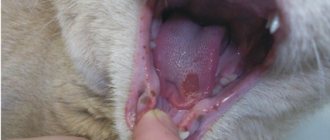
Veterinary specialists in clinical practice often encounter various diseases that affect the skin of pets. One of the common reasons why cat owners go to a veterinary hospital is an abscess.
Cats that have free access to the street are especially often exposed to the pathological process. It is yard animals that more often come into contact with the outside world, receiving injuries from their relatives during fights, when scratched by branches and thorny bushes. It is worth noting that despite the fact that pets who prefer a quiet home lifestyle can also suffer from a developing abscess.
An abscess is a pathology that is an affected area on a cat’s body filled with purulent exudate as a result of the development of pathogenic microflora. Most often, domestic cats are diagnosed with dental abscesses that develop against the background of periodontal disease and lack of timely treatment. As a result, this leads to serious violations.
The second most common diagnosis is an abscess obtained during a fight with relatives or dogs. The damage received by the animal is not always detected by the owner in a timely manner; accordingly, the introduced infection leads to the formation of suppuration and abscess.
An abscess can develop against the background of bites during fights with relatives. It is in this case that a deep, puncture-type wound surface is formed. Opportunistic microflora is always present in the oral cavity of domestic cats and dogs. When a cat licks a wound, it becomes infected.
The healed wound surface is isolated from the outside world, and the infection is located inside. Rapidly multiplying pathogenic microorganisms provoke the appearance of pus. The body cannot cope with this on its own and an abscess develops.
The appearance of an abscess on any part of the animal’s body provokes painful sensations and the pet’s general well-being worsens. The danger of the formation of purulent inflammation lies in the high risk of necrosis of the area and subsequent sepsis. The main method of therapy is surgical excision and the administration of therapeutic doses of antibiotics.
How to recognize
If a small red spot appears on a cat's skin, which enlarges and becomes soft, an abscess is suspected. Later, pus accumulates in this place, the seal turns yellow, and the pet experiences pain.
What is an abscess
This is an inflammatory process of the upper layers of the skin, into which dirt or a foreign body has entered. They penetrate the integument through wounds or abrasions.
Pathology can also develop in the oral cavity when a bone or splinter gets stuck in the soft tissue.
What microorganisms cause
An abscess (abscess) occurs due to the introduction of streptococci and staphylococci into the wound. Microorganisms actively multiply inside the skin, the immune system tries to destroy them, remove them from the body, and suppuration begins.
Difference from phlegmon
An abscess detected in time does not pose a serious threat to the health of the animal if treatment is started immediately.
You should beware of purulent diseases such as phlegmon.
With this pathology, inflammation develops in the deep tissues of the skin; it does not have clear boundaries, which leads to the development of gangrene.
Why does a boil occur?
A furuncle in a cat is a focal inflammation of the hair follicle and sebaceous gland, it is purulent and necrotic in nature, caused by staphylococcus bacteria (white or golden), see photo below. Simply put, the hair “bag” becomes inflamed, into which pathogenic bacteria and tissues around it enter. The process takes place under the skin, the affected tissues die (necrosis) and turn into pus, which is located in a kind of “vessel” that restrains the boundaries of inflammation. On the surface of a fully mature boil, you can see (sometimes more than one) gray-green dot - a rod.
The disease is not “universal”, but there are a number of breeds prone to the formation of boils. Most often, lesions appear on the chin - the cat scratches its face with its claws and causes an infection. Veterinarians identify a number of reasons that can trigger the occurrence of boils:
- Violation of conditions of detention, care, nutrition - lead to a decrease in the body's immune defense.
- Hypothermia, frostbite or skin burns, sudden temperature changes.
- Avitaminosis.
- Concurrent infectious diseases.
- Metabolic disorder or hormonal imbalance (estrus, false pregnancy, disease of the thyroid or adrenal glands).
- Chronic fatigue, anemia.
Important! Improper treatment of boils leads to relapses, but the affected area may become larger.
Types of abscesses
Depending on the location of the purulent process, abscesses in cats are divided into several types.
Surface
Location: upper layers of skin. Purulent capsules are small in size, do not cause blood poisoning, and do not pose risks to the health of the animal.
Deep
In this type, the pathological process involves muscle tissue and fat. The presence of a purulent capsule can be determined by palpation.
Odontogenic
Occurs in the oral cavity in the presence of advanced periodontitis. Often the process affects the roots of the teeth.
Paraanal
This is a pathology of the glands located in the anal area.
Neoplasms in the neck and head area
Purulent inflammation occurs when the skin is injured during a fight or injured in another way, and then becomes infected.
Symptoms
In a cat, an abscess can form several times throughout its life. In this regard, the animal owner must clearly understand how to promptly recognize the development of purulent inflammation in order to provide timely assistance.
The abscess develops gradually, one stage follows another. The earlier the inflammation was detected, the higher the chances of successful and painless treatment. Early stages of abscess formation, especially subcutaneous ones, can be successfully treated with conservative treatment without the use of surgical excision.
Inflammatory processes accompanied by the formation of purulent exudate are quite easy to identify if you regularly examine your pet for damage. The same applies to abscess of the paraanal glands. This pathology does not develop suddenly; it is preceded by characteristic changes.
For all types of purulent inflammation localized under the skin, the following signs are observed:
- Hyperemia of the affected area on the skin or mucous membrane (diagnosis of an abscess at this stage is possible by palpation; it is more difficult to do this visually).
- Severe swelling (a cavity begins to form in the affected area as the inflammatory process develops).
- Fluctuation is a kind of edematous swelling that occurs against the background of accumulation of purulent exudate in the cavity.
- Areas of baldness - hair begins to fall out at the site of the lesion (a similar symptom is especially pronounced when an abscess forms on the paw).
- The appearance of areas of necrosis - develops at later stages in animals suffering from insufficient functioning of the immune system (in cats with a good immune status, the resulting abscess bursts on its own, and the contents come out, otherwise, the pyogenic microflora begins to corrode the surrounding healthy tissue, provoking the development necrosis).
An abscess that occurs in a cat on the cheek from the inside or outside, as well as in the jaw, ear or upper part of the head, is characterized by an increase in local body temperature, decreased appetite, and severe pain. The cat looks weak.
In the absence of timely therapy, there is a risk of infection of healthy tissue structures located in close proximity to the abscess. Necrosis subsequently develops, and the infection can penetrate the systemic bloodstream. Sepsis (blood poisoning) develops, which can lead to the death of the pet.
Failure to treat a perianal abscess in a timely manner is especially dangerous. This is due to the fact that in the absence of therapy, which includes conservative and surgical techniques, a self-opening abscess with exudate provokes the formation of a fistula. Sepsis often develops against the background of a perianal abscess.
Forms of abscesses
Depending on the course of the disease, there are several forms of abscesses in cats:
cold: characterized by a sluggish course, with relapses turning into a chronic form;- superficial: can develop if you independently open a subcutaneous abscess in a cat, rarely accompanied by complications;
- deep: purulent compaction is observed in the deep layers of the skin or muscles, immediate treatment in a hospital is required;
- acute: only surgical opening will help; if left untreated, the prognosis is unfavorable;
- benign: goes away on its own, does not require special therapy, is accompanied by purulent discharge of white or yellow color;
- malignant: may indicate insufficient immunity, accompanied by an unpleasant odor in the mouth
The veterinarian will be able to accurately determine the area of inflammation and identify the form of the disease during the examination.
Reasons for the formation of suppuration
An abscess forms on a cat’s body due to dirt getting into even small wounds. Skin damage occurs for various reasons.
Injuries
The skin is often damaged during fights between animals. In the oral cavity, wounds occur when eating small bones, branches, or gnawing hard objects.
Failed injection
Often the infection gets into the wound when injections are given at home, on your own. An unsterilized instrument, incorrect dosage, temperature and consistency of the injected substance can lead to the development of an abscess.
Failure to comply with hygiene standards
In a dirty room, germs get into even the smallest scratch.
If the owner does not keep the pet’s mouth clean, dental diseases with abscesses develop.
Why can cats develop an abscess?
An abscess, as a rule, develops as a result of infection in a wound of even a small size. Most often, wounds on the body or mucous membranes of an animal occur as a result of:
- fights between cats, especially during heat;
- eating small bones and solid food, as well as in the absence of oral hygiene of the cat (in this case, the oral mucosa is affected);
- scratches and punctures from branches, grass, pebbles, thorns, needles;
- subcutaneous injections of poorly soluble drugs;
- non-compliance with sanitary standards for intravenous, intramuscular or subcutaneous administration of drugs (for example, an infection can be caused by an unsterile needle, as well as if sterility standards are not observed);
- bird attacks;
- bites from other animals.
An abscess does not always occur at the site of the lesion. It all depends on the size and depth of the wound, as well as the bacterial microflora that got into it. Thus, most often suppuration is caused by staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, anaerobic bacteria, and mycoplasmas.
Which animals are at risk?
The following categories of pets are most at risk of developing suppuration:
- stray - they most often get into fights with other animals;
- males, especially up to the age of seven, fight more often than females;
- uncastrated pets who often visit the street - this category is considered by other cats as potential rivals, which is why skirmishes also flare up;
- cats and cats with weakened immune systems.
Cats that go outside are at risk for developing abscesses
Animals at risk
The risk of purulent abscesses is higher in stray cats: they are more likely to get into fights with other members of the species and live in unsanitary conditions.
Other categories:
males under 7 years of age have a strong sexual instinct and often fight while walking;- non-castrated animals are perceived by other cats as serious rivals and are injured in fights;
- cats and cats if their immunity decreases for any reason.
Outdoor pets often suffer from purulent abscesses.
Signs of suppuration development
In cats, purulent abscess is a common occurrence. It is important for the pet owner to know all the symptoms of the pathology in order to respond promptly and correctly to its appearance.
An abscess goes through 5 stages of development:
- Redness of a small area of skin . The pathological process can only be identified with a detailed examination. The animal does not experience any discomfort when the disease occurs.
- Edema . As the infection spreads, a cavity forms under the skin, which gradually fills with pus and swells.
. The purulent capsule is completely filled with contents, increases in size, and becomes convex.
Fluctuation- Baldness . Hair begins to fall out on the affected areas of the skin and they become completely bare. During this period, the owner can easily determine the presence of pathology.
- Tissue necrosis . Ideally, if the animal has a strong immune system, if there is severe suppuration, the purulent capsule should rupture, and the contents will come out to the surface of the skin. In weakened animals, the inflammatory process continues and healthy cells become infected.
Diagnostic procedures
An abscess can appear in pets after sterilization or under the influence of other negative factors. When the first symptoms develop, you should contact a veterinarian who will help you properly treat the disease without causing complications. Before treatment, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out to determine the source of the abscess, its type and severity. The cat needs to undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
- laboratory testing to determine the causative agent of the disease;
- antibiotic sensitivity test.
During differential diagnosis, the presence of a hematoma in the animal should be excluded.
No less important is differential diagnosis, which helps to distinguish an abscess in a cat from pathologies such as:
- cystic formation;
- benign or malignant tumor;
- granuloma;
- hematoma;
- lymphoextravasate.
Treatment
After detecting a pathological process in a pet, you must immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
The sooner you start treating an abscess, the fewer negative consequences for the animal’s health will arise later.
Medicines
In the first stages of infection, pharmaceutical or veterinary drugs are used.
Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents are used. For these purposes, broad-spectrum antibiotics of the penicillin series are recommended: Tetracycline, Penicillin, Sinulox. The duration of therapy is from 7 to 14 days.
Surgical intervention
More often, an abscess requires opening in a hospital setting.
The place of suppuration is cleaned of hair and treated with antiseptics. Painkillers are administered, and the abscess is opened with a sterile scalpel. The pus from under the skin is cleaned out and drainage is installed.
After 3 days, the drainage tube is removed, anti-inflammatory ointments (Vishnevsky, Tetracycline) are placed in the wound, and a sterile bandage is applied. It is changed daily, tissue treatment is carried out twice a day.
To exclude the development of re-infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
Treatment at home
Squeezing out ulcers on an animal’s body yourself is strictly prohibited. Without knowing the technology of tissue cleansing, you can direct the flow of pus under the skin or reinfect the infection.
There is a high risk of blood poisoning, which leads to irreversible consequences.
Prognosis without treatment
If the pet is not given medical care, this will lead to tissue necrosis, infection of healthy cells, and infection in an open wound. As pus spreads under the skin, the outcome can be fatal.
Prevention of the development of purulent formations
Cat owners should try to prevent any disease in their pets. Preventive measures are the best remedy for the development of an abscess.
Necessary activities:
- castration;
- limiting walks on the street and contact with yard animals;
- vaccination according to schedule;
examination and sanitation of the oral cavity, brushing teeth twice a week;- exclusion of small bones and rough foods from the diet;
- regular inspection, identification of skin damage, their timely disinfection and treatment;
- sterilization of instruments during medical procedures at home;
- treatment for fleas, ticks, lice;
- maintaining sanitation and hygiene.
As soon as a kitten gets into the house, it needs to create all the necessary conditions for proper development, provide age-appropriate food, and provide timely veterinary care.