatment with special drugs.
Also, the possibility of surgical intervention cannot be ruled out, since cysts are constantly growing, putting pressure on surrounding tissues and impairing blood circulation.
In addition, the bubble with parasites may burst, the fluid will spread in the cat’s body, which will further aggravate its condition.
Nematodes (white roundworms) (Toxocara, hookworm, uncinarium)
Roundworms (nematodes) also infect the gastrointestinal tract of cats, and their favorite location is the small intestine. Unlike white tapeworms, round worms reproduce and live inside the cat for several generations.
They can fill the entire intestine, even to the point of developing obstruction. Nematodes do not always leave the cat's gastrointestinal tract along with feces. They secrete eggs, the presence of which can be easily determined in the laboratory.
If your cat's stool contains thread-like white worms that look like spaghetti and squirm and make circular movements, then these are most likely nematodes. The intestines are clogged with parasites, they become crowded, some of the individuals pass out along with the feces. There are also frequent cases of nematodes coming out with vomit.
Types of parasites
- Toxocaras are thin, long white worms (6-10 cm) with a sharp end. It most often affects kittens aged 1-3 months who eat invasive raw meat, rodents, flies, or become infected in utero. After digesting the food eaten, Toxocara larvae emerge from the eggs and move into the kitten’s lungs.
After some time, the grown worm larvae irritate the walls of the lung, cough up and are swallowed again. Worms actively multiply in the small intestine of a kitten. When the intestines empty, the eggs come out and settle on the grass, where they are eaten by mice, livestock or insects. Toxocariasis is dangerous for both cats and humans.Worm eggs can be found on furniture, children's toys, and can also be carried by flies. When eggs are ingested in the body of a child or adult, the larva does not develop into an adult, but migrates to other organs and becomes encapsulated, which causes a number of ailments.
- Hookworms are smaller worms 2-3 cm long.
They feed on the blood of kittens and cats and can cause anemia and death of young animals. The location of hookworm is the small intestine. Kittens become infected with worm eggs through contact with sick animals, food and water. The larvae grow, injure the intestinal mucosa and cause swelling.When actively multiplying, hookworms can lead to complete blockage and obstruction of the intestine. Due to the massive accumulation, some of the worms die, which often leads to intoxication with decay products. Against the background of existing anemia, this process ends in the death of the kitten.
- Uncinaria are small white nematodes 1-1.5 cm in size.
They cut through the mucous membrane of the small intestine and feed on blood. The life cycle is similar to hookworms. Life expectancy in a cat’s body is up to 2 years.
What do worms look like in cats?
Roundworms in cats are white with a yellowish tint. Visually, they are similar to thin fishing line or spaghetti pasta. They have a hard shell. The length of adult individuals ranges from 1 to 10 cm. The body is not segmented.
Signs of the disease
Common signs of increasing roundworm infestation include:
- poor appetite;
- a swollen, dense and painful abdomen in kittens (due to food refusal);
- weight loss;
- anemia, which is manifested by pallor of the mucous membranes;
- liquid cat feces (sometimes mixed with blood or white worms);
- vomiting of live helminths (with blockage);
- hyperthermia;
- dull, tousled fur.
- cough (during Toxocara migration).
Important! In severe stages of infestation, the intestinal walls may rupture and worms may escape into the abdominal cavity, which leads to internal bleeding and death of the cat.
Prevention and treatment of worms
Specific treatment of nematodes in kittens and cats is carried out using veterinary anthelmintics based on milbemycin, pyrantel, and moxidectin. But due to the widespread prevalence of mixed infestations (when round and tapeworms are found in one animal), veterinary companies produce broad-spectrum medications.
Anthelmintics contain 2-3 active components, one of them kills nematodes, and the second destroys cestodes. Examples of medications are given above.
The course of treatment for nematodes includes several stages:
- Getting rid of worms by taking medications 2-3 times, with an interval of 7-10 days (if there are not too many worms).
- Antitoxic therapy, which is aimed at removing decay products from dead worms in the intestines (injection solutions).
- Vitamin therapy.
- Gentle therapeutic nutrition.
If there is a complete blockage of worms and obstruction of the small intestine in a cat, veterinarians strongly recommend surgical treatment. The operation is abdominal and is performed under general anesthesia.
As measures to prevent the development of nematodes in cats and the safety of young animals, it is necessary:
- treat animals from external and internal parasites before mating;
- It is mandatory to carry out routine deworming of pregnant cats in the last third of pregnancy;
- Treat lactating cats for helminths 2-3 weeks after birth (carefully choose the drug);
- carry out preventive treatments for kittens starting from 3 weeks of age 2 weeks before vaccination;
- treat adult healthy pets for worms (regardless of the conditions of keeping and walking) 4 times a year, for fleas - monthly.
Every owner wants to see their cat healthy, well-groomed, affectionate and playful. However, showing excessive care and concern for their pet, owners often neglect the recommendations of doctors on preventive measures for deworming cats.
The reason is that many people mistakenly consider their home to be sterile. But by feeding your cat a tasty meat tablet against worms once a quarter, you can protect all family members from various ailments.
What to do if your cat has white worms in his stoolLink to main publication
Source: https://litbro.ru/veterinariya/belye-glisty-v-kale-u-kota
White long worms in cats and their symptoms
Routes of infection, carriers: Small crustaceans of fresh water bodies, raw fish, rodents. Fleas and lice eaters.
Name of the disease and characteristics of the pathogen:
- Diphyllobothriasis. White worms, sometimes with a brownish tint. The length of the parasite reaches 1-1.5 meters in cats and up to 10 meters in humans. These helminths parasitize the intestines.
Diphyllobothriasis - these helminths parasitize the intestines
Description of symptoms: Dull fur, decreased appetite. Constipation and diarrhea, vomiting containing blood. Without treatment - anemia and convulsions.
Drug: Fenasal, Praziquantel, Fenalidon, etc.
- Dipylidiasis. A grayish helminth, 20-30 centimeters in length. Lives in the intestines.
Description of symptoms: Decreased appetite, rumbling in the stomach, nausea and vomiting, loose stools.
Drug: Skoloban, Fenasal, Praziquantel, etc.
- Alveococcosis. Small worms are 1-4 mm. They live in the intestines.
Alveococcosis lives in the intestines. In the later stages, it manifests itself with hepatopulmonary symptoms and leads to death.
Description of symptoms: It proceeds hidden for a long time. In later stages, it manifests itself with hepatopulmonary symptoms and leads to death in humans and animals.
Drug: Filixan, Cetovex, Fenasal.
Routes of infection, carriers: Enter the body through the skin or esophagus.
- Hookworm. A blood-feeding parasite 2 mm long.
Hookworm is a blood-feeding parasite 2 mm long.
Description of symptoms: Decreased appetite, activity. Loose stools, vomiting. The animal drinks a lot. Anemia, cough.
Drug: Pyrantel and drugs based on it. Fembendazole, Febantel.
- Toxascariasis. Roundworms usually reach a length of 3 to 5 cm. They live in the intestines, sometimes in the gall bladder, liver and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Toxascariasis - live in the intestines, sometimes in the gallbladder, liver and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract
Description of symptoms: Decreased appetite, activity. Loose stools, vomiting. The animal drinks a lot. Anemia, cough.
Drug: Pyrantel, Fembendazole, Ditrazine.
Routes of infection, carriers: Shellfish, fish from rivers when eaten and from coastal vegetation.
Name of the disease and characteristics of the pathogen:
- Paragonimiasis. Parasites 0.3-1 cm live in the lungs, forming cysts with destruction of organ tissue.
Paragonimiasis - parasites 0.3-1 cm live in the lungs, forming cysts with destruction of organ tissue
Description of symptoms: Cough, loss of appetite. Increase in temperature (not always). Vomiting with foam, loose stools.
Drug: Praziquantel.
- Opisthorchiasis. A helminth about 0.5 cm long that lives in the liver and destroys its tissue.
It can parasitize the gallbladder and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Opisthorchiasis is a helminth about 0.5 cm long that lives in the liver and destroys its tissue.
Description of symptoms: Painful abdomen, loss of appetite with episodes of bulimia, vomiting with bile, loose stools. Body temperature is increased
Treatment: comprehensive, individual.
Note! The described symptoms are not absolute signs of each specific type of helminthiasis and depend on the severity and duration of the disease, as well as on many other factors! If the infection is latent, its signs may not appear at all, which does not mean that the animal does not need treatment.
Take a test for worms
Treatment
What to do if the owner suspects worms in his pet? At the first sign of worms in cats, you should contact your veterinarian. Since infestation indicates that there are many parasites in the pet’s body. It is not recommended to treat your pet with medications at home.
First, the veterinarian will take tests to identify the type of parasite, and then prescribe the only correct medications that will help cure the cat. For example, if you give an animal a medicine that helps eliminate tapeworms, it will not be effective against other types of parasites.
List of drugs
Usually the veterinarian prescribes:
- Pirantel. This is a mild remedy against roundworms. It does not kill the parasites inside the cat, and only immobilizes them. Thus, it does not lead to intoxication of the body and is safe. Worms can be found in your pet's feces after defecation.
- The drugs praziquantel, fenasal, and phenalidone are effective against infection with flatworms.
- If you treat roundworms with detrazine or fembendazole, you can quickly achieve the desired result.
- Praziquantel helps kill the fluke that attacks the lungs.
- Milbemax is effective against roundworms.
- Complex treatment under the supervision of a veterinarian is necessary if the animal is infected with opisthorchiasis, which affects the liver.
Basic rules for taking medications
- Medicines should be given to the cat in the morning before meals.
- It is necessary to strictly observe the dosage of the drug.
- Sometimes, as prescribed by the veterinarian, before giving the cat medicine it is necessary to cleanse the intestines.
- Medicines in tablet form should be crushed and placed on the root of the tongue. Thus, the pet will be forced to swallow it.
- It is quite effective to add medications to food.
- If an animal behaves aggressively, it must first be restrained so that it does not injure itself.
After 14 days, the cat needs to be given the medicine prescribed by the veterinarian again.
General signs of helminthic infestation
Consequences of helminthiasis
Tapeworms can cause serious illness in cats.
- Diphyllobothriasis. The disease is caused by long helminths of the genus Diphyllobothrium (wide tapeworm), reaching 1-2 meters. Cat worms can live for several months. It can exist in the human body for up to 20 years.
- Symptoms of the disease include nervous system disorders. The cat becomes irritable and aggressive. Signs of anemia appear, stool changes, nausea and repeated vomiting occur. There may be discharge from the eyes, the coat loses its smoothness and shine.
- Infection with diphyllobothriasis occurs by eating raw fish or thermally poorly processed fish dishes. The incubation period lasts up to one month, during which there may be no signs of the disease.
- Dipylidiasis. The disease is caused by flatworms of the genus Dipylidium (cucumber tapeworm). The color is gray-white or pinkish, the length can be about 30 cm. The habitat is the intestines. Mature segments of the parasite resemble cucumber seeds.
- A cat can become infected from intermediate hosts - fleas and lice-eaters. During the illness, there is loss of appetite, weight loss, vomiting and lethargy. The cat becomes nervous and irritable.
- Alveococcosis. Caused by small worms of the genus Alveococcus. Alveococci have a length of no more than 4 mm. From the moment the larva enters the body until it matures into a sexually mature individual, 3 months pass. The functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted. The animal suffers from diarrhea, which is followed by constipation. Vomiting and sudden weight loss occur. A cat can become infected if it eats a sick rodent.
- Hydatigerosis. The causative agent of the disease is the cestode strobilocercus, which parasitizes the small intestine. The length can reach 60 cm. The cat looks weakened, lethargic, eats poorly, and is losing weight. Diarrhea and vomiting occur. Infection occurs by eating rodents.
Why are white worms found in feces, or how does pinworm infection occur?
- Parasites are transmitted through dust that contains their eggs;
- objects touched by a sick person;
- eggs can be spread by flies and cockroaches. The female, entering the body, mates with the male, migrates to the large intestine, where it receives nutrients and lays eggs. After a month, the female moves into the rectum, then crawls out of the anus, lays up to 15 thousand eggs in the anal area, which mature after 6 hours.
This process is usually accompanied by itching. Accordingly, a person scratches the anus, contributing to the further spread of helminths. From under the nails, parasites get onto objects, food, and the hands of other people, especially for children who do not always follow the rules of personal hygiene. Eggs remain on underwear, clothes, bedding, and towels, which contributes to their spread.
That is why treatment of enterobiasis is difficult, because you need to get rid of not only helminths, but also treat all the things that the patient has come into contact with.
General symptoms of worm infestation
If you are not too lazy to regularly prevent helminthic infestation and constantly monitor your pet, then even in a sick animal the signs of the disease will not be very pronounced, since worms in domestic cats will not have time to reproduce in huge quantities.
If you neglect medical measures, you can allow the animal to become rapidly damaged by worms, and often even several types. Sometimes this leads to the death of the pet.
Known general signs of helminthic infection are: dull and falling out hair, conjunctivitis of the eyes, alternating constipation and diarrhea, lethargy, tight abdomen, non-specific odor from the mouth.
The disease clearly affects the animal’s appetite: some cats begin to eat a lot, but do not gain weight; Other pets refuse to eat, choosing only their favorite treats.
How can you become infected with worms?
Let's summarize where worms come from in a domestic cat. Firstly, being a predator, it eats prey (birds, rodents) along with parasite eggs. Even after catching a beetle or fly, an animal can become infected with any helminths.
Secondly, the cat swallows helminth eggs along with raw meat, raw freshwater fish, river water, so it is better to protect pets from such a diet. Third, most worms are transmitted through feces.
Fourthly, when a cat licks itself, it swallows the eggs of parasitic worms that stick to its fur and paws even at home, because people bring parasites into the house on their shoes and clothes. A person can become infected with helminths from a cat, most often through saliva and feces.
Symptoms of animal infection
At home, it is impossible to diagnose the presence of worms yourself, since sometimes the symptoms can be vague. The condition of the animal depends on the type of parasite that infected the body. The cat must be shown to the veterinarian, he will take the necessary tests. For example, the exact type of parasite can be accurately detected in stool.
You cannot engage in self-diagnosis, since it is quite problematic to determine the type of worms yourself.
How dangerous are worms for cats and humans?
It can be assumed that what kind of worms are in cats, such parasites are transmitted to the owner. The danger of worms that have settled in the body is that they actively feed on blood, lymph, and tissues of various internal organs, which leads to the inevitable depletion of the patient’s vitality.
Any parasitic worms poison the body of animals and humans with toxic substances that are a consequence of their vital activity and death. Decomposition products also lead to allergic reactions and severe poisoning. In addition, parasites use suction cups and fixing hooks to injure organs, causing vascular ruptures and necrosis.
The appearance of symptoms of helminthic infestation, such as constipation and bloating, may indicate intestinal obstruction.
If the lesion occurs in a cat, then it may die, since a huge number of worms block the lumen of the poor animal's intestines, and it cannot empty it naturally. And these are not all the reasons why worms in cats are so dangerous; In any case, treatment should be immediate.
White worms in a cat’s feces: what to do and what to do?
The presence of parasites in an animal’s body is a pressing problem for domestic cats. The fact whether the pet is walked on the street or lives exclusively in the apartment is not significant.
An animal can become infected by eating raw meat or poorly cooked fish, licking scraps from a trash can, or simply lying among street shoes. White worms in cats are often found even in healthy-looking animals. When faced with a problem, the owner must treat the pet and take preventive measures.
What to do if your cat has white worms?
Worms enter the animal’s body through the digestive tract, which is where their spread begins. By sticking to the walls of the mucous membrane, worms cause local irritation, erosion, and minor hemorrhages. Feeding on the host's blood, the parasites take away some of the nutrients. Toxins released during the life of worms poison the body.
Larvae or worms can be seen in the cat's feces and on the fur around the anus. Sometimes the worm hangs directly from the anus.
The animal must be shown to a veterinarian. A stool test for worms may not be informative. Therefore, a specialist does not always prescribe such a study. Determining the type of worms is important when choosing treatment.
The pathogen is determined based on the clinical picture and etiology (when the doctor, based on the stories of the pet owner, determines what events preceded the infection, which will indicate to him the source of infection and the type of pathogen).
What type of worms are these?
- round (nematodes);
- tape (cystodes);
- flat (flukes or digenetic flukes).
Why is it important to determine the type of pathogen? Because one drug may be effective against only one class of worms and not affect others.
The presence of white worms in an animal’s feces indicates one of the two most common diseases of parasitic origin:
- In the first case, the causative agent is Toxocara, a type of cat roundworm.
- In the second - dipylidium or cucumber tapeworm.
Toxocariasis
Feline toxocara most often affects kittens under three months of age. In adult animals, the worm larvae become encapsulated and do not develop until sexual maturity. The owner may notice thin, long white worms ranging in size from 6 to 10 cm in the kitten’s stool. This type of helminth is a nematode. Externally, the parasite resembles a thread-like formation with a pointed end.
The infection can be transmitted from mother to fetus, in which case the kittens are born already infected. Reservoir hosts (capable of transmitting infection) can be various animals (for example, rodents) and insects, including earthworms and flies. A kitten becomes infected through contaminated objects, after swallowing insects, eating raw meat or rodent carcasses.
In the pet's intestines, worm eggs mature into larvae and migrate to the lungs. From there, they cough up and return with saliva to the gastrointestinal tract, where they transform into adults capable of laying eggs.
Characteristic signs of the disease:
- dull coat;
- weight loss;
- apathy;
- sour eyes;
- bloated stomach;
- coughing;
- temperature increase;
- vomiting, diarrhea mixed with blood.
A severe degree of infestation can cause the death of the animal. The helminthic mass clogs the intestinal lumen, impairs the passage of food, and in the worst case, leads to rupture of the intestinal walls.
Danger of infection for humans
Toxacara cat eggs are ubiquitous in the environment. Their microscopic dimensions (60-90 microns) do not allow them to be visualized without special equipment. They may be present on the animal's fur, getting there during licking.
Young children are especially at risk of infection because they spend a lot of time on the floor, often pick up and lick dirty objects, and play in a dirty sandbox. For adults, the infection awaits on unwashed fruits and vegetables. Toxocara can be carried by ordinary flies that have previously sat on a contaminated surface.
Humans and other mammals are reservoir hosts for Toxocara, in which the worm cannot develop to a sexually mature individual.
However, in the intestines, eggs are able to turn into larvae and migrate through the bloodstream to the lungs, liver, brain, eyes and other organs.
Having reached its habitat, the larva forms a dense capsule around itself, which clogs the blood vessels and disrupts blood circulation in the organ.
In humans, infection is often asymptomatic. The parasite will begin to manifest itself only when the larvae migrate into organs and tissues.
The extent of the disease will depend on the ability of the immune system to resist infection.
Due to an insufficient response, in rare cases, serious neurotic pathologies or diseases of the visual organs may develop, leading to complete blindness.
Toxocara can certainly be called dangerous to humans, but basic hygiene rules, such as washing hands before eating and handling food, greatly reduce the risk of infection.
Dipylidiasis
The disease is caused by a tapeworm, the cucumber tapeworm. In the body of an animal, the parasite reaches a length of 50 cm. Single individuals do not cause much discomfort. However, with a massive accumulation, worms can cause intestinal obstruction and lead to the death of the cat.
The disease is characterized by general symptoms such as bloating, indigestion, emaciation and loss of appetite. Toxins released by the worm can provoke neurotic disorders in the cat. Pets with a severe degree of the disease experience seizures resembling epileptic seizures.
The animal becomes infected mainly from fleas. The worm's segments (individual segments of its body) are released into the environment with the pet's feces. Outwardly, they look like cucumber seeds, reaching 5-6 mm in length.
Small white worms in a cat can stick to the fur from the anus, but most often the owner discovers the parasites by cleaning the litter box after the pet.
Movable white flatworms will be visually detected in the feces.
The segments of the worm are a shell that hides a cluster of eggs. After the wall is destroyed, the eggs come out. They are partially found on the animal's fur, but in this state they are not dangerous.
The flea, being a larva, swallows eggs, from which the parasite develops in the body of the insect to a cysticercoid - an invasive stage (capable of causing infection). The animal, while licking itself, swallows an infected flea. In the cat's body, the parasite develops into an adult, gaining a foothold in the intestines.
Treating white worms in cats
For the specific treatment of roundworms in kittens, drugs based on mebendazole and albendazole are used. Veterinarians often advise giving a cat the human drug “Vermox” in tablet form at a dose of 20 mg/1 kg of body weight for three days. The medicine is fed on an empty stomach once a day.
The broad-spectrum drug Milbemax . Its main components are Milbemycin oxime and Praziquantel, which are active against most common nematodes and cestodes.
The medicine is available in tablet form in a separate dosage for kittens and adult cats. The dose is calculated based on the proportion of 2 mg Milbemycin oxime and 5 mg Praziquantel per 1 kg of animal weight. The medicine is given once with food.
Prevention of re-infection
Helminthiasis is a dangerous disease for any animal. Worms from cats can be transmitted to humans. Compliance with basic hygiene rules will protect against infection, and regular prevention will keep your pet healthy.
Source:
Deworming (sorry, about worms...)
Pregnant animals are prescribed in the last third of pregnancy, lactating animals - 2-3 weeks after birth, only those drugs that have appropriate indications in the instructions (for example, Milbemax), otherwise they can harm the health of the offspring.
It would be correct to drive away worms 10-14 days before mating. If this has not been done, kittens should be wormed no earlier than 21 days after birth.
Unfortunately, infection of kittens with worms can even occur in utero, during childbirth and breastfeeding.
If the animal has a severe
helminthic infestation (the kitten was picked up on the street), parasites are visible in the feces, the animal is vomiting worms, then anti-worm medications should be given under the supervision of a doctor, since the simultaneous death of a large number of helminths can cause poisoning of the body and there will be a need for an IV.
Source: https://zoomak.ru/prochee/belye-chervyachki-v-kale-u-koshki.html
Treatment by a veterinarian
Treatment of worms in cats should be carried out under the guidance of a veterinarian. It cannot be done independently. Despite the fact that there are special deworming products for cats on the market that can be quite effective, they can also cause additional digestive disorders in the animal and may not completely free the cat from worms.
Before you try to rid your animal of helminths on your own, you should definitely consult a veterinarian so as not to harm your pet and quickly cure it of parasitic worms. After all, sometimes you don’t even know the correct diagnosis, what worms look like in cats, let alone medications. And the situation is quite dangerous, because if there are too many large individuals that die and decompose, the animal can die.
Treatment with folk remedies
When resorting to self-treatment with folk remedies, you act at your own peril and risk. It is worth noting that some veterinarians prescribe traditional methods of treatment when it comes to saving an animal whose body may not withstand additional intoxication from anthelmintics.
First, let me tell you that under no circumstances should it be used against worms in cats. This is celandine, extremely toxic to the cat’s body, but it will not harm worms, and in case of an overdose it can lead to death.
In general, all recommendations for treating cats for worms with folk remedies are quite controversial, and they cannot be called completely reliable. Basically, these are analogues of “human” means.
- Pumpkin seeds are the most common remedy, as their inner shell contains the amino acid cucurbitin, which is poisonous to flatworms. Pumpkin seeds are safe for cats and other animals. It is important that the seeds are raw (dried but not roasted). The seeds (for an adult cat, a dose of 5 g) must be peeled from the hard shell (leave the inner film) and crushed well to a powder, thoroughly mixed with lard (pork fat) or refined sunflower oil and force-fed to the animal for 5 days;
- Onion water is the second no less controversial, but relatively safe method against worms. Cut the onion into 4 parts, pour boiling water (250 ml), drink it to the cat in the morning on an empty stomach for a week. However, we warn you that onions are toxic to cats, and such treatment may lead to cat poisoning;
- Many experienced cat owners recommend giving a decoction of fennel or chamomile The cat is unlikely to drink the broth on its own, and then you can either force-feed it or add a little peppermint to the broth;
- A water infusion of tansy is a method that will not harm (but it is not a fact that it will help). Dried flowers should be poured with boiling water (200 ml) and left in a warm place for an hour. The resulting infusion is filtered and force-fed to the cat 2-3 times a day. For an adult, it is enough to inject up to 2.5 cubes (from a syringe without a needle) at one time. After drinking the infusion, the cat should not be fed for an hour. Treatment is carried out within a week;
- Enemas with carrot juice . Heat the juice squeezed from grated carrots to a temperature (38–39°C) and insert it into the anus. Inject no more than 20 ml at a time. After insertion, the tail should be pressed to the anus and the animal should be held in this position for 10–15 minutes. However, there is no data on the effectiveness of this method.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know:
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ()
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
This service is a small help in finding cures for parasites. To start using it, select the type of parasite. If you don’t know what kind of parasite you are infected with, this parasite identification tool will help you by symptoms.
We recommend reading
Toxoplasmosis in dogs: routes of infection, symptoms and treatment
01/29/202102/01/2021ecoliv94
Worm inspector for cats: instructions for use, cost
01/27/202102/02/2021ecoliv94
Products for cats against ticks and worms: list of the best
01/25/202102/3/2021ecoliv94
Dirofen against worms for cats and dogs: instructions for use, price, analogues
01/25/202102/3/2021ecoliv94