The very mention of worms is an unpleasant topic for most cat owners. But even with the most careful care and proper living conditions, the animal is not immune from parasitic infestation. This fact can poison the life not only of a pet that has accidentally become infected with worms from other animals, but also of the owner, because some parasites pose a danger to people. To minimize the risk of infection, it is necessary to make preventive anthelmintic measures part of regular cat care.
As preventive measures, veterinarians can prescribe broad-spectrum anthelmintic drugs for cats, which have a gentle effect on parasites and minimize harm to the cat’s body during anthelmintic measures. Read the article about veterinary shampoo Doctor, which will help cope with various external parasites in cats.
Helminths and their types
Helminths are worms that parasitize the organs and tissues (most often in the intestines) of animals. The deworming process is a set of measures aimed at eliminating worms from the body.
This process can be therapeutic or preventive in nature. Regular prevention can minimize the risk of parasite infection. Therapeutic deworming is a rather complex procedure, since identifying the symptoms of the disease in a cat can be difficult.
Worms in cats
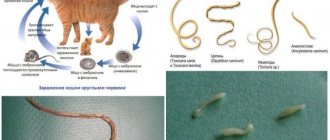
Now a little about what kind of worms cats have and what they look like. Parasitic worms include flatworms or tapeworms (cestodes), flatworms or flukes (flukes), and roundworms (nematodes), which are sometimes called lungworms because they are found in cats and in the lungs. Diseases caused by roundworms are called nematodes, tapeworms are called cestodiases, and diseases caused by flukes are called trematodes.
Thus, the classification of parasites that pose a danger to cats is as follows:
- Flatworms:
- cestodes (tapeworms), in particular tapeworms and tapeworms;
- trematodes (flukes), for example, opisthorchis.
- Roundworms (nematodes):
- roundworm;
- toxocara;
- hookworm.
Most often, cats are affected by tapeworms and roundworms; flukes are much less common.
Nematodes
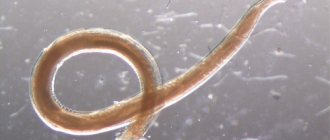
- Nematodes. These are small, thin worms, the spread of which occurs when their carriers come into contact with other animals, eating excrement contaminated with worm eggs, through the milk of a sick mother. Helminths feed on blood, clinging to the intestinal walls of their host. They pose a particular danger to kittens. Humans can also become infected with nematodes. Roundworms are the most common type of worm in cats. Outwardly, these worms resemble spaghetti. Their greatest accumulation is observed in the small intestine. A massive accumulation of parasites provokes blockage of the bile ducts and can even cause intestinal obstruction.
- Toxocars . The length is about 5 cm, they live in the gall bladder, intestines, esophagus and liver. Infection occurs by ingesting helminth eggs or through the womb (for kittens, this type of parasite poses the greatest danger, since intestinal rupture can occur due to the reproduction and growth of worms).
- Roundworms. Externally they resemble white or slightly yellowish laces; grow up to 20 cm in length; with severe infection, some of the adults may come out along with feces.
- Cestodes. The body length of these worms varies from 10 to 80 cm. The body of the helminth consists of a large number of segments (segments). A cat can become infected with them through contact with an intermediate host (for example, by eating a flea or rodent that was a carrier of the cestode). In sick pets, you can notice segments of cestodes that look like grains of rice: they are often found on the fur in the anal area, as well as in the pet’s waste products.
- Cucumber tapeworm. A pet becomes infected through fleas and lice that live on its fur. The body length of the worm is 30 cm or more. The parasite attaches to the intestinal walls using special spines on the scolex, thereby damaging the mucous membrane of the organ.
- Wide tape. These worms can reach 2 meters in length (and in the human body - 11 meters or more). Infection most often occurs through eating raw river fish.
Cucumber tapeworm
Types of lungworms
Pulmonary helminths live, as you might guess, directly in the respiratory tract of sick animals . Three species are widespread in the wild: Aelurostrongylus abstrusus, Paragonimus kellicotti and Capillaria aerophilia.
All of them require intermediate hosts for development, without whose participation a cat cannot be infected. For example, the Aelurostrongylus parasite requires land snails or slugs. Many veterinary reference books say that infection occurs when cats eat them. But in practice, it’s quite difficult to find a cat who would willingly eat slugs.
The situation is that animals become infected by eating small rodents and birds , which are more common eaters of shellfish. In general, if your cat even occasionally walks outside and hunts for someone, he may well get lungworms. By the way, almost all raccoons suffer from lung helminths: they love to eat crayfish, slugs and snails, which is why the “saturation” of their body with parasites can be prohibitive.
Note that the infection is most severe in cats under two years of age. It is in them that helminthic infestation is the most “stressful” due to the huge number of parasites in the organs of the respiratory system. Symptoms depend on the specific type of parasite, the animal’s body response, and other factors. Sometimes the owners may not even realize that there is anything wrong with their pet, while in other cases the cat begins to constantly cough and sneeze, develops an apathetic state, and the animal refuses food.
Worm eggs and infection mechanism
One of the main sources of helminth infection is fleas, which not only cause severe itching of the skin, but also carry worm larvae, which is why it is so important to protect the animal not only from parasitic worms, but also from external parasites.
Helminths pose a threat to both outdoor and indoor cats.
The causes of infection with cat worms can be the following:
- Presence of external parasites (lice eaters, fleas).
- The presence of raw fish or meat in the pet's diet.
- Contact with helminth vectors.
- Infection of kittens in the womb.
Often, even after freezing and washing, contaminated meat poses a danger because parasite larvae still remain in it.
As for river fish, cysts are found quite often and in almost all its species. It is an intermediate host for a large number of parasitic worms.
Symptoms of worms in cats
Signs of the presence of worms in cats largely depend on the type of helminth that affected the animal. Nevertheless, there are general symptoms of helminthic infestation, among which, first of all, it is necessary to note changes in the behavior of a cat with worms: depressed general condition, poor appetite or its complete absence.
Treatment of worms
Painful manifestations can vary in severity, which also depends on the type of helminth and the number of worms in the body. At first, symptoms may be absent or mild.
Commonly observed signs of worm infestation include the following:
- Intestinal dysfunction, which entails nausea, vomiting, alternating diarrhea and diarrhea, the loss of appetite mentioned above (or vice versa, increased appetite). Sometimes you can observe worms in a cat’s vomit; a particularly dangerous case is when a kitten vomits like this.
- Sometimes coughing attacks occur (in particular, when infected with roundworms).
- Dry surface of the nose, dull eyesight, strong discharge from the eyes or nose, yellowness of the mucous membranes.
- Anemia (especially in kittens).
- Faded hair, disheveled hair, hair loss.
- Enlarged liver.
- Particles of helminths or whole worms in the animal’s stool.
- Weight loss.
- Itching and irritation in the anus, the appearance of a rash, hair loss near the anus.
- The appearance of blood clots in fecal matter.
- Severe infestations provoke intoxication of the body, and in some cases, paralysis of the hind legs.
- Noticeable enlargement of the abdomen (hard on palpation).
- Miscarriage or premature birth.
- Developmental delay in kittens.
In many cases, the symptoms of worm infection are similar to those of infectious diseases. Deworming to treat an infection can have serious consequences, including death. Therefore, it is very important to establish an accurate diagnosis through laboratory tests and physical examination.
Weight loss
Thus, even if the disease is mild in your pet, you should immediately consult a veterinarian.
What harm do helminths cause to cats?
Worms cause mechanical damage through their fixation devices (hooks, spines, teeth), chitinous weapons of the outer shell. During the migration of worms, a violation of the integrity of the organs where they are localized occurs (intestinal walls, blood vessels, liver passages, etc.).
A frequent companion to helminthiasis is blockage. A typical example of such a pathology is the blocking of the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract by balls of parasitic worms.
Symptoms of worms in cats. During their life, helminths secrete secretions that cause intoxication of the cat’s body. The negative toxic effect of metabolic products is manifested by lysis (disintegration) of nearby tissues and toxic changes in them.
The decomposition of the parasite as a result of its natural death or under the influence of drug therapy has no less influence on the process of general poisoning, as a result of which secondary or concomitant symptoms of invasion arise.
Helminthiasis largely determines the course of bacterial or viral infections, usually complicating the pathogenic process. Often parasites are the impetus for the manifestation of a disease that is in a dormant state. Tissues injured by helminths become a “gate” for the penetration of microbes into the cat’s body and serve as the beginning of the development of the infectious process.
Treatment of helminthic infestation
Worming cats is a very important undertaking, so before treating for worms, you should decide what is best to give your cat.
In most cases, sick cats are prescribed complex anthelmintic drugs. These dewormers for cats are effective against all types of helminths. But medications can be prescribed that also affect specific types of worms.
Modern medicines have virtually no side effects. However, it is very important to observe the dosage, adhere to the veterinarian’s instructions, and also take into account all contraindications.
Anthelmintics are available in the form of tablets, suspensions and drops. Among the most effective drugs are:
- piratnel;
- drontal;
- prazicide;
- vacationquantel;
- prosit;
- pratel.
To treat lungworms in cats, anthelmintics are used - Stronghold, Advocate, Milbemax.
It is worth noting that helminthic infestation can be represented by several types of parasitic worms at once. That is why it would be preferable to choose a drug with a wide spectrum of effects at any stage of infection.
All of these drugs provide effective treatment for your pet at home.
Drontal
Before using deworming medication for your pet, you should get rid of fleas and other ectoparasites. If this is not done, treatment will be useless, since the source of infection (flea) will again transmit helminth eggs to the animal.
It is noteworthy that there are universal products on sale for eliminating internal and external parasites. They are produced in the form of drops on the withers. In particular, a drug such as Stronghold has proven itself well.
It is necessary to ensure that the cat swallows the dose of medicine completely. To prevent your pet from spitting out the tablet, you can use one of the following methods:
- crush the tablet and mix it with milk, sour cream, pate or other treat that the cat likes;
- you can use a device called a piller to push the tablet into the animal’s mouth;
- crush the tablet into small pieces and dissolve in a small amount of water, and then inject the liquid into the cat’s mouth using a syringe without a needle.
For treatment to be effective, deworming is repeated after two weeks. Severe infestation requires longer anthelmintic therapy. The effectiveness of treatment is monitored through laboratory tests.
There are cases in which it is undesirable to carry out deworming:
- when the cat is severely emaciated and weakened (this condition can be caused by infectious diseases);
- during pregnancy and feeding newborn kittens;
- young age (kittens are at an age when, according to the instructions, the use of an anthelmintic drug is unacceptable);
- the cat is of advanced age (you should carefully read the instructions and consult a veterinarian).
How to find out that a cat has worms if their eggs are not found in the feces
Lungworms are manifested by a cough, but coughing can be a symptom of other diseases. Based on this, the only real way to protect an animal is to prevent helminthic infestation.
This procedure is absolutely painless, and now there are pills that are taken once and not necessarily on an empty stomach. Fleas are carriers of some types of worms, so if you find fleas on a cat, there is a high probability that there are also worms.
Symptoms of worms in cats. To rid a cat of parasites, you need to know what type of worms the animal is infected with. For example, a drug can be effective against roundworms and harmless against tapeworms.
It is advisable to take broad-spectrum drugs under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Consequences and possible complications
By parasitizing the animal’s body, helminths cause significant harm to it, which can lead to dire consequences or complications:
old cat
- Mechanical damage. Worms attach to the intestinal walls and tissues of other organs, thereby compromising their integrity. In particular, by damaging the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, parasites cause minor necrosis and bleeding. A large accumulation of worms clogs the intestinal lumen, which can lead to its rupture and, consequently, the death of the pet.
- Metabolic disease.
- Toxic effects , causing poisoning of the body and allergic reactions. As a result of the vital activity of helminths, substances that are toxic to the host’s body are released. In addition, dead worms decompose. All this leads to significant poisoning of the animal.
- Trophic impact. Worms take some of the host’s vitamins, beneficial microelements and hormones, absorb blood, enzymes and digestive juice. As a result, your cat is constantly lacking essential nutrients.
- Decreased immunity. Through tissues damaged by worms, pathogenic microorganisms enter the blood of an infected cat, provoking inflammatory processes. As a result, various complications arise, since the body, weakened by parasites, is not able to fully resist infectious diseases.
Prevention measures
The following measures will help prevent your pet from becoming infected with helminths:
- contact of a healthy pet with infected animals should not be allowed;
- it is necessary to regularly treat the cat with products against external parasites;
- The cat should be fed with high-quality food and only fresh food, completely eliminating raw fish from the diet;
- It is recommended to store shoes in closed lockers;
- medications for the prevention of helminthiasis are given 2 weeks before the intended mating and vaccination;
- You need to keep the cat litter box and dishes clean.
By following these rules, the owner will significantly reduce the likelihood of his pet becoming infected with worms.