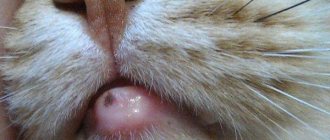
Diagnosis of the condition
An unpleasant sensation that causes a strong desire to scratch is itching. This condition in an animal is an obvious sign of skin damage. In veterinary medicine, there are 2 types of disorders:
- Localized type, when one or several places on the pet’s body begin to itch. Sometimes scratches appear only on the face, as well as on the neck and cheeks.
- Generalized type, which involves the appearance of sores on the entire body of the animal.
If you notice that your cat is itching a lot and drops of blood appear in the scratching areas, you need to contact a specialist at a veterinary clinic. To begin with, the pet is examined for the presence of blood-sucking parasites, which can cause severe stress in both couch potatoes and walking individuals. Scratch marks from bites are most often found on the chin, cheeks, neck, and tail. If fleas or ticks are not detected, then we are talking about other, more serious reasons.
After questioning the owner, the doctor will scrape the damaged area on the pet’s skin. Examination of the sample in the laboratory helps to identify the causative agent of the disease. Additional tests may also be ordered.
Once the exact disease is determined, the veterinarian prescribes treatment and gives additional recommendations on nutrition and care for the recovering patient.
Unfortunately, owners go to the veterinary clinic too late: when they discover severe wounds, bleeding scratches or bald patches on the pet’s body. This is the next stage of the pathology, which causes severe discomfort and can lead to severe infection. The duty of a good owner is to notice and respond to the problem in a timely manner.
Causes and symptoms
Manifestation of allergies
If the owners notice that the cat has scratched its neck until it bleeds, crusts have appeared behind the ears, or hair loss is observed, then it is worth checking whether it has an allergic reaction to food or other substances. Often a pet combs the hair in the neck area when exposed to the following irritants:
- dust;
- household chemicals;
- mold;
- hygiene products;
- plant pollen.
The scab or rash first appears on the neck and soon spreads to the head and body. If a cat tears the wounds, then wet areas form in their place, which are likely to become infected. Rashes due to an allergic reaction cause severe pain and itching for the pet, which negatively affects the general condition of the animal.
Veterinarians warn owners that in case of allergies, the first step is to eliminate the allergen. If the wounds on the cat’s neck do not go away, then contact a veterinarian who will prescribe antihistamines.
Effect of fleas
With numerous flea bites, the pet may scratch the wounds due to severe skin itching.
If a cat has a scratchy wound or a red spot on its withers, then the likely cause is the activity of small blood-sucking parasites. Most often, fleas bite a cat on the neck, resulting in severe skin itching. The disorder can be recognized by the following additional symptoms:
- constant scratching in the neck area;
- formation of bleeding wounds;
- discomfort and pain.
Subcutaneous mite: can it cause wounds?
When such parasites are active, owners may notice that the cat has scratched the skin until it bleeds, and hair may fall out in the problem area. For a long time, the pathology can go unnoticed, since the mite lives under the epidermis. If the problem is not corrected in time, the pet will severely scratch the wounds, causing extensive sores to appear on the neck. Tick activity can provoke the following disorders:
- sarcoptic mange;
- demodex, etc.
Ringworm activity
Fungal infection leads to the development of ringworm, which is accompanied by scabies.
A scab or wet spot on the neck may appear in a cat due to such a disorder. This disease is widespread not only among the feline family, but also among other pets. First, the animal's fur falls out in the problem area, after which severe itching and redness appear. With ringworm, the cat scratches its neck, causing the fungi to spread to other areas. If you do nothing and do not treat the pathology, then soon the whole body is covered with a solid crust, which is why the pet can die.
Wounds due to dermatitis
If a cat scratches its neck until it hurts, this may signal the progression of a dermatological disease. Deviation in a cat can be triggered by viruses, bacteria, fungi, and dermatitis occurs against the background of allergies and under the influence of many other factors. The table shows the types of dermatological diseases in the cat’s neck area and their brief description:
| Type | Peculiarities |
| Miliary | Accompanied by small rashes |
| Progresses against the background of other diseases | |
| It is possible to determine the cause of such dermatitis and wounds on the neck only through diagnostics in a veterinary clinic | |
| Often manifests itself as an allergic reaction | |
| If the disease is not treated in time, the rash spreads to the head and other parts of the body. | |
| Bacterial | Cat scratching occurs due to the activity of pathogenic microorganisms |
| Dermatitis is accompanied by severe itching | |
| The more skin a cat has torn, the more difficult it is to treat the disease. |
Dermatitis in a cat that occurs against the background of bacterial activity does not heal on its own, but requires timely treatment. If therapy is not prescribed on time, the wound area increases and there is a high probability of developing an abscess, fistulas and nodes.
Infestation by exogenous insects
. The presence of these insects leads to the occurrence of various diseases. The most dangerous of them include:
- flea dermatitis;
- mite damage: sarcoptic mange, notoedrosis.
When a flea bites, a wound with their saliva remains on the animal's body, causing severe itching. The cat begins to vigorously scratch the affected area, which leads to the infection getting inside. The inflammatory process in combed areas is manifested by redness and hair loss.
Fleas not only contribute to the occurrence of infectious diseases, but are also carriers of worm eggs (helminths).
When infected with ticks, the clinical picture in cats is as follows:
- severe itching on dry areas of the skin;
- hair loss;
- formation of ulcers on exposed areas.
Notoedrosis in cats is manifested by the presence of Notoedres cat mites and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- itching and severe scratching;
- rash in the form of blisters;
- the appearance of crusts on itchy areas;
- hair loss;
- loss of skin elasticity, appearance of cracks infected with bacteria and fungi.
. These tiny bloodsuckers are 0.2-0.4 mm long and have a long proboscis. Thanks to this, they easily gnaw holes in the skin and make a large number of moves in it. Once on the animal's body, the parasites begin to actively lay larvae. In this regard, already 1.5 months after their appearance, their numerous offspring are present on the cat’s body.
The main symptom of this disease is severe itching, which gets worse in the evening. First of all, the tick infects areas on the animal’s head, neck, and near the ears, where blisters and redness immediately appear. After a while, these places become covered with dried crusts. The animal becomes restless, constantly itches and meows. Constantly scratching itchy areas, the cat cannot sleep, loses its appetite and experiences weight loss.
Therapy involves not only getting rid of bloodsuckers, but also healing damaged skin areas, as well as restoring the pet’s immune system.
We suggest you read: Tests for pinworms in a child
Important! At the first signs of sarcoptic mange, the cat should be shown to a specialist.
Causes of itching in cats
A cat chews itself and scratches itself when its skin becomes itchy.
There are several reasons that cause this condition:
- lichen;
- helminthiases;
- endocrine system problems;
- failure in the hormonal system;
- influence of stressful situations;
- the occurrence of skin diseases (fungus);
- there are insects in the fur that feed on blood;
- allergic reaction.
First, the animal is checked for fleas. This is the main reason why your pet starts to itch a lot. Flea bite marks persist for about 1.5 months, causing itching. If there are no insects in the animal's fur, it must be shown to a veterinarian.
Lice, lice, mites, flea dermatitis and other parasites that cause itching
Infection with ectoparasites occurs through outdoor shoes. The skin becomes inflamed if there are traces of scratches or small wounds on it.
If they are not treated in time, the animal will scratch them. Suppuration will appear, which will lead to baldness or sepsis. Sulfur ointment or powder is used to treat wounds. The drug in powder form called Yuglone is the most effective and is recommended for use by veterinarians.
Infection with helminths as a cause of itching
If the animal is infected with worms, then:
- the pet itches and licks the anus area because it feels severe discomfort in this place;
- appetite deteriorates, stool changes, changes occur in the digestive tract;
- there are noticeable changes in the cat’s behavior (he is too excited or in an apathetic state);
- the skin is dry and flaky, and the coat becomes dull.
Hormonal and endocrine disorders
Major disorders of the hormonal and endocrine system:
- Improper functioning of the thyroid gland . At the same time, the fur becomes tangled, itching and dandruff appear. In some cases, cats go bald.
- Cushing's syndrome . Due to a malfunction of the adrenal cortex, the skin loses its elasticity and becomes thinner. Comedones appear on the back and sides of the animal.
- Diabetes . _ The disease manifests itself in the form of local baldness, dry skin, seborrhea, and dull hair.
Causes of itching and scratching
Sometimes scratching in a cat may not be associated with diseases, but may be caused by seasonal factors. So, during spring and autumn molting, cats begin to itch and lick themselves more intensely. By doing this, they are trying to improve blood circulation and bring the coat into complete order.
You should be wary when a cat scratches the same place. He jumps up sharply (even if he was sleeping) and begins to furiously comb out something invisible to the eye. If you observe this behavior for several days, and hair has already begun to fall out at the site of the scratching, it’s time to go to the veterinary clinic so that they can determine one of the probable causes of the problem.
The appearance of worms
Even a domestic cat that does not go outside can become infected with helminths. Parasite eggs enter the body through raw meat, unwashed grass picked on the street by a caring owner, outdoor shoes and human clothing. When worms begin to actively reproduce, the following symptoms appear:
- Severe discomfort in the anal area. The mustachioed friend rubs against the carpet and licks the area too often.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, difficulty with bowel movements.
- Loss of the beautiful natural shine and silkiness of the coat. Severe peeling appears on the skin.
- Discharge and inflammation of the eyes.
- Obvious changes in the behavior of the mustachioed friend. He becomes overly restless, or maybe, on the contrary, looks at everything with indifference.
- Lungworms and heartworms cause coughing and shortness of breath.
In this case, the cat is dewormed twice, with an interval of 10-14 days (details are indicated in the instructions for the drug). To avoid such problems in the future, make it a rule to carry out deworming quarterly.
Bacterial diseases
One of the most diagnosed bacterial diseases is pyoderma. This disease causes your pet to itch until it bleeds. The main cause of damage is long-term consumption of low-quality dry food, which contains few useful elements. Pyoderma is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe baldness;
- severe itching;
- skin peeling;
- scabs on the body;
- purulent inflammation with cloudy liquid.
Bacteria penetrate the epidermis and then go deep into the skin. This is especially true for short-haired or hairless breeds. Without prompt medical treatment, your pet's death is possible. Self-treatment of pyoderma is excluded.
Otitis externa
Infections of the ear canals provoke severe itching, forcing the mustachioed friend to shake his head and scratch his muzzle until it bleeds. Inflammation is quite dangerous to health, so treatment should not be delayed. In severe cases, surgery may be required. The most obvious signs of external otitis are:
- deterioration in behavior - excessive restlessness, unusual meowing;
- scratching the ears;
- frequent head shaking;
- painful sensations when pressing on the auricle.
Advanced cases are fraught with complications in the form of redness of the auricle, increased temperature, thickening and swelling of the inflamed organ. Purulent discharge is possible.
Otitis media is diagnosed and treated at a veterinary clinic - the doctor conducts tests and prescribes medications. Therapy takes up to several weeks.
Ringworm in a cat
Ringworm is a disease caused by a fungal infection. If previously lichen was considered incurable, now there are a large number of medications that relieve this problem.
It is very important to identify the pathology at an early stage so that the animal does not become a threat to surrounding family members or relatives, since lichen is a rather contagious ailment. If an animal has picked up a fungus, you can notice a number of characteristic features:
- baldness on the paws, ears, back;
- the appearance of bleeding wounds;
- formation of scabs on the body;
- change in character, lethargy, apathy;
- lack of appetite.
If signs are detected, the patient must be shown to a veterinarian. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. To do this, he will take tests and illuminate the patient’s body with an ultraviolet lamp - the fungal spores will phosphoresce. It is important to strictly follow your doctor’s instructions to speed up recovery and reduce the threat of infection. Self-medication for lichen is contraindicated.
Skin parasites
Cat scratching can be caused by different types of insects: lice, mites, coccidia, ear mites and fleas. Due to infection, the coat loses its shine and becomes very thin. The skin itself becomes very dry and flabby. The cat becomes restless and experiences sudden bouts of itching.
Even a cat that does not walk outside and does not interact with other animals cannot be protected from the appearance of parasites. Infection occurs through infected clothing or shoes of the owner and family members. As a result, the animal develops a desire to scratch itself, and hair falls out in certain areas of the body. The doctor prescribes solutions and ointments to the patient. They can reduce discomfort and reduce the parasite population.
Allergic reactions
Allergies are triggered by different types of food or chemicals. The nutritional cause of sores is associated with the animal eating harmful foods or low-quality industrial feed. Allergies can also occur when a cat’s diet changes.
When visiting the veterinarian, you need to remember what your pet has eaten over the past 7-10 days. You need to talk about changing food and treats from the master's table. The doctor does tests for different allergens, and then prescribes a neutral diet. Antihistamines and ointments are prescribed as medications. These products help reduce itching and reduce the number of sores on your mustachioed friend’s body.
Non-food allergies are even more troublesome because they can be caused by anything. To begin with, the owner should change the bowls, bedding or bed, and also prevent the pet’s body from coming into contact with things washed with synthetic detergents.
It is almost impossible to determine the cause of this pathology using tests. Ulcers with scabs do not allow you to get an accurate result, so most likely it will be a false positive. In addition, non-food allergies can be seasonal. For example, during the flowering period of different plants, a reaction to pollen begins, and during dry weather, symptoms to dust may occur.
The most effective thing to do is to show maximum attention and determine what exactly is bothering the cat. Only the owner can accurately notice all changes in the cat’s behavior when a suspected allergen appears/excludes.
Hormonal imbalances
Sometimes problems with the skin appear due to diseases associated with impaired hormone secretion. Improper functioning of the endocrine system provokes many symptoms, the appearance of which requires contacting a veterinary clinic. The most common ailments associated with hormonal imbalances are:
- Thyroid dysfunction, which causes tangled hair, flaking, severe itching and noticeable baldness.
- Cushing's syndrome, causing severe pain and partial hair loss on the sides and back. The skin becomes very dry and loses elasticity.
- Diabetes mellitus, which causes loss of shine and thinning of hair. The cat scratches its body until it bleeds and drinks a lot.
In a veterinary clinic, the doctor prescribes general tests of blood, urine, feces, and takes scrapings for laboratory tests. Only a thorough examination will help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medication.
Stress and mental disorders
In rare cases, if a specialist cannot confirm the above ailments, scratching is associated with certain mental disorders. The cat begins to lick itself vigorously, which provokes the appearance of wounds and ulcers. They form on the front and hind limbs, in the scapular region. The owner should pay attention to the fact that the cat has become nervous, aggressive, and continues to lick itself, despite the increasing pain. The wounds grow rapidly and become deeper, but the animal does not pay attention to this.
The doctor will recommend the use of sedative medications. The course of medication should cause the ulcers to dry out. This occurs due to the cessation of active licking and a decrease in overall tension.
The cause of a mental disorder can be anything - from moving to a new house to a banal fright. It is important to create a calm atmosphere around and be attentive to the cat.
Why does a cat scratch its neck?
There are many reasons that cause itching other than flea infestation. The problem may lie either in the activity of other parasites or in individual intolerance to certain substances.
Parasites
When the most obvious cause of neck scratching, namely fleas, has been ruled out, you should not immediately stop looking in this direction, because other types of parasites may also bother the animal. So, itching can be provoked by:
- Subcutaneous mites that cause demodicosis - a disease that affects the skin and coat of a pet. In the localized form of the disease, the lesion occurs in a separate area of the body, for example, on the neck. In this case, the skin turns red, pustular rashes appear, the integument peels off, and the hair on the head, ears and neck falls out. The animal is primarily concerned about severe itching and the appearance of bleeding wounds, which are further scratched with claws. Cat subcutaneous mites of any kind are not infectious to humans. Two types of such parasites can live on a cat’s body: Demodex cati, which is conditionally pathogenic (it is part of the normal flora, but under favorable conditions it can multiply and cause disease),
- gatoi, a scabies mite that belongs to a pathogenic species and can be transmitted from one individual to another.
The gatoi scabies mite causes severe itching in cats and can be transmitted to other pets, but not to humans.
Dermatological diseases
Skin diseases can be caused by both changes within the body and pathogenic microorganisms:
- Fungal dermatological diseases (dermatomycoses) are a common cause of problems in cats, caused by mold and yeast infections. The most common disease in this group is lichen, the causative agent of which is the fungus microsporum, epidermophyton or trichophyton. The disease affects the hair follicles and skin. Ringworm is contagious and can be easily transmitted from cat to person, so owners should be vigilant, especially if there are small children in the house. The disease manifests itself in symptoms: round redness appears on the body, which itches and bothers the animal;
- peeling of the skin and hair loss are observed, which most often affects the area of the head, neck and limbs;
- When a secondary infection occurs, scratching can transform into festering wounds.
Ringworm most often affects the head, neck and extremities, causing itching, flaking skin and hair loss.
- traumatic - due to mechanical damage to the skin on the neck, burn or frostbite;
Allergic reaction
A nonspecific immune reaction to an irritant can occur in animals as often as in humans. Possible allergens that can cause itching in the neck area:
- feed;
- flea drops on the withers and an anti-flea collar;
- medications;
- shampoo and other hair care products.
An allergic reaction can be limited to local itching and redness, which causes the animal to itch a lot, or cause additional, more dangerous symptoms, including life-threatening swelling of the airways (Quincke's edema).
Video: a cat has an allergic reaction to a flea collar
Parasites
Another cause of itchy skin and scabies can be parasites; scabies mites (sarcoptic mange) are more common in pets. In this case, damage can be found on the cat's elbows, ankles, and ears.
However, only a doctor can make a more accurate diagnosis. To do this, he will make several deep scrapings and, if parasites are found, he will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Itching scabies
This is a tick that parasitizes the head and neck of an animal. The result is damage to the inner layer of skin. Scabies itch feeds on lymph and particles of the inner layer of the epidermis. The parasite lays eggs there.
Symptoms:
- The appearance of red bumps on the skin.
- The appearance of thick crusts on the affected areas.
- Transformation of crusts into papules filled with liquid.
- Thinning of hair in affected areas.
Ear mite
It is a parasite that causes ear scabies (otodectosis) in cats. It settles in the skin folds of the ears and feeds on lymph, skin cells and blood.
Signs of infection:
- Itching in the ears. The cat scratches its ears and shakes its head.
- Redness appears in the folds of the ears.
- The amount of wax in the ears increases.
- A brown coating with an unpleasant odor appears in the ears.
Ixodid tick
This is the most dangerous parasite, a carrier of bacteria. The tick is quite large and feeds on cows. Upon examination, it resembles a gray grape (if it has drunk blood). If the strike appeared recently and did not have time to drink blood, it looks like a small spider.
Causes diseases such as:
- Infectious anemia.
- Damage to the blood and lymph nodes.
- Damage to the spleen and liver.
Such diseases are difficult to tolerate and take a long time to treat. Therefore, the best option is prevention (collars, sprays, drops).
Fly larvae
Fly larvae often appear in open wounds of cats. The insect lays eggs in the animal's wound, causing a disease called myiasis. The larvae feed on living cells, tissues, and fluids from the body.
Course of the disease:
- Larvae emerge from the eggs, they molt, grow, and actively feed on tissues and cells from the wound.
- The larvae penetrate deep into the skin, bringing the infection deeper and deeper. Connective and muscle tissues are damaged.
- The wounds hurt, itch and fester, the animal becomes restless,
- Scratching wounds leads to bacterial infections.
Treating scratches at home
When it is not possible to quickly contact a veterinarian, the pet still needs help. If you do nothing, the situation begins to worsen, and the sores become very painful. You can understand that the pathology is becoming more complicated by the cat’s reaction - he tries to hide and does not allow the sores to be examined.
Another dangerous factor is the risk of infection of the sores. This leads to irreversible consequences and even death. This happens due to ignoring the pathology, as well as improper treatment. Therefore, if you find a sore or scratch, you should not immediately smear it with human products - it is better to observe your pet and then consult a doctor.
Sometimes the owner cannot quickly take his mustachioed friend to the hospital, but the doctor is able to prescribe medications over the phone. This will help somewhat reduce discomfort and remove the threat of the disease spreading throughout the body. It is important to remember that this does not cancel a visit to the clinic, but only provides a temporary relief effect.
The formation of abscesses and abscesses requires surgical intervention. The doctor promptly removes pus from deep wounds and washes them. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are then prescribed to restore the patient's weak immune system.
If the inflammation is not very extensive and does not provoke severe pain, then treatment at home is more like preventive measures. If there is no infection, the wounds begin to heal within a couple of days. To disinfect and relieve discomfort, sores are wiped with calendula tincture or hydrogen peroxide. You should not use alcohol solutions, because they will cause even more harm to the cat’s skin. It is best to buy a herbal mixture at the pharmacy and prepare the infusion yourself according to the instructions.
Bacterial or fungal inflammation
Various opportunistic microorganisms living on your pet's skin do not harm a healthy animal. But if your cat’s body has been weakened, for example, due to some disease or lack of vitamins, then the population of “harmful” fungi and bacteria increases, causing the cat’s skin condition and general well-being to deteriorate.
The doctor will check for inflammation caused by fungus or bacteria and also conduct a smear examination. As a rule, this inflammation is not the main cause of the disease.
What to do if treatment is unsuccessful?
With correctly prescribed therapy, the effect is noticeable from the first days: the animal itches less and the ulcers begin to dry out. If there is no improvement within 5-7 days, you should definitely visit a veterinary clinic.
Even if the veterinarian prescribed the drugs, but there is no result, contact us again. It also happens that an examination by another doctor or in another veterinary clinic helps.
The main thing is not to let things take their course and achieve improvements in the cat’s condition. Otherwise, you will have to treat not only the root cause, but also secondary infections.
Treatment
If a pet has neck sores, a fellinologist should examine the victim. The first is the presence or absence of fleas. Arthropods often inhabit the neck. A thorough examination reveals the agile insects, their whitish eggs and black excrement. Sometimes lice or lice eaters are found.
Therefore, the first action is to treat the cat against ectoparasites. The following types of control agents are used:
- Destructive emulsions.
- Anti-flea collars.
- Drops for application to the back.
- Aerosols.
Flea dermatitis
If the ectoparasites are destroyed, but the wounds and ulcers do not disappear or expand, you need to get rid of the following diseases:
- Subcutaneous mites.
- Allergic reaction.
- Lichen.
- Eczema.
Subcutaneous mites
If the cat is itching, but there are no fleas or they have recently been expelled, the cause of the disease should be looked deeper. Skin scrapings may reveal hypodermal mites. Most often, Demodex and Notoedrus are found in cats.
Before applying medications to the affected area of the neck, the hair is cut to open access for the action of the medications and to monitor the cat’s condition over time. Treatment of the disease is carried out using the following groups of medications:
- Symptomatic.
- General strengthening
- System
Symptomatic remedies are put in front because if the diagnosis is unclear, one cannot waste time allowing the development of the pathological process. These are external, cleansing skin from scabs and anti-inflammatory agents in the form of ointments, gels or aerosols. Complex systemic preparations that have acaricidal, antimicrobial, antimycotic, and anti-inflammatory effects are moistened onto the prepared surface.
At the same time, medications are used that increase immune defense
Subcutaneous mite
Allergic reaction
The second most common cause of hypersensitive reactions after flea dermatitis is food allergy. If this type of pathology is suspected, diagnostic procedures are combined with therapeutic ones. Finding out which component causes dermatitis is a difficult task. Therefore, the animal is given hypoallergenic food, while simultaneously undergoing desensitization therapy with medications containing Dexamethasone. When improvement occurs, restorative drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. It may take months for you to fully recover.
Another type of allergy, atopic dermatitis, develops against the background of an innate predisposition to violent reactions to irritants. Such a cat is excluded from breeding.
The disease is incurable, but methods that can minimize complications have been developed. In addition to symptomatic treatment, the cat is isolated from the irritant. If there is a suspicion of hypersensitivity, the substances with which the flea collar is impregnated are snatched, it is removed. During the flowering of allergenic plants, the cat is not allowed to walk, and the apartment windows are left closed. It is possible that you will have to change the litter in the cat's litter box.
Fungal infection
Lichen
Among fungal infections, Microsporia is the most common. The spores are resistant to medications and can cause secondary infection.
Antimycotic drugs are divided into the following drug groups:
- External. Solutions, gels, and ointments are used. To facilitate access to the active substances, six are cut off. Licking is prevented by using an Elizabethan collar.
- Oral. Tablets have severe side effects, so they are used when external medications are ineffective.
- Parenteral. Immunomodulators are used, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs for severe cases of the process.
Eczema
For weeping eczema, drying agents are used, and dry eczema is treated with moisturizing external medications. The acute course requires the use of analgesics, as well as steroidal antiphlogistics. The composition of ointments includes antimicrobial agents. The use of immunomodulators speeds up the healing process.
We invite you to join our Zen channel and group on VKontakte or Odnoklassniki, where new articles for pet owners are published.
Similar articles:
- My cat has a nosebleed - what should I do?
- Inflammation of the lower lip in a cat
- Clear nasal discharge in cats
Ringworm and other skin lesions in cats caused by fungi
If an adult animal or kitten itches, but there are no fleas, the itching is often associated with the action of a fungus on the skin.
Trichophytosis, ringworm
Trichophytosis is a fungal disease that can be transmitted to people. This is especially dangerous for children, and it is much easier to cure a pet than a person. The disease manifests itself as hair loss in a local area and increased itching of the affected area. As a result of infection, since the pet is constantly itching, an abscess covered with a hard shell often forms under the skin of the bald spot. In this case, it is necessary to remove the pus, but the procedure must be performed by a veterinarian in a clinic setting.
You should not diagnose the disease yourself, since it is easy for an amateur to confuse ringworm (the popular name for trichophytosis) with other effects that have similar manifestations:
- sunburn, especially typical for representatives of short-haired breeds;
- damage from exposure to chemicals;
- hormonal alopecia.
If the diagnosis is established, special ointments offered by veterinary pharmacies are used.
Dermatomycoses
They arise from the infectious effects of fungi. Pets become infected from other animals, unwashed food, dirty objects, and unfavorable living conditions. The disease is often carried by mice.
Characteristic manifestations are scratches, wounds, scratches, reminiscent of those caused by fleas, covered with crusts, constantly itching, disturbing the cat and forcing it to itch.
Why you can't stop itching
If you have not yet visited the veterinarian, you should not smear the sores with anything at all - this will distort the results of scrapings and tests, which will complicate the diagnosis. You should not immediately offer your animal antihistamines - firstly, you may not guess the dosage, and secondly, the blood test will be invalid.
Once the veterinarian has prescribed medications and ointments, there is no need to relieve itching - most medications already contain substances that reduce discomfort.
Finally, anti-itch medications in humans can cause allergies in cats, which will only make the problem worse.
Otitis
Ear infections can also cause unbearable, severe itching, causing the cat to shake its head and scratch its face and ears vigorously.
In advanced cases, you may notice redness and swelling of the auricle, as well as discharge of pus from the ear itself.
The first sign of otitis in cats is severe itching in the ears.
Secondary symptoms:
- Inflammation of the skin inside the ear.
- Sharp or aching pain (the cat becomes lethargic or aggressive, scared).
Causes:
- Injuries. Contact with foreign objects, scratches, fights between tribesmen.
- Parasites (ear or subcutaneous mites). They damage the skin and soft tissues, a bacterial infection is added and otitis media develops.
- Allergy. In this case, the cat scratches the skin inside the auricle, an infection gets there, which is the cause of otitis media.
- Infection with staphylococcus, streptococcus, etc.
- Incorrect care.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a fairly common disease in animals. In cats it is usually more complicated than in other pets. It can be located on the neck, head or paws. At the beginning of the development of the disease, hair falls off from the affected area of the skin. The exposed dermis wrinkles, turns red, and becomes covered with rough yellowish-brown scales.
© shutterstock
If you look closely, you can see a white coating on the sore . This is the fungus that causes shingles. The affected skin is very itchy, the cat constantly scratches the sores on the neck, thereby spreading the fungus further. Ringworm spreads quickly and, if your pet is not treated, soon the poor thing's entire body will be covered with one continuous scab. The animal may die.
Therapy for such a disease requires complex treatment. If possible, it is recommended to shave the cat's head so that the lichen does not spread (after all, the fur may be infected). The animal is treated using :
- ointments (“Nystatin”, “Griseofulvin”), etc.;
- oral medications (“Ketoconazole”, “Griseofulvin”), the dosage of which is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease.
The room in which a cat infected with ringworm lives must be disinfected. Daily wet cleaning is mandatory. It is better to isolate the animal, and burn the things it touched if disinfection is not applicable to them. Such precautions are necessary to ensure that the sore does not attach itself to one of the family members.
Infectious skin diseases
Itching in an animal can be caused by an infection that has penetrated into the thickness of the skin through scratches, small wounds, or flea bites. Local inflammation causes the cat to itch furiously, but bacterial infections can be treated well. Veterinarians advise using sulfur ointment or Juglone powder externally. These drugs cope equally well with dermatomycosis and bacterial infections. Systemic treatment may require antibiotics, but these medications should only be given to your pet as directed by a doctor.
Interesting!
Juglone powder, dissolved in an oil base, was rubbed into the skin for ringworm behind the cat's ear. After a few days, the lesion shrank, and after a week of use it disappeared completely. Juglone is a black walnut extract that is used in America to treat parasitic diseases. The drug has a bactericidal, sedative, antifungal, antiprotozoal and immunomodulatory effect. According to expert reviews, the product copes well with skin problems in animals. We have only recently begun to treat dermatoses with this medicine, and the drug is difficult to find on the market.
Juglone Infectious skin lesions in cats are secondary and are not transmitted to humans. Most often, people are the source of infection for cats.
Prevention of allergic dermatitis caused by fleas
Increased sensitivity to flea saliva is an individual feature of the immune system of an allergic cat, so it is impossible to get rid of it once and for all. However, the likelihood of developing dermatitis becomes many times less if you follow the following rules:
- avoid contact with flea-infested animals;
- remove outerwear and outdoor shoes away from pets;
- regularly inspect the wool for the presence of insects and traces of their vital activity;
- keep the apartment clean and conduct a weekly inspection of cat litter and toys;
- use anti-flea collars or drops;
- carry out regular deworming, since intestinal parasites provoke allergic reactions;
- for bathing, use special hypoallergenic zoo shampoos;
- Compose your cat’s diet correctly and, if necessary, use food supplements and vitamin preparations.
Share with friends!
Cat fleas
Fleas on a cat are perhaps the most common problem in an animal. Even if the cat is domestic and has never been outside or had contact with other animals, this does not guarantee that it has not picked up fleas. After all, even the owner can bring them in from the street, along with shoes or on clothes.
And as soon as abnormal combing of the animal has been noticed, the first thing to do is to examine the cat for the presence of fleas. This procedure is not difficult to carry out. Use two hands to separate the pet's fur on a certain area of the skin. In the parting of the fur, as a rule, you can notice the uninvited “tenants” of the animal. And in advanced cases, fleas can be seen with the naked eye.
This cat disease is perhaps the easiest to treat. In veterinary pharmacies and pet stores, there are sufficient quantities of products to help get rid of fleas. These include drops, sprays, and all kinds of ointments. Also, to consolidate the procedures for getting rid of fleas, you can use repellent collars that are impregnated with special liquids that repel insects.
Here, the pet owner can make the choice himself, based on his budget and the degree of neglect of the disease.