Method of use and dosage of deworming tablets in cats
Worms in cats.
The best option is when the method of use and dosage of anthelmintic tablets is prescribed by a doctor. If this is not possible, then you need to take into account the fact that the dose of the drug is calculated individually depending on the weight of the cat. Dosage details should be read in the annotation for the drug. For example, the popular drug Drontal is dosed at the rate of 1 tablet per 4 kilograms of animal weight, and the Pratel tablet is used in half per 5 kg of weight. Taking anthelmintic tablets as a preventive measure is carried out once in the morning before meals. Treatment of helminthic infestations requires repeated administration of the drug one week after the first. During pregnancy, cats are given anthelmintic tablets 14-20 days before the expected birth or after 2-3 weeks.
Small kittens are given tablets as needed from 2-3 weeks of age. Prophylactic administration of anthelmintic tablets must be repeated every 3-6 months, especially in cats that have access to the street or constantly eat raw meat or fish.
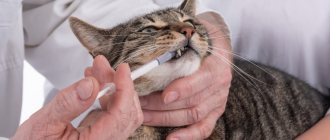
The crushed tablet can be mixed with the main food, or given to the cat whole, placing it in the open mouth of the animal at the base of the tongue: this will trigger the conditioned swallowing reflex, and the cat will quickly swallow the drug. For small kittens, the necessary part of the tablet is mixed with food or milk.
Cases of overdose of anthelmintic tablets in cats are extremely rare. Only small kittens often receive a larger dose, for whom it is more difficult to correctly calculate the dosage. In such situations, manifestations of general intoxication are possible, but not from the tablets themselves, but from the massive decomposition of a large number of simultaneously affected helminths.
If you suspect that you have administered the dosage of the anthelmintic tablet incorrectly, and your cat has seizures, trembling legs, or shortness of breath, try to urgently consult a veterinarian.
Subcutaneous parasites in cats
All parasites that live in the layers of skin in cats are conventionally called “subcutaneous mites” or internal parasites in cats. Among them the most famous are:
Types, names and photos
Demodex
(Demodex cati). Microscopic worm-like organism. Lives in the hair follicle of the animal, moves at night. It feeds on excess subcutaneous fat. When immunity declines, the tick manifests itself by releasing toxic waste. Insufficient nutrition causes its death after 2-3 weeks. As the tick decomposes, it causes inflammation in the cat.
Scabies
. Localizes near the ears and on the face. Deeply affects the subcutaneous layer. Can lead to blood poisoning.
Notoedres cati
. It goes unnoticed for a long time. It provokes the development of scabies, which is often replaced by fungus and dangerous bacterial infections.
Reasons for appearance
The reasons for the appearance of subcutaneous parasites in cats are as follows:
- Interaction with the owner’s clothes and shoes, on which he could bring ticks;
- Contact with infected relatives;
- Lack of hygiene;
- Failure to complete vaccination on time;
- Lack of inspections.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of subcutaneous parasites in cats are:
- Itching;
- Redness;
- Irritation and inflammation;
- Dandruff rash;
- Hair loss in some areas;
- Lethargy;
- Loss of appetite;
- The appearance of weeping wounds;
- The appearance of pustules.
Infection with intestinal parasites
Cats and cats can become infected with all kinds of intestinal parasites, including pinworms. Various symptoms indicate that animals are infected with worms of this kind, although most often no external changes are observed. Signs of pinworm infection may include vomiting several times a week and frequent diarrhea. But in any case, pets should be carefully monitored and the situation monitored every day. After all, a cat may look healthy and its owner may not immediately understand the essence of the disease.
Pinworms in cats are a potentially serious problem that can have a negative impact on their health. Pinworms hide especially carefully in the body of an adult animal, quietly and slowly destroying it from the inside.
Cats living at home can become infected with helminths in the following ways:
- from flies, fleas, rodents, which are carriers of parasites;
- as a result of eating raw and poor quality food;
- due to contact with other animals;
- from dirty shoes;
- after a street walk.
A cat infected with worms can transmit them through its milk to born kittens, which are quite difficult to tolerate this infection. Pinworms cause disruption of the normal intestinal microflora and can cause various infectious diseases in pets.
Helping your pet get rid of helminths
If a cat lives in your house, then you are often faced with the problem of the appearance of worms, in particular pinworms, they cause unpleasant troubles and torment for the animals. Even if your pet never goes outside for a walk, the likelihood of pinworms is considerable. If the cat has a strong immune system and is in good health, then helminth infections may not have visible symptoms. But otherwise, the presence of pinworms can lead to serious consequences.
The animal should be regularly examined, its bowel movements monitored and treated for worms at least twice a year. To rid an animal of intestinal worms, annual vaccination is necessary to avoid serious complications. If there are several cats in the house, then treatment should be carried out simultaneously for all. Anti-pinworm medications are used several times with an interval of ten days. Given that no deworming medicine has any effect on the worm larvae, several methods should be used to kill intestinal parasites.
The most popular medications used to rid a cat of pinworms are:
- Drontal - a product used for the treatment and prevention of helminths.
- Pyrantel is a tablet that destroys pinworms in a short time.
- Poliverkan - special sugar cubes for killing worms.
- Profender – drops for adult cats against helminths. This product is not recommended for newborn kittens.
All of the above drugs act effectively and quickly, relieving the animal of an uncomfortable painful condition.
Causes of infection
The main reason why any cat living at home is affected by the parasite is the problem of improper nutrition. Various products such as meat, fish or poultry may contain helminth eggs in significant quantities. They can die only with sufficient heat treatment, the temperature at which reaches 180 degrees, or with prolonged freezing (about a week). If a pet is constantly fed raw meat, then the risk of eggs entering the gastrointestinal tract and infection increases to its maximum.
The most likely cause of infection is cats that constantly walk outside. The cat constantly comes into contact with street animals that may have pinworms and their feces, as well as with the ground. In soil and vegetation, pinworms can remain active for infection for many months.
Another route of infection is provided by the host himself. If the animal does not walk on the street, but lives only at home, it can get parasite eggs from the owner’s shoes or clothes that he was wearing outside. More often, this type of infection is facilitated by feeding the pet dry food, which contains practically no useful elements and vitamins.
The clinical picture is not very noticeable, but some signs attract attention:
In the initial period of the disease, in the first few days, one may notice enlarged lymph nodes, increased body temperature, a dry and hot nose, sneezing or coughing. As the disease progresses, gastrointestinal disorders develop
It manifests itself mainly in the form of liquid or liquefied stool, which may contain mucus or blood. Sometimes the cat's abdomen becomes noticeable: it becomes swollen, and gas is released. The cat does not allow you to touch its belly; its behavior is restless. Then dyspeptic disorders occur, the cat loses its appetite, and in most cases vomiting occurs.
Not a single dish makes you want to eat, even your favorite one. Unusual behavior appears, which is characterized by eating inedible things. The cat may eat pebbles, paper or anything else, preferring solid objects. Symptoms of intoxication become more and more pronounced. The waste products of the parasite have an increasing impact on the cat’s body. The animal is lethargic, apathetic, sickly in appearance, behaves aggressively, gets tired quickly and looks drowsy. Allergic reactions are possible, which manifest themselves in itching and redness of the skin. The animal is constantly itching, leaving bloody scratches. Pinworms have their own peculiarity. When a sexually mature individual, while in the body, needs to lay its eggs, it descends to the lowest part of the intestine to the anus. Then the pinworm secretes a special secretion so that the laid eggs have the opportunity to attach, leaves the offspring and returns back to its usual place of attachment. This process causes severe itching in the anus. The cat begins to rub this area on the floor and tries to wash itself in this area as often as possible.
Ways of infecting an animal with parasites
Even domestic cats that never go outside are not protected from helminthiases.
Most often, the owner himself is to blame for the fact that parasites have settled in his pet’s body. One of the most important reasons for the occurrence of infection is improper diet, in particular feeding your pet raw meat and fish.
Most worms and their eggs die only during prolonged heat treatment and many days of freezing. Eating raw river fish by a cat leads to a disease called opisthorchiasis.
Cats walking outside further increase the risk of infection. Contact with feces, other animals, water and soil, where helminth eggs remain viable for a long time, leads to infection.
And the owner himself brings eggs and parasites from the street on clothes and shoes, which can also get to the cat.
A factor contributing to infection is the presence of fleas in the cat. Fleas can be intermediate hosts for cucumber tapeworm larvae.
An animal can pick up worms from a person infected with pinworms. Enterobiasis is a disease characterized by frequent repeated self-infections. Female pinworms lay eggs outside the host (human) and easily land on clothing, bedding, and household items. A cat can swallow pinworm eggs with dust and lick them from the fur. But in the body of a cat, pinworms cannot go through the entire life cycle, therefore, despite entering the cat’s stomach, further development of the disease does not occur. And if the owner notices whitish worms in the pet’s feces, then these are not pinworms, but other helminths. There is a high probability that this is a tapeworm known as cucumber tapeworm, which causes a disease called dipylidia.
Types of worms in cats
There are many varieties of helminths. What kind of worms do cats have?
- Flat helminths: trematodes (flukes) and cestodes (tapeworms - tapeworms and tapeworms).
- Roundworms: (roundworms, toxocara, hookworm).
- White nematodes.
Pets can be bothered by all types of worms, but the most common types are roundworms and tapeworms. They affect the intestines, gall bladder, lungs, liver and even the heart, depending on the degree of infection and the type of worm. Parasites feed on lymph, blood, tissues and deplete the host’s body. In the most advanced cases, invasion can lead to the death of the animal.
Tapeworms in cats
Flat or tapeworms in cats reach a size of 10-70 cm, their body is divided into a large number of segments, from which the larvae develop. These worms parasitize in the small intestine and provoke vomiting and lead to weight loss in the pet. Tapeworms are dangerous because they are transmitted through fleas to other pets. Cats also become infected with them when they eat small rodents, raw fish, and insects that carry pinworms.
In a pet affected by tape parasites, it is easy to notice segments of the worm in the stool around the anus, similar in appearance to grains of rice. Worms in cats damage mucous membranes, feed on tissues and blood, and release toxic substances into the body. Severe infection can cause blockage, rupture of the intestines and lead to the death of the pet.
Roundworms in cats
It is important to know what worms look like in cats in order to help your pet get rid of them in time. Roundworms are small parasites, the most common of which are roundworms, which look like spaghetti
Their size does not exceed 5 mm; longer specimens are less common - up to 10 mm; the animal may not survive in such cases. Two weeks after infection, helminth eggs can be easily detected in the stool.
The maximum number of parasites is observed in the small intestine; they feed on blood; with a strong accumulation, blockage of the bile ducts occurs. This group of worms is dangerous for cats; their waste products cause intoxication of the body. In small newborn kittens, roundworms can cause life-threatening anemia.
White worms in cats
Nematodes are small, thread-like, white helminths up to 2 cm in length. Worms in cats drink blood, clinging to the walls of the small intestine. Nematodes pose a mortal danger to your pet’s well-being, especially for kittens. Infection can occur through contact with the feces of a sick relative or contact with particles of soil infected with pinworms. Kittens often become infected through their mother's milk. Signs of worms in a cat (nematodes):
- diarrhea;
- anemia;
- wounds on the skin, especially on the paws;
- darkening or blackness of feces, presence of blood in the stool.
Prevention of helminthiasis in cats
We looked at what worms cats have and now all that remains is to figure out how to avoid becoming infected with them.
The most important aspect to guarantee the health of your pet is compliance with preventive measures that exclude:
- Animal eating rodents
- Communication with street relatives
- Including raw meat and fish in your diet.
In addition, it is necessary to regularly carry out drug deworming. For exclusively domestic animals, at least twice a year. If your pet walks freely on the street, then every three months he needs to be given anti-worm medications.
It is necessary not only to maintain personal hygiene, but also to periodically disinfect living areas, keep the animal’s sleeping place and the dishes from which it eats clean. This will help avoid infecting both your cat and everyone else who lives in your home with helminths.
General signs
All parasitic infections do not manifest themselves from the first days of infection. The first symptoms appear only after the end of the incubation period. But even during the development of infection, changes in behavior and other alarming symptoms can be noticed.
Worms in cats can be suspected based on the symptoms of parasitic infection.
Parasitic infections are similar in many ways, so scientists were able to create a list of common symptoms that will help to understand that a cat has worms. Here he is:
- First of all, appetite worsens or, on the contrary, increases, depending on the type of parasites and the stage of development of the infection. Eating behavior may change, for example, the pet refuses its favorite food or treats, preferring something that it did not like before.
- The activity of the digestive system is disrupted. There may be diarrhea, indigestion, bloating, flatulence, and vomiting.
- Symptoms from the respiratory system may also be observed. The most common symptom is coughing attacks and difficulty breathing.
- A cat infected with worms may suffer from bowel problems. There may be blood or blood clots in the stool.
- A cat may have one or both eyes sour. Nasal discharge may also appear. Often, a parasitic infection manifests itself as purulent discharge from both the eyes and nose.
- The pet becomes lethargic and the level of activity decreases. Sometimes lethargy can suddenly give way to periods of nervous excitement and aggression. This symptom appears especially often if parasite toxins affect the pet’s nervous system.
A pet infected with worms looks sick and lethargic
- If the nervous system is damaged, the hind limbs may fail, lameness or complete paralysis may appear. Veterinarians must send animals with such symptoms for analysis to check for the presence of parasites in the body.
- Long-term development of parasites in the body leads to sudden hair loss and a change in its appearance. Bald patches may appear, the coat becomes dull and sparse.
- There is itching in the anal area, redness, and rash.
- It is also possible that symptoms from the liver may appear - it can be felt on palpation, which indicates its enlargement. The mucous membranes acquire a yellowish tint as a result of impaired excretion of bile.
If your kitten has one of the listed signs of worms, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. You should not try to diagnose your pet's problem yourself.
Important! Many symptoms of a parasitic infection are similar to those of colds and viral diseases; there is a high risk of diagnostic error. Only a veterinarian can say exactly what caused the cat’s discomfort.
How to treat cats at home
If you need to give your pet medicine at home, you can use one of the methods.
- The tablet is crushed and diluted in a small amount of water. The resulting composition is drawn into a syringe without a needle, which is carefully placed behind the animal’s cheek and the medicine is poured in. After this, the cat’s mouth is closed so that it does not spit out the composition.
- The tablet does not need to be diluted in water - in this case, the cat is placed in the arms, with its back to the owner’s body, the mouth is opened and the tablet is placed there. After this, the mouth is closed and the animal’s neck is lightly stroked until it swallows the medicine.
- You can mix the crushed medicine with the food. As a rule, this method works quickly.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is not very noticeable, but some signs attract attention:
In the initial period of the disease, in the first few days, one may notice enlarged lymph nodes, increased body temperature, a dry and hot nose, sneezing or coughing. As the disease progresses, gastrointestinal disorders develop
It manifests itself mainly in the form of liquid or liquefied stool, which may contain mucus or blood. Sometimes the cat's abdomen becomes noticeable: it becomes swollen, and gas is released. The cat does not allow you to touch its belly; its behavior is restless. Then dyspeptic disorders occur, the cat loses its appetite, and in most cases vomiting occurs.
Not a single dish makes you want to eat, even your favorite one. Unusual behavior appears, which is characterized by eating inedible things. The cat may eat pebbles, paper or anything else, preferring solid objects. Symptoms of intoxication become more and more pronounced. The waste products of the parasite have an increasing impact on the cat’s body. The animal is lethargic, apathetic, sickly in appearance, behaves aggressively, gets tired quickly and looks drowsy. Allergic reactions are possible, which manifest themselves in itching and redness of the skin. The animal is constantly itching, leaving bloody scratches. Pinworms have their own peculiarity. When a sexually mature individual, while in the body, needs to lay its eggs, it descends to the lowest part of the intestine to the anus. Then the pinworm secretes a special secretion so that the laid eggs have the opportunity to attach, leaves the offspring and returns back to its usual place of attachment. This process causes severe itching in the anus. The cat begins to rub this area on the floor and tries to wash itself in this area as often as possible.
However, the presence of the above symptoms does not always make the owner suspect that his pet has a parasite. In most cases, a person understands that his pet has helminthiasis only when he discovers white larvae in the animal’s feces.
Treatment
Treatment of enterobiasis always begins with the selection of an anthelmintic drug for the child. Many of these medications are quite strong and toxic, and therefore parents should understand that a parasite remedy for children and a similar medicine for adults are not the same thing. Only a doctor should choose a drug and prescribe a dosage.
For children from six months to a year and a little older, it is usually more difficult to choose an anthelmintic drug. It is necessary that the medicine be poisonous to parasites, but not poison the body of the little one. In pediatric practice, the most commonly used drugs are “” and “Nemotsid”.
"Pirantel"
The drug exists in a very convenient form of release for children - in suspension. The active substance of the same name causes neuromuscular blockade in parasites. It affects both adult worms and young individuals. A single dose for babies is calculated based on the child’s weight - 10 mg of suspension for each kilogram of the baby’s weight
For children under six months of age, if necessary, the drug is also prescribed, but it should be given with great caution, and the doctor calculates the dosage individually. A single dose is usually sufficient
Children 5-6 years old can be given the drug in tablet form.
"Piperazine"
This is a softer and more gentle drug. It causes paralysis in parasites, but does not kill them completely, and therefore the individuals simply do not have time to release toxins into the child’s body, which are produced upon death. That is why Piperazine is considered the most preferred treatment for pinworms in children.
However, it should be noted that the product is only available in tablets. To get rid of pinworms, you need to take the medicine in a strict age-specific dosage (it is indicated for each age in the instructions for use) for 5 days. A week later the course is completely repeated.
"Vermox"
This drug is available in tablets. The active ingredient, mebendazole, prevents pinworms from eating fully, disrupting their glucose absorption process. Deprived of food, the worms die quite quickly (within 2-3 days) from exhaustion. The drug does not have a pronounced negative effect on the body, and therefore it is often used not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of helminthic infestations.
During treatment, children from two to five years old are given a quarter of a tablet once. Then, after two weeks, the same dose of the drug is given again, and after another two weeks, another one. The same scheme, but a different dosage - half a tablet - is used for children from five to ten years old. Older children and teenagers are given a whole tablet according to the same scheme.
"Nemozol"
This drug kills pinworms in a comprehensive manner - paralyzing them and depriving them of glucose. This medicine is one of the most prescribed in pediatric practice. "Nemozol" is considered one of the most effective anthelmintic drugs. The product is available in tablets and suspensions.
Manufacturers advise taking the suspension with fatty foods, so the active ingredient - albenidazole - is absorbed faster. For children from one to two years old, a single dose of 1 dessert spoon of suspension is recommended. Children over 2 years old are given 20 ml of the drug once. Tablets can theoretically be given to children from 3 years of age. Single dose - 1 tablet.
Rectal suppositories
If you really don’t want to give your child tablets and suspensions, then with the doctor’s permission you can use drugs that come in the form of rectal suppositories. This is not the cheapest or most economical treatment option, but in terms of effectiveness, suppositories are almost as effective as medications that need to be taken orally.
For children over six years old, you can use Nigella Sativa and Wormil candles. "Vormil" can be bought for children who are already 2 years old. The suppository is administered into the rectum once in the evening before bedtime, after which it is recommended to repeat the course after three weeks.
Tablets and medicines for pinworms for children
Enterobiasis in childhood is the most common parasitic disease. Statistics indicate that every child has been infected with pinworms at least once in their life.
To rid a child of a parasitic infestation, he will need pills for pinworms. They should be prescribed by a doctor based on test results. Even if parents independently discover pinworms in their child’s stool, they should consult a doctor. Only a specialist can correctly select the dose of the drug, determine the frequency of dosing, etc. It should be remembered that not all medications for pinworms can be used in childhood. Most of them have age restrictions.
How dangerous are pinworms for children?
Very often, enterobiasis occurs latently and symptoms of the disease may be absent altogether. However, this does not mean that pinworms do not pose a risk to a child's health.
- Functional disorders of the digestive organs. The intestines are most often affected. The child complains of abdominal pain, he is tormented by flatulence, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Allergic reactions. Their development is provoked by the toxic waste products of pinworms.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome. Children with enterobiasis get tired faster, begin to lag behind in their studies, and their performance decreases.
- The presence of pinworms has a negative effect on the appetite of children.
- Girls with long-term enterobiasis are susceptible to the development of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system. In addition, parasites can provoke enuresis.
- The quality of night's rest is deteriorating. Sleep becomes restless, children begin to grind their teeth at night. This significantly damages the tooth enamel.
Parasites that are in the migration stage are dangerous. They can cause pneumonia and bronchitis and can penetrate organs other than the intestines.
How to treat pinworms in children
Tablets for pinworms for the treatment of children should be selected by a doctor. Almost all of them are very toxic and, if used incorrectly, can harm the health of a child.
Pirantel
Pyrantel is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of worms in children. It can be used to treat enterobiasis in children under one year of age, but the dosage must be strictly observed.
Contraindications to taking the drug are individual intolerance to the components that make up the drug.
Side effects include:
- Vomiting, nausea, digestive disorders.
- Increased body temperature.
- Allergic reactions, skin rash.
Pirantel is prescribed to children depending on age in the following dosage:
- From 3 to 6 years 250 mg.
- From 6 to 12 years 500 mg.
- From 12 years and older 750 mg.
The calculation is based on a dose of 10 mg/kg body weight. The drug is taken once. A week later the course is repeated.
Piperazine
Piperazine is an anthelmintic drug used to treat enterobiasis. It is often prescribed for antiparasitic therapy in children under one year of age.
Contraindications to taking the drug:
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- Organic lesions of the central nervous system.
To treat enterobiasis in children, Piperazine will need to be taken for 5 days. Then take a week break and repeat the course. The number of courses can be from 1 to 3. In between taking the drug, the child should be given a cleansing enema. For this purpose, you can use a solution based on soda and boiled water. You need to take half a teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate per glass. Dosage for the treatment of children of different ages (single dose):
- Children under one year of age 200 mg.
- 2-3 years 300 mg.
- 4-5 years 500 mg.
- 6-8 years 750 mg.
- 9-12 years 1 year
- 13-15 years old 1.5 g.
Side effects:
- Nausea, abdominal pain.
- Headache.
- The drug should be prescribed with caution for the treatment of patients with renal failure, as there are risks of developing neurotoxic complications.
Zentel
The drug Zentel with the main active ingredient Albendazole is prescribed for the treatment of enterobiasis in children over one year of age. The drug is available in the form of a suspension and tablets.
Contraindications for use:
- Less than a year old.
- Albendazole intolerance.
- Ages under 3 years for tablet form.
- Diseases of the retina.
- Pregnancy, lactation period.
Dosage:
- 2-3 years 10 ml suspension once.
- 1-2 years 5 ml suspension once.
- After 3 years and older, 400 mg of the drug once.
Side effects:
- Skin rashes and skin itching.
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
- Increase in body temperature.
- Hepatitis.
- Hair loss (until completion of treatment) and other side effects characteristic of Albendazole.
Mebendazole
Mebendazole is a broad-spectrum drug that is most often used to treat enterobiasis in adults and children over 2 years of age.
Contraindications for use:
- Under two years of age.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Hypersensitivity to Mebendazole.
- Severe liver dysfunction.
Dosage:
- Children from 2 to 10 years old: 25-50 mg once.
- Children 10 years and older: 100 mg once.
If necessary, the course can be repeated after 14-28 days.
Side effects:
- Abdominal pain, nausea.
- Dizziness.
If the drug is taken for a long time and in high doses, then the development of eosinophilia, anemia, leukopenia, headache, hematuria and other side effects is possible.
Levamisole
Levamisole is not prescribed for the treatment of children under 14 years of age. Levamisole acts on pinworms and other worms in such a way that they become paralyzed and are excreted from the intestines along with the feces.
Contraindications to taking the drug:
- Age under 14 years.
- Hypersensitivity to Levamisole.
- Hematopoietic dysfunction.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Pregnancy, lactation.
- Glucose intolerance.
The dosage for patients over 14 years of age is 150 mg. The drug must be taken once.
Side effects:
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Increased heart rate.
- Dizziness, insomnia, encephalopathy.
- Allergic reactions.
Niclosamide
Niclosamide is an anthelmintic drug whose action is aimed at paralyzing the muscular system of parasites, as a result of which they become unable to remain in the intestines and are excreted along with the feces.
Niclosamide is used to treat taeniasis, hymenolepiasis, diphyllobothriasis and taeniarynchosis.
Contraindications for use:
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding.
- Individual intolerance to the components of the drug
The drug can be used to treat parasitic infestations in children over 2 years of age. For children under two years of age, Niclosamide can be prescribed only for health reasons.
Calculation of daily dose:
- Children under 2 years old – 0.5 g.
- From 5 to 12 years 1.5 g.
- From 12 and older – 2-3 years.
The tablets must be chewed thoroughly or pre-crushed. The average duration of treatment is 4 days.
Possible side effects:
- Skin itching, urticaria and other allergic reactions;
- Nausea;
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence;
- Photophobia;
- Neurodermatitis.
Symptoms
During the incubation period, it is not possible to notice signs of the presence of pinworms in the body. The first and most characteristic sign appears already at the final stage of the worms’ life cycle - when eggs are laid. Females secrete a special acid that causes severe, unbearable itching in the anus.
Itching sensations intensify in the evening and can also torment the child at night. If the baby begins to worry and constantly tries to scratch his butt, this is a reason to carefully examine the anus. He looks irritated and red; if you look closely, you can see small semi-oval, irregularly shaped pinworm eggs. If the scratching is severe, then a secondary bacterial infection cannot be ruled out.
Enterobiasis in a baby is somewhat more difficult to notice, because the area around the baby’s bottom turns red not so rarely for other reasons - diaper rash, contact dermatosis. However, the anxiety of an infant who cannot yet adequately respond to itching and scratch what itches will be much more severe than with contact dermatosis. It will also intensify in the evening and at night.
Children often develop additional symptoms - abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. They will not be pronounced, as with an acute infection; rather, such signs are sluggish and latent, unstable. In other words, diarrhea may be replaced by constipation, and vomiting will not be as frequent. But attentive parents will be able to notice that something is wrong.
Roundworm toxins can affect the nervous system. But this is only possible with extensive helminthic infestation; a small number of parasites cannot cause sleep disturbances, irritability, headaches, or tearfulness. If this condition is accompanied by evening scratching of the butt, you need to run to the doctor as soon as possible - the number of pinworms in the body is large.
True, during the daytime a child in such a situation will also go to the toilet for minor needs much more often, and the volume of urine will be small.
Abundant white and creamy discharge with an unpleasant odor from the genitals in girls may indicate the onset of an inflammatory process in the reproductive system. Children who are prone to allergies may begin to suffer from allergic attacks, eczema and dermatitis. The manifestations of such a parasitic allergy will be different, depending on how the pinworm antigen is perceived by the baby’s immune system. Most often this is a skin rash, but there can also be an allergic cough, runny nose and even inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
A child with enterobiasis has a weakened immune system. If at this moment you give a reactogenic vaccination, for example, DTP, then the reaction to it will be more violent - with fever, manifestations of an allergic nature.
What are the types of worms in cats?
Helminthiasis diseases differ from each other depending on which worm affects the body. Parasites are divided into three main groups:
- Roundworms or nematodes in cats have a length of 2 millimeters, but sometimes can reach 10 centimeters (in particularly advanced cases of the disease). With such a severe form of helminthiasis, the animal may no longer be saved. This type of parasite lives primarily in the small intestine, consuming the host’s blood and causing life-threatening anemia, which is often found in kittens. Worm eggs are found in the animal’s feces 14 days after infestation.
Roundworms or nematodes in cats
- Tape or cestodes are flat helminths, having a length of 10 to 70 centimeters, the body of which is divided into a large number of segments in which worm larvae develop.
These types of worms can be transmitted through flea bites, making them more contagious than other types of worms. In an animal infected with tape parasites, helminth segments can be found on the fur around the anus, which in appearance resemble grains of rice. Cat feces will also contain such inclusions.
This type of helminth can be transmitted through flea bites
- Trematodes or flukes. They occur much less frequently than the two previous types and cause damage to the liver and pancreas with corresponding symptoms requiring laboratory tests.
Worms affect the gastrointestinal tract, muscle tissue, and sometimes the heart in cats; they can cause serious conditions and even death of the animal. Let's look at a photo with the names and brief characteristics of each parasite, list the symptoms of diseases caused by them, and also find out what treatment is carried out for worms.
Trematodes or flukes cause damage to the liver and pancreas with corresponding symptoms
Internal (intestinal) parasites in cats
Cats can harbor many types of helminths in their bodies. There are 3 main types of internal intestinal parasitic worms in cats - nematodes, cestodes and trematodes. We will tell you about them in detail - about the reasons for the appearance, symptoms of internal parasites in cats, as well as other features of each species. Most often, these parasites can be visually detected in the feces of cats. Here is as much detail as possible about all worms in cats.
Nematodes (roundworms)
| Name and features | Reasons for appearance | Symptoms |
| The most common worms are roundworms, of which there are a huge number of varieties. Most often, the cat's body is affected by roundworms. Their length can reach 5 cm. The worms move through the contents of the small intestine. but can also affect other internal organs. When there are too many of them, the worms can clog the intestines or bile ducts. Cause allergies and severe poisoning of the body. Nematodes feed on the blood of an infected animal. |
|
|
The most famous nematodes include roundworms. Roundworms are one of the most dangerous parasites in cats, which, among other things, are also transmitted to humans. For treatment of these worms, universal types of anthelmintics are recommended. The drug is administered to the animal orally in two doses, with 14 days between them. Disinfection of “cat things” is carried out. If re-treatment is required, another drug is prescribed.
Cestodes (tapeworms)
| Name and features | Reasons for appearance | Symptoms |
| These flatworms can reach up to 70 cm in length. They live on the walls of the small intestine. White worms and their segments with larvae resembling sesame seeds are passed in the feces. Segments can be found on the animal's bedding, or in severe cases of the disease - in the vomit. A frequently encountered representative of tapeworms is the cucumber tapeworm. It is 20-30 cm in length. Affects the intestines. Causes a dangerous helminthic disease - dipilidia. |
|
|
Treatment of cats for internal parasites such as tapeworms aims to destroy the causative agent of the disease. Anthelmintic drugs based on praziquantel and febantel are used. As a preventive measure, the animal is treated with insectoacaricidal preparations against insect parasites, in particular fleas that carry tapeworms.
Trematodes (flat flukes)
| Name and features | Reasons for appearance | Symptoms |
White filamentous helminths parasitize both the intestines (white parasites in cats) and other internal organs - the liver, bladder and even lungs. Although they are rare, their harm is enormous and the disease can be fatal. Cats are parasitized by 2 types of trematodes:
|
| The symptoms of the disease are the same as when infected with other helminths. |
For prevention purposes, it is recommended to deworm your pet with special anthelmintic drugs. They also treat the animal. You must strictly follow the instructions and remember that you need to select medications by category:
- For the treatment of kittens;
- For pregnant cats;
- For adults.
Detailed video on how to remove internal parasites from cats. How to treat, how to diagnose correctly, etc.:
What to do if cats become infected with worms?
Diagnostics
To identify such helminths, it is enough to do an analysis of the animal’s feces.
If there is a suspicion of pinworms, the owner should observe the pet's feces. Parasites can often be seen with the naked eye. If worms are not found in the feces, but the symptoms are severe, it is recommended to contact a veterinary clinic. To identify parasites, stool is examined for worm eggs, with repeated analysis after 2-3 weeks.
Treatment with drugs
Medicines are prescribed by a veterinarian; self-medication can worsen the condition. To expel pinworms from a cat, medications are prescribed, such as:
- "Prasitel";
- "Drontal";
- "Polyverkan";
- "Pyrantel";
- "Embowin."
Folk remedies
Herbal decoctions can be given to a cat only after consultation with a veterinarian. Using wormwood tincture in alcohol is effective. To do this you need 10 drops. dilute a little with water and pour into the animal’s mouth using a syringe without a needle. Pinworms in cats can also be expelled with decoctions of chamomile, fennel, and tansy herbs. Preparation:
To rid your pet of infestation, you can use tansy.
- Take 5 g of the plant and pour 200 ml of boiling water.
- Leave for 1 hour, filter.
- Give to the cat 60 minutes before. before meals 3 r. per day 5 ml.
This is interesting: The cat sleeps a lot, is this normal: we’ll tell you in general terms
Cucumber tapeworm
Cucumber tapeworm (lat. Dipylidium caninum), or dog tapeworm, is a helminth from the class of cestodes (tapeworms) that is the causative agent of dipylidiosis. The adult worm mainly parasitizes the body of a dog or cat, but is rarely found in humans. Human infection occurs through accidental ingestion of an infected flea, dog lice, or through the saliva of animals. Young children who come into contact with their pets are especially susceptible to the disease.
Structure
The length of an adult worm is about 10-70 cm. The width of the parasite's body reaches 2-3 mm. The scolex (head) has a proboscis and four suckers. The anterior part of the head section contains hooks arranged in 8 rows, with which the helminth is attached to the walls of the host's intestines. Ripe segments (proglottids) look like cucumber seeds, hence the name of the parasite. Each segment contains small cocoons. They develop eggs, the size of which is up to 0.05 mm. They come out after mature proglottids become independently active and enter the external environment.
Life cycle
The definitive hosts of parasites are dogs, sometimes cats, and in rare cases people (usually small children). Intermediate hosts are fleas and dog lice eaters. The life cycle begins when active segments are excreted from the host in feces. After the destruction of their shells, the eggs come out. Then some of them, remaining on the dog’s body, in the bedding or on the floor, are swallowed by the larvae of intermediate hosts. Inside them, the parasite larva (oncosphere) penetrates the walls of the digestive system into the body cavity and develops into the next form - cysticercoid.
The final animals are also representatives of the canine family (dogs, wolves, foxes) cats, raccoons. When a person or animal swallows an infected adult flea, infection occurs. The parasite enters the body of the final host and immediately attaches to the wall of the small intestine. There, the helminth develops into an adult worm, which reaches maturity about a month after infection. The life cycle is completed when the segments with eggs are released into the external environment with feces.
Prevalence
Cucumber tapeworm is ubiquitous. The greatest threat of infection is observed in animal kennels and dog walking areas.
In humans, infection with cucumber tapeworm is very rare. But if this does happen, it is more often in young children. Only 16 cases of this parasite in humans have been reported over the past 20 years, and almost all involved children. Such cases have occurred in Europe, the Philippines, China, Japan, Argentina and the United States.
Young children and toddlers are at greater risk of infection due to their particularly close contact with pets. People become infected accidentally by ingesting an infected flea, pet saliva, or eating contaminated food.
Symptoms and treatment in pets
Cucumber tapeworm does not usually cause symptoms in dogs or cats, and most pets do not show any symptoms other than increased appetite. One of the possible signs may be the animal's attempts to rub its butt on the ground or floors in the house, which is caused by pain and itching when the mature segments of the worm come out along with the eggs.
For treatment, tablets that are sold in veterinary pharmacies and contain praziquantel are sufficient.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is based on the detection of proglottids, eggs, or the parasite itself in the stool. The eggs are round or oval in shape, averaging 35-40 microns in size, and include oncosphere larvae equipped with six hooks. Eggs are observed in the form of packages of 5-15 (sometimes more) pieces.
Symptoms
In most cases, the infection is asymptomatic. But sometimes these symptoms can be noticeable: mild diarrhea, bloating, colic, anxiety, constipation, dizziness, increased salivation, decreased appetite, abdominal and head pain, pale skin, itching and pain in the anus when proglottids come out, weight loss for no apparent reason .
The child may have released proglottids (worm segments), which remain active for some time and resemble larvae.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out with praziquantel in a single dose of 5-10 mg/kg. Or, alternatively, niclosamide - 2g for adults as a single dose or divided into two parts and taken one hour apart.
For the purpose of prevention, it is recommended to remove fleas from animals.
Worms in kittens - main types
Many novice cat owners ask what worms look like in cats. In fact, there are many types of parasites that infect animals. Some scientists say about eighty. But kittens have worms, the symptoms of which are most common. There are three main groups of worms: nematodes, cestodes and trematodes. They will be discussed here.
Worms in kittens - cestodias
Cats become infected with these worms by eating raw meat, mice, and fish; they are carried by fleas. Diphyllobothriasis - the invasion is caused by a long, up to one and a half meter flatworm.
Failure to treat worms in cats can have serious consequences. Alveococcosis is caused by a small worm that lives in the small intestine. It is not very dangerous for the animal, but these worms in cats are transmitted to humans.
Signs of worms in a cat associated with this parasite appear in the form of weight loss, anemia, and sometimes vomiting blood.
Dipylidiasis is caused by a flatworm 20-30 centimeters long. Parasites attach to the intestinal wall, thereby destroying the mucous membrane. Animals lose weight and develop diarrhea with mucus and blood.
Worms in kittens - nematodes
Nematodes: Toxocariasis is caused by small worms that live in the intestines and bile ducts. They are transmitted either through food or in utero. Signs of worms in a cat appear in the form of weight loss, vomiting, diarrhea, and sometimes anemia.
If cats have such worms, treatment and medications must be used, because they often cause blockage of the bile ducts and intestinal obstruction. Hookworm is associated with a roundworm, about 2 mm long. It feeds on blood; if kittens have such worms, the signs will manifest themselves in the form of anemia.
Worms in kittens - trematodes
Trematodes: paragonimiasis or lungworms. Infection occurs through eating raw fish and seafood. When these worms are present, cats may experience general symptoms - loss of appetite, fever, snoring during sleep, shortness of breath. In some cases, foamy vomiting and diarrhea are observed.
The liver fluke is a worm that parasitizes the liver; infection also occurs when eating raw fish.
Signs of worms in cats are expressed in severe pain (it prevents one from touching the stomach), periods of gluttony alternate with complete loss of appetite.
Vomiting or diarrhea with bile may occur. In such cases, deworming tablets for cats must be given along with medications to protect the liver.
Worms in kittens - Dipylidiasis
The disease is caused by a cestode, which parasitizes the small intestine of kittens. The intermediate hosts of this parasite are fleas and lice eaters. Worm eggs are released in the feces of an infected pet. Fleas swallow eggs.
A kitten becomes infected by biting off fleas infected with cestode larvae. Sick kittens are exhausted, apathetic, they have a perverted appetite, alternating diarrhea and constipation. A sick pet's fur is disheveled and the eyes are leaking. He experiences itching in the anal area, so he constantly rides on his butt.
Symptoms of helminthic infestation in cats
Parasites, settling in a cat’s body, cause various pathological processes and disrupt the functioning of internal organs and systems. Intestinal helminths adhere to the intestinal walls, thereby depriving the animal of nutrients and causing mechanical damage to the epithelium. As a result, cats develop vitamin deficiency, allergic reactions, dysbacteriosis, and exhaustion. Toxins released by helminths as a result of vital activity and during the decomposition of dead worms poison the animal’s body.
The disease can occur latently or have a pronounced clinical picture. This depends on the degree of infestation, the age of the cat and the presence of concomitant diseases that weaken the immune system.
General signs of helminthic infestation:
If you notice symptoms, you should consult a doctor immediately
- change in eating behavior - refusal to eat, lack of appetite;
- diarrhea, constipation and their alternation;
- there may be blood and mucus in the stool;
- nausea, urge to vomit;
- increase in temperature;
- signs of lung disease - coughing;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- purulent discharge from the eyes, conjunctivitis;
- spontaneous abortion or premature birth;
- bloating;
- with massive infestation, signs of intoxication appear - drowsiness, increased fatigue, the condition of the coat worsens, and its uneven loss begins;
- thinness;
- convulsions;
- kittens have developmental delays;
- the presence of worms in feces.
When infected with tapeworms, helminth segments are excreted in the feces, some of which may end up in the anal area. And then the cats begin to drag their butts along the floor, because fragments of parasites cause severe itching.
Since many helminthiases have similar symptoms, before starting treatment you should find out the specific pathogen. To do this, diagnostic tests must be carried out in a veterinary clinic.