Helminths (parasitic worms) that parasitize the body of pets can live in a variety of vital internal organs: intestines, liver, lungs, heart.
Endoparasites release dangerous toxins, disrupt metabolic processes, weaken the immune system and the body's resistance. At the same time, heartworms in cats from the genus Dirofilaria pose a particular danger to the health and life of furry pets. They belong to the group of cardionematodes (round helminths). The disease is caused by dirofilariasis.
What are heartworms?
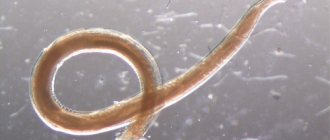
Heartworms are parasitic roundworms 26-40 cm long and about 1.5 mm thick. Females are twice the size of males. They are localized in the body of cats in the pulmonary artery, cardiac sac (pericardium), and aorta. Some species can parasitize the eyes, brain, spinal cord, and peritoneal tissues. Damage to the peripheral and central nervous systems can cause death in infested animals
Important! Heartworms pose a serious danger not only to the health of four-legged animals, but also to humans. Therefore, cat owners must take preventive measures to prevent their beloved pet from becoming infected with dangerous endoparasites.
Cardionematodes, localized in the heart and blood vessels, disrupt blood flow and the functioning of a vital organ .
Blood cannot flow freely to the internal organs, and especially to the lungs, which leads to oxygen deficiency and disruption of cellular metabolism. The vessels become thinner and lose their elasticity. Dirofilariasis refers to anthropozoonosis, a deadly helminthiasis.
General information
In veterinary medicine, this disease is called dirofilariasis . Initially, the disease was distributed exclusively in North America, but gradually it spread much wider. The pathology is caused by helminths from the genus Dirofilaria, which can live in the heart, lungs and large blood vessels. Often the disease is very severe; the sick animal develops severe disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, which in itself can lead to death. In addition, throughout the entire life cycle, parasites secrete a huge amount of toxins, which, due to the “unusual” location of the worm, enter directly into the blood.
Important! They are dangerous for humans, not to mention dogs, cats, ferrets and other wild and domestic animals. Until now, scientists have not yet compiled a definitive list of mammals that may be intermediate and final hosts of parasites.
How does infection occur?
The definitive hosts of cardionematodes are representatives of the canine family (raccoons, wolves, foxes, jackals), including domestic dogs. Wild cats, muskrats, ferrets, noses, and sea lions are susceptible to heartworm infection. Intermediate carriers are mosquitoes of the genus Aedes, Culex, Anopheles .
Cats are parasitized by two types of heartworms:
- D.immitis. The larval forms of this species (imago) live mainly in the right parts of the heart and the pulmonary aorta. They provoke the cardiopulmonary form of dirofilariasis.
- D.repens, dirofillaria tenus. Adult, sexually mature helminths are localized in muscle structures and subcutaneous fatty tissue. They cause a complex form of helminthic infestation and provoke conjunctivitis.
The carriers of cardionematodes are mosquitoes . The bodies of blood-sucking insects are parasitized by the larvae of heartworms – microfilariae. After the bite, their further development over the course of 5-6 months occurs in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the definitive host. Having transformed into sexually mature endoparasites, cardionematodes migrate with the bloodstream to the vessels, lungs, and heart.
The life cycle of adult worms under favorable conditions in the body of an infected animal can range from five months to two years. Microfilariae remain active for 2.5-3 years.
Important! Round heartworms are initially found in the blood vessels that run from the heart to the lungs. If the cat is not given timely treatment, endoparasites move to the heart. The death of heartworms in the body of infected animals leads to the development of serious complications.
It is worth noting that heartworms pose a greater danger to cats than to dogs, which can harbor anywhere from one to 230 individuals. In cats, the vessels have a smaller diameter, so large helminths can cause blockage. The blood is not saturated with oxygen. Anemia, intoxication, and pneumonia develop. Therefore, the mortality rate among cats infected with dirofilariasis is higher than among dogs.
Both street and indoor cats that do not leave their home or apartment can become infected with dirofilariasis. A critical factor can be called mosquito bites, mosquitoes that carry endoparasite larvae. Outbreaks of dirofilariasis are recorded mainly in the summer-autumn season, which is associated with the activity of blood-sucking insects in the southern regions.
The risk group includes weakened, emaciated animals, kittens with a fragile, unformed immune system, as well as furry cats that suffer from viral leukemia or are infected with the feline immunodeficiency virus.
Causes of disease
The disease develops as a result of damage to the cat’s body by two types of helminths:
- Dirofilaria repens . Worms of this type spread in muscle tissue and subcutaneous tissue. This family of helminths causes the skin form of the disease.
- Dirofilaria imitus . Parasites tend to be localized in the heart muscle and pulmonary artery. Helminthization by dirofilaria imitus is extremely dangerous for the animal. Adults can cause blockage of the blood flow, and this is 100% fatal.
The culprits of infection are fleas and mosquitoes. When they bite a pet, they introduce helminths into the bloodstream. Before this, the parasites multiply in the intestines of the insect and gradually accumulate in its oral cavity. After entering the cat's circulatory system, the larvae of the worms spread throughout the body.
Most often, the development of the disease occurs in the warm season - in summer and early autumn, at which time the conditions for their reproduction are optimal. And all because the first mosquitoes appear in late May-early June, and helminths travel through the animal’s bloodstream for 2.5-4 months after infection.
Symptoms of dirofilariasis in cats
If a cat is infected with heartworms, severe helminthic infestation disrupts the functioning of not only the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, but also other internal organs. During their life activity, cardionematodes produce endotoxins, which, given the localization of parasitic worms, enter directly into the blood. The death of helminths can provoke severe intoxication of the body, poisoning .
Dirofilaria in cats worsen the condition of blood vessels, provoke heart failure, hepatitis, pancreatitis, ascites, pleurisy, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, nephritis, conjunctivitis. By parasitizing the lungs, heartworms cause acute inflammation. The liver, kidneys, and spleen are enlarged. Sick cats experience severe muscle pain. When the central nervous system is affected, clonic and tonic convulsions, paresis, and paralysis of the limbs are noted.
Important! Cats, unlike other animals, become infected with heartworms and die very quickly. In this case, characteristic clinical symptoms may be subtle. Often the disease is latent (hidden) in nature, especially with minor invasion.
The main symptoms of dirofilariasis in cats:
- disruption of digestive processes;
- diarrhea followed by constipation;
- lack of appetite, refusal of favorite treats;
- depression, drowsiness, apathy;
- severe exhaustion;
- periodic vomiting, nausea;
- anemia, pallor, yellowness of mucous membranes;
- fast fatiguability;
- shortness of breath, dry frequent cough;
- inadequate response to external stimuli.
On auscultation, wheezing and whistling sounds are clearly audible in the lungs. Breathing is rapid and shallow. In the cardiopulmonary form of helminthic infestation, the symptoms are very similar to those observed in asthma. The death of endoparasites can cause sudden respiratory failure and provoke shock. This condition can be fatal for a furry pet.
In cats with dirofilariasis, in addition to other symptoms, skin manifestations are possible - allergic rashes, itching, the appearance of neoplasms, purulent blisters, ulcers on the body. The condition of the coat deteriorates; it falls out, becomes dull and disheveled.
Types of worms with photos and descriptions
Worms in cats, symptoms and their treatment depend on the type of parasite that has settled in the body. The types of worms in cats with photos and descriptions that lead to the following types of helminthiasis will help identify their presence.
- Dipylidiasis - the worm larva enters during grooming when a lice-eater or flea is swallowed. These are grayish worms about 25cm long that attach to the intestinal walls and feed on its tissues. The cat becomes apathetic and is not interested in food, his stomach often growls, vomiting and diarrhea are present. Treatment is praziquantel and fenasal.
- Alveococcosis - upon contact with infected rodents. Small worms that parasitize the small intestine, 1-4mm in length. The disease has no pronounced symptoms, is treated with fenasal and cetovex, and is dangerous to the health of the owners. The main measure is prevention and timely analysis at the first suspicion.
- Diphyllobothriasis - when eating raw fish and small crustaceans. Long worms, up to one and a half meters in length, parasitic in the intestines. Symptoms are pronounced - dull coat, lack of appetite, vomiting with blood, constipation and diarrhea, and with severe infection - anemia and intestinal obstruction. Treatment is praziquantel and fenasal.
- Toxacardiosis - in the womb or with food. The worms are 3-5 cm long, round in shape. The helminth does not show activity for a long time; with severe infection, the animal loses a lot of weight, even with normal nutrition, it vomits, and bloody diarrhea appears. Kittens infected in the womb die from rupture of the small intestine. Treatment: pyrantel, fembendazole.
- Hookworm infection - penetration through the skin or when it enters the esophagus. Small worms up to 2 mm, live in the intestines and feed on blood. The disease is characterized by chronic cough and bloody vomiting, leading to anemia. The cat does not eat or show activity, drinks a lot of water. Treatment: pyrantel, febantel.
- Paragonimiasis - enters the body along with raw shellfish meat. Oval worms are small in size, the larvae of which are localized in the lungs of the animal and destroy their tissue. Signs: severe hoarse cough and convulsions, fever, diarrhea, foamy vomiting, refusal to eat. Treatment is praziquantel.
- Opisthorchiasis - feeding a cat raw fish. The worm is a liver fluke or cat fluke, up to 0.5 cm long, sometimes migrates to the gallbladder and pancreas. Signs are pain (the animal reacts aggressively to touching its stomach), gluttony alternates with indifference to food, diarrhea and yellowish vomit appear. Treatment is only comprehensive and under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Roundworms in cats
The most common type of parasites that take root in the body of cats are roundworms or nematodes. They are collectively called roundworms. Kittens are most susceptible to infection.
Roundworm infection
Roundworms in cats - hookworms and roundworms - appear when they eat infected rodents or ingest the feces of a sick animal. Kittens are most susceptible to the disease - worms enter their bodies in the womb or along with her milk.
These helminths parasitize the intestines, which leads to anemia and high mortality in kittens due to intestinal obstruction. However, hookworm infection is most common in dogs.
Lungworms in cats
Flukes are lungworms in cats, the adults of which live in the intestines and migrate to the lungs to lay their eggs. Worm cysts enter the animal's body with raw fish and water from fresh water bodies, when eating an intermediate host - a bird, snail or rodent.
Lungworm infection
Helminth larvae irritate the trachea and cause severe coughing. They provoke diarrhea and vomiting, fever and fever, and cause pulmonary failure.
Pulmonary parasites also include air capillaries, which settle in the nasal cavity and upper respiratory tract of a cat. Symptoms of these worms are most often mild - runny nose, increased body temperature, weight loss, noise when breathing.
Tapeworms in cats
Tapeworms in cats can reach colossal sizes - from 10cm to 1m in length. They are carried by fleas. The worms are made up of segments or segments that can be found in feces - they resemble grains of rice. They can also be seen on the fur around the tail.
Infection with tapeworms
The owner of the animal cannot become infected from a segment of the parasite, unless he himself swallows an infected flea.
The disease is severe and has a number of obvious signs:
- the cat rides on its butt, trying to relieve irritation and anal itching;
- “grains of rice” are visible to the naked eye in his excrement;
- The animal has a tight and round large belly with pronounced ribs.
Threadworms in cats
Thread-like worms in cats are quite rare and have a specific shape, similar to hair. They parasitize at the junction of the large and small intestines, entering the cat's body as larvae along with water or food.
Adults emerge after three months and destroy the circulatory system of the intestine, biting into its walls.
You may be interested in: Worms in dogs
Diagnosis of filamentous worms is possible only by stool tests. But they are similar to parasites that live in the bladder and respiratory tract. Therefore, only a specialist can identify the disease.
Heartworms in cats
Heartworms in cats are often fatal. But cats are more resistant to infection by these parasites than dogs. Worms can migrate in the animal's blood, affecting its nervous system and respiratory organs.
Heartworms in cats
Just like in dogs, cats may not show obvious symptoms of heartworm infestation. Minor signs of the presence of helminths will be shortness of breath and cough, lethargy and periodic vomiting. Their symptoms are similar to feline asthma.
The death of an adult worm in the body of an animal can lead to toxicosis and respiratory failure, causing severe shock. The larvae spread through mosquito and flea bites.
Diagnostics
The presence of dirofilaria in the bloodstream and in the body of infested animals can be determined only after biochemical and serological studies.
When making a diagnosis, anamnesis data, the epizootological situation in the region, and the results of physical examination methods (auscultation, palpation, percussion, inspection) are taken into account. Ultrasound, fluoroscopy, ultrasound cardiography, tests for the detection of heartworms, and other methods do not determine the presence of cardiac nematodes in animals.
Diagnosis of the disease
Dirofilariasis is a difficult disease to define. To identify it, a number of diagnostic examinations are used:
- Serological analysis . Test sample for the presence of antigen of an adult parasite. The success of the event directly depends on the age and number of helminths. The disease at an early stage may not appear during serological testing.
- Radiography . Not the most reliable way to identify parasites. It happens that in a sick pet the result of an x-ray operation may be normal. But in general it is meant that the procedure reveals the state of the disease, the stage of progress or regression.
- Echocardiography . The most informative diagnostic method. The procedure includes an ultrasound of the heart muscle to detect pathological conditions and the presence of heartworms. As a rule, echocardiography gives an accurate conclusion about the pet’s condition.
Treatment of heartworms
In traditional veterinary medicine, there are many effective treatment methods that are used to treat heartworms in cats and other domestic animals. Treatment if a cat is infected with cardionematodes should begin as soon as the pet shows the first symptoms of illness or if a helminthic infestation is suspected. In this case, the prognosis is favorable.
Effective therapeutic therapy for a sick pet should be prescribed by the attending veterinarian, based on the results of diagnostic studies. Self-medication will only worsen the condition of a sick cat and will not lead to the desired result. In addition, most heartworm anthelmintics are more suitable for use in dogs than in cats .
Important! Considering that more than three cardionematodes are rarely localized in the body of cats and these animals are not an ideal host for heartworms, cases of self-healing are known in veterinary medicine. But given the danger that endoparasites can cause to the body of infested animals, we do not recommend neglecting treatment.
Cats infected with heartworms are prescribed complex systemic anthelmintic drugs that act on all stages of heartworm development, and corticosteroids.
Effective veterinary medications for the treatment of dirofilariasis in cats:
- Milbemax.
- Advocate.
- Stronghold.
- Ivermikten.
In case of thromboembolism, severe damage to the cardiovascular system, the cat is given supportive, symptomatic therapy. To normalize cardiac activity, veterinarians prescribe pacemakers and cardiac glycosides. In severe cases, detoxification therapy is carried out and a therapeutic diet is prescribed. Immunostimulants, vitamin-mineral complexes, supplements, enzymes, and restorative medications may also be prescribed. For the cutaneous form of dirofilariasis, general and local treatment is used. If the respiratory system is affected, cats are prescribed Prednisolone, drugs that dilate the bronchi, antispasmodics, and oxygen.
Important! If a cat is diagnosed with dirofilariasis, antipyretics (Aspirin) and anti-inflammatory medications are contraindicated in therapeutic therapy.
If you care about the life and health of your beloved furry, strictly follow the veterinarian’s recommendations. Before giving your cat medicine, carefully read the instructions for the veterinary medicine. Do not exceed the indicated dosage. Despite the fact that modern anthelmintics, although they belong to the category of low-toxic medications, they can provoke side symptoms and intoxication.
In the first two to three days after taking the anthelmintic, carefully monitor the cat’s condition. If the condition worsens, with pronounced side symptoms, immediately contact your veterinarian.
Heartworms
- 1 Why are parasites dangerous?
- 2 How do parasites get into the heart?
- 3 Types of parasites living in the human heart
- 4 Symptoms of worm infection
- 5 Diagnosis of dirofilariasis
- 6 Treatment of dirofilariasis
- 7 Prevention of helminth disease
The heart is the main organ; the quality and duration of a person’s life depends on its work. Parasites - heartworms in humans - can reduce the quality of work and speed up its work. Cardiologists say that even the number of times an organ beats per minute can have a significant impact on life expectancy.
Some parasites can reside permanently or temporarily in the human heart, adversely affecting human health.
How dangerous are parasites?
It is vital to expel parasites from the body, as they take all useful substances and release toxic toxins.
Changes in the functioning of vital organs lead to various kinds of pathologies. This is a well-known fact, but how dangerous are the parasites that settle inside, and how do they get there? Worms in a person’s heart can appear from various sources - food, water, insect bites and others. Heartworms are the result of mosquito bites. These insects are carriers. After being bitten they die.
Once in the blood, the parasites begin to develop and live their own lives. The heart and the blood that passes through it become the breeding ground for them. They change the chemical composition of organ tissues, feed on blood and its cells, depleting it, change tissue layers, which leads to complications. In addition, heartworms take beneficial substances from the body of their host and leave toxic ones in return.
Unpleasant neighbors cannot be ignored. They live and have a detrimental effect and cause poor health, and also cause cosmetic defects. In particular, the skin becomes dry, flabby and loses its color. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you need to contact a specialist who will conduct research and prescribe treatment.
Return to contents
How do parasites get into the heart?
The main carriers of these parasites are animals. Worms reach humans through insect bites (mosquitoes, fleas, lice, ticks). After an insect bite, the larvae enter the human body and begin their development and migration. The worms cannot directly enter the main muscle of the body. This happens in other ways. It is also worth saying that worms are unable to get there in the larval stage, but only after they have overcome this stage of development.
Parasites penetrate the heart through blood vessels, and some species prefer to be localized in this organ.
Worms of the human cardiovascular system begin to live due to their appearance in the following organs:
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
- stomach, where parasites end up due to poor hygiene, as well as due to the consumption of dirty and unprocessed food;
- intestines, here the worms settle after passing through the stomach, in the intestines they begin to develop, multiply and attach to the walls;
- liver, in this organ the worms enter the bloodstream, migrate from the intestines, and seals-bubbles appear in the liver, in which fluid accumulates;
- vessels and veins, here the worms end up in the bloodstream from the intestines, liver and stomach, it is from here that they enter the main muscle of the body;
- From the heart, the worms migrate to the lungs, which leads to even greater complications.
Human infection does not occur instantly. Parasites are able to live in different organs without showing signs of their presence. This condition can persist for several years and only after that they reach the heart. Therefore, it is important to monitor the smallest signals from the body that indicate infection.
Return to contents
Types of parasites living in the human heart
Not every parasite can travel such a long path from the stomach and intestines to the heart. Only certain species are capable of this:
- cisterns are the most dangerous worms that affect the heart muscle;
- hookworms are another type of dangerous parasite that can live in the main organ.
Tankerworms are a type of tapeworm that is transmitted through contaminated meat. The danger of these worms is that they are the larval stage of the pork tapeworm. Their vital activity contributes to an increase in the volume of fibrous tissue in the human heart. The main target of these worms is the pig's body.
Hookworms are parasites that live exclusively in the human body. This becomes possible only after the worms go through several stages of development in the soil. Only sexually mature individuals are able to gain a foothold in the human body. The symptoms of hookworm development and its vital functions are the same as those of other helminths that have settled in the human body. The only difference is hives or an allergic reaction that did not exist before.
Return to contents
Symptoms of worm infection
Invasion, that is, infection of the body by worms occurs gradually. At the initial stage, difficulties appear in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. This instability is explained by the fact that worms secrete toxins. The first signs are diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, and excessive gas formation. With an increase in the number of helminths in the body, vomiting, fatigue up to loss of consciousness and loss of appetite appear. Some patients report dizziness and sleep disturbances.
It is important to remember that the first signs of helminthiasis can easily be confused with other diseases. Most often they are confused with poisoning or an infectious disease. Until there is a correct diagnosis, worms are able to reach vital organs.
In the later stages of development, a person experiences shortness of breath, arrhythmia, and pulse irregularities. Often, worms (dirofilaria) live in the right ventricle of the heart and in the blood vessels of the heart. If the worms have settled in the liver, then the person begins to suffer from pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and colitis. Therefore, it is better not to delay going to a specialist, but to do everything to prevent the spread of worms throughout the body.
Return to contents
Diagnosis of dirofilariasis
Heart parasites develop in the main organ for about two years. The signs and duration of manifestation of the disease depend on the number of larvae and the rate at which new ones appear. With a small number of them, the symptoms of the disease are not detected or are too weak. If each individual brings 25 larvae at a time, then the manifestations will be obvious and sharp. In order to identify worms and begin treatment, doctors conduct several important studies:
- an electrocardiogram allows you to see the work of an organ on a graph;
- an echocardiogram makes it possible to determine the presence of parasites;
- X-rays make it possible to see in which area the main accumulation of worms;
- general blood and urine tests allow doctors to diagnose various inflammatory processes and malfunctions of organs and systems;
- tests of feces and urine for the presence of larvae and other substances indicating the presence of parasites in the body;
- special studies are carried out according to Knot, which make it possible to diagnose dirofilariasis;
- Other studies are also used - MRI and computed tomography.
Thus, helminths living in the main human organ are identified using modern and informative methods. After this, the doctor will be able to make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Today, heartworms can be treated; the main thing is to consult a specialist in time and undergo the necessary tests. Thanks to modern technologies in medicine, it is possible to completely remove worms from the patient’s body. After such procedures, most patients live a full life.
Return to contents
Treatment of dirofilariasis
If worms are found in a person (dirofilaria), then treatment should be started immediately. First of all, the doctor determines the stage of development of the parasites. After this, the specialist can select an individual treatment regimen. Today, the treatment of heartworms is a traditional scheme, when the patient takes drugs that relax the muscles of the worm, and a surgical technique, when the doctor removes all the parasites directly from the heart during surgery. If one helminth is identified that lives in the muscle, then drug therapy is carried out.
It is important to know that the presence of parasites and their death from drug therapy lead to their decomposition inside the organ, migration to other organs located nearby, and to intoxication of the body.
Therefore, the best way to remove helminths from the heart is surgery. After surgery, the doctor prescribes drug therapy to help normalize the functioning of the organ. Doctors say that the best treatment is prevention, and this is true. After all, thoroughly washing and preparing delicious food is better than undergoing a dangerous operation.
Return to contents
Prevention of helminth disease
People develop them not so much due to insect bites, but in most cases, infection occurs from poor hygiene and poor-quality food. Therefore, experts advise washing your hands thoroughly, purchasing and eating high-quality food products, thoroughly washing fruits and vegetables before eating, and heat-treating all products. An important point for prevention is careful hygiene of domestic animals, separation of their equipment and food from human equipment and food. This is the only way to protect yourself from the appearance of harmful neighbors that lead to complex and life-threatening diseases.
Prevention
Dirofilariasis belongs to the category of difficult-to-diagnose helminth infections that are deadly for cats. The only way to prevent your cat from contracting heartworms is preventative deworming.
If a cat is walking along the street, depending on the drug used, for the purpose of prevention, an anthelmintic is given once every 35-55 days. For pets that do not leave the house, anthelmintic drugs can be given once every two to three months. In this case, be sure to take into account the epizootological situation regarding dirofilariasis in your region.
Important! In addition to deworming, treat your cat’s fur two to three times a year to remove ectoparasites – fleas and lice eaters. ticks and other blood-sucking insects. When traveling with your animal to the forest or nature during the mosquito season, treat the cat with repellent.
It is equally important to create optimal living conditions for the cat, proper, systematic care. Protect your pet from stress and consider a balanced diet. If your pet is kept on a natural diet, be sure to give vitamins, mineral complexes, and medications to strengthen the body’s immune potential.
Is dirofilariasis dangerous for people?
In relation to humans, information about dirofilariasis is not clear. The first, good news is that having a sick animal in the house is not dangerous for family members. The disease is not transmitted through contact between a pet and a person; it cannot even be classified as a “disease of dirty hands.”
The second news is not so rosy. A person can get sick. But not from a mustachioed pet, but from insects. Usually these are mosquitoes, but sometimes there can be fleas and ticks. Most often, infection occurs during trips to nature, while performing agricultural work.
The course of the disease in humans differs from that in cats. The larvae that penetrate the human body definitely die. There is only one endoparasite left - a female that has not reached sexual maturity. But it doesn’t travel through the bloodstream like a cat’s. The parasite makes its home under the skin. In its place of residence, first a small compaction forms, then a tumor and then a node. Doctors often confuse dirofilariasis with phlegmon, fibroma, cyst and other diseases that provoke neoplasms.
The main prevention against serious illness is the regular treatment of pets with disinfestation agents. Destruction and prevention of endo- and ectoparasites is the best protection for your favorite animals.
Symptoms of helminthiases
Signs of parasite infection are behavioral in nature, when the cat begins to behave in a special way, as well as physiological - changes in digestion, metabolic processes, and appearance become obvious.
General symptoms
There are basic or general signs of the presence of worms in an animal, but they are symptomatic of a number of diseases, so prior consultation with a veterinarian is required.
Typical manifestations of infection include:
- Bloating, barrel-shaped;
- Changes in appetite, its complete loss or vice versa – frequent demands for food;
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract), manifested as vomiting, diarrhea, constipation;
- Discharge from the eyes of a purulent type, in the form of dried crusts;
- Weight loss, with appetite present;
- The coat becomes dull and falls out, which is explained by decreased immunity;
- Blood or worms themselves are observed in the stool.
Symptoms may vary and other signs may be added depending on the type of parasite. It is recommended to determine which worms the animal is infected with, since medications will be selected based on this.
Symptoms of tapeworm infection
When infested with tapeworms, in addition to general symptoms, the following may be observed:
- Complete refusal to eat;
- Irritation and a rash appear on the anus, the cat constantly licks the anus;
- The worms themselves are visible in the feces, fragments from the rectum may be visible (outwardly they look like grains of rice);
- Weight loss sharply;
- Apathy, the pet’s playfulness is lost;
The presence of tapeworms can be confirmed using tests, since external symptoms alone are not enough for diagnosis.
Signs of intestinal helminth infection
How can you tell if your cat has worms? Many pet owners cannot immediately determine the presence of helminths in their pets, but they, in turn, actively develop and cause serious discomfort to the cat.
To find out that pathogenic organisms have appeared in the animal’s body, you should first pay attention to the pet’s behavior. But often the signs of the presence of worms are similar to the symptoms of many infectious diseases.
The presence of certain symptoms of worm disease may vary depending on the degree of helminth damage to the cat, in other words, on the number of worms in the body. With weak invasion (infestation), signs of the disease may be absent altogether. You can note the main symptoms that may indirectly indicate a possible cat infection with worms:
- depression, poor or perverted appetite, weight loss, fatigue, if this is a kitten, then retardation in growth and development;
- ruffled fur;
- the presence of yellowness of the mucous membranes and enlargement of the liver (with trematodes) or their anemia (with cestodes);
- indigestion (constipation followed by diarrhea, and vice versa, vomiting);
- a cough may appear periodically (this occurs during the migration of roundworm larvae throughout the body);
- discharge from the eyes;
- itching in the anal area;
- in severe cases, symptoms of body intoxication may appear: convulsions, leg paresis, etc.;
- miscarriage or premature birth;
- the presence of blood and mucus in the cat’s feces.
Tape
Routes of infection, carriers: Small crustaceans of fresh water bodies, raw fish, rodents. Fleas and lice eaters.
Sometimes whole worms or their fragments can be seen in the stool or around the anus.
Common symptoms of helminthic infestation are:
- Vomit
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Bloated belly
- Anemia
- Convulsions
- Cough
- Itching of the anal passage
- Labored breathing
- Hair loss
- Dull coat
- Rumbling in the stomach
- Increased thirst
- Poor appetite
- Increased appetite
- Pica
- Weight loss
- Lethargy
- Apathy
It is worth noting that the signs of helminthic infestation are very similar to the symptoms of other diseases. Therefore, in most cases, it is very difficult or impossible to determine on your own whether your cat is infected with worms.
Worms are often diagnosed in humans, especially in children. These parasites have a simple structure and belong to the class of flatworms or roundworms.
Worms enter the human body in the form of eggs, from which larvae and adults subsequently emerge. The eggs of worms in humans can migrate to the place of their vital activity.
The first symptoms that the body is infected with worms appear depending on how many helminths are in the human body. Most often they appear during the first two weeks.
If helminths are not treated, complications may begin.
What do worms lead to?
Symptoms of infection
There are many ways a pet can become infected with intestinal parasites. There are cases that a newborn baby has so many worms that their length can be 2 times the length of the animal. In this case, contact with the parasite occurred in the womb. The cat must first be treated for fleas 3 weeks before mating, and then anthelmintic treatment must be carried out.
The larvae of various helminths can be found almost everywhere - on the grass, in the ground, on plants. For this reason, you should not think that if a cat is constantly at home and does not walk outside, he will not be able to pick up worms. You can bring helminth eggs into your house from the street along with dirt on your shoes, or you can bring them on your clothes.
Yes, some worms are transmitted from animals to humans.
Different types of worms are transmitted in different ways. A cat can become infected with worms through food (raw or poorly cooked fish or meat), or by eating insects, such as flies or rodents.
Worm eggs brought into the house on shoes or clothing can get inside the animal. A cat can become infected through contact with infected animals and through saliva.
Fleas are also carriers of worms.