Definition
As you know, an ulcer is a damage to the skin or mucous membrane that is difficult to heal or does not heal at all. Often such pathologies are associated with autoimmune diseases or cases where the body’s defense system practically does not function. Jacobs ulcer is one of the latter types. The mouth and lips are affected, but in severe cases, ulcers can appear on the cheeks and spread to other parts of the body, including even the stomach. Note that the pathology is relatively rare, and therefore lesions on your pet’s lips are probably explained by a more prosaic reason. But it still wouldn’t hurt to show him to the vet.
Interesting! In 97% of cases, the disease affects exclusively purebred cats. The more high-born the animal, the higher its chances of getting sick. This is due to the large number of gene mutations accumulated during selection. Outbred cats practically do not suffer from this disease.
Why is this ulcer dangerous? Firstly, constantly ulcerated areas of the skin and mucous membranes are “tidbits” for pathogenic microflora. Bactria quickly colonize these places, which is fraught with purulent inflammation and sepsis. Secondly, veterinarians have already proven for sure that Jacobs ulcer is fraught with the appearance of fibroids/sarcomas. These are extremely aggressive forms of cancer that are almost always fatal.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures for ulcerative dermatoses depend on the type and severity of the disease; treatment methods are prescribed by the doctor based on the results of diagnostic studies.
Pyoderma
This skin infection is treated with antibiotics; the course of therapy usually lasts from 2 to 4 weeks, even if visible signs of the disease disappear sooner. In addition, to heal skin damage, I use external agents - antibacterial ointments and creams. In veterinary medicine, Amoxicillin, Sinulox, and Cephalexin are used, giving them to the animal 2 times a day at the rate of 25 mg per 1 kg of body weight. When choosing a drug, the veterinarian is guided by its effectiveness against the detected microorganism, the speed and duration of action, and the number of possible side effects.
Eczema
This type of dermatosis involves complex treatment, including treatment of skin areas affected by ulcerations with antiseptics (usually hydrogen peroxide or alcohol), hormonal ointments and antipruritic suspensions. For oral administration, the cat is prescribed immunostimulants and vitamins; the diet of the sick animal includes fermented milk products that help restore normal microflora.
Folliculitis
Treatment of the disease involves systemic and local therapy. The affected areas are treated with antiseptic agents and healing ointments and creams; if necessary, purulent ulcers are opened. In most cases, the cat is prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy with Beytril, Zoetis, Sinulox or Gentamicin, as well as taking drugs that enhance immunity. If a cat is prone to inflammation of the follicles, veterinarians recommend purchasing an ultraviolet lamp and periodically giving it a “home solarium.”
Notoedrosis, demodicosis, scabies
Ulcerative dermatoses caused by subcutaneous mites are difficult to treat; it takes quite a long time for a cat to fully recover. This is because antiparasitic drugs only kill mites, while their eggs remain undamaged; the last generation will be born in about a week. Consequently, the animal has to be treated repeatedly, with a break of several days.
In veterinary medicine, complex therapy with external agents is used to treat cats for skin diseases such as notoedrosis, scabies or demodicosis. Apply:
- Acaricidal (destroying parasites) ointments, creams, suspensions: Demos, Butox, Stronghold, Neostomazan.
- Keratolytic (softening and exfoliating) preparations Octolin, Akriderm, Belosalik, Skinoren.
Atopic dermatitis
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in cats involves a combination of measures aimed at suppressing the development of pathogenic microflora and stopping the manifestations of an allergic reaction. Broad-spectrum antibiotics (Tobramycin, Cefazolin, Neomycin) and antihistamines (Diphenhydramine, Clemastine) are prescribed. To reduce the hyperactivity of the immune system, immunosuppressive drugs (for example, Cyclosporine) are used.
Important! Under no circumstances should you try to cure your cat of ulcers on its body without contacting a veterinarian. Even if with the help of ointments or sprays it is possible to relieve the symptoms to some extent, the cause of the disease will remain, and after a while its manifestations will resume
And during this period, the disease can acquire a chronic form, it will be much more difficult to cure it, not to mention the danger of infecting other animals living in the house and people with dermatosis.
What causes Jacobs ulcer?
So, what causes Jacobs ulcer in a cat? Alas, we do not know the reliable causes of the disease. There are several theories that explain the development of ulcers:
- Allergic or autoimmune etiology. Some veterinarians suggest that Jacobs' ulcer may appear in animals that are regularly exposed to certain allergens. Since ulcers are almost entirely formed by the “bodies” of eosinophils, a large number of which indicate an allergy/autoimmune pathology, the theory can be considered valid.
- Viral etiology. Other experts believe that Jacob's ulcer develops exclusively in those cats that have had any viral infection in the past. Viruses can greatly suppress the immune system, and therefore this theory also has the right to life.
- Parasitic etiology. It is possible that the saliva of fleas and other ectoparasites can cause not only allergic dermatitis, but also something more serious...
- Finally, among European veterinarians there is an opinion that Jacobs ulcer is largely due to the presence of some genetic defects . Taking into account what we have already said about the “symbiosis” of this disease and purebred cats, this hypothesis may also be correct.
Cat care, diet during illness
In order for your pet to recover faster, he needs to create special conditions. During treatment, it is recommended to place the animal in a warm, quiet place, to which other four-legged inhabitants of the home have limited access. It is advisable to place bowls with food and water, as well as a tray, near the bed. The pet will not have to move much, which will allow him to save more energy to fight the disease.
To destroy the virus, all contaminated surfaces should be treated with a disinfectant solution prepared from water and bleach taken in a ratio of 32:1. The remaining items should be wiped with a napkin soaked in soapy water. Your cat's bowls and litter box should be cleaned regularly.
To make breathing easier, your tailed pet should be given inhalations or periodically brought into the bathroom, in which hot water is turned on and the door is tightly closed. Nutrition plays a special role in treatment. If your pet eats ready-made dry food, it is recommended to switch it to wet products of the same brand during treatment. If your cat eats natural food, you should add to its diet:
- pureed vegetables;
- porridge;
- bouillon;
- chopped meat;
- boiled fish fillet.
It is better to switch the animal to 3-4 meals a day. If your tailed pet does not have an appetite, it is recommended to prepare food for him from products with a distinct appetizing smell. The water in the bowl should be changed twice a day. It should be at room temperature.
Clinical manifestations
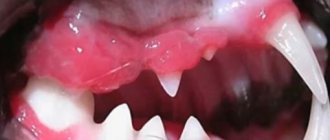
What are the symptoms of Jacobs' ulcer in cats that can help you determine if your cat has the disease? It's simple - a small red spot first appears on the upper lip. Note that in most cases, pathology manifests itself in this place. Situations where the primary ulcer develops on the lower lip or in the oral cavity are much rarer.
Over time, a small and almost imperceptible spot gradually turns into a huge and foul-smelling eczema. If nothing is done, then soon the signs of inflammation increase, and the unpleasant-smelling spot begins to ulcerate, deepen, and soon turns into a deep defect with dubious prospects for healing. In advanced cases, it comes to exposing gums and teeth; photos of such animals resemble scenes from horror films! Don’t start the process, take your pet to the veterinarians right away!
Important! How to distinguish Jacobs ulcer from other pathologies (chemical burns, trophic ulcers)? It's simple: with this type of ulcer, the cat does not experience any pain or any signs of discomfort.
Let us emphasize once again that a cat with this disease behaves completely normally, does not itch, and does not show signs of pain. The appetite is normal, there are no problems with digestion or excretory function. But! All this applies only to the initial stages of the disease! If a cat’s cheek is already completely “corroded” and his teeth are sticking out, then he will have a painful reaction, and what kind of one... Here secondary infections and a general weakening of the body make their contribution. The animal gradually loses its appetite and becomes lethargic.
Diagnostics and therapeutic measures
How to determine if a cat has this particular disease? In general, there is nothing complicated: the absence of pain and itching are quite specific signs on the basis of which a diagnosis can be made. In doubtful cases (when a cat has just developed a spot on its lip), a biopsy can be performed by taking a small piece of tissue from the border between healthy and pathologically altered tissue.
Microscopic examination reveals eosinophilic proliferation, which can already serve as a sufficient reason for making a diagnosis. In addition, a biopsy helps to exclude/confirm the oncological origin of the ulcer. Unfortunately, this possibility must also be taken into account. Oddly enough, a blood test often does not give anything useful: despite the fact that the ulcer itself is full of eosinophils, their number in the blood itself can be completely normal.
A recent illness of viral or bacterial etiology should also be considered a strong argument “in favor” of Jacobs ulcer. Many specialists are more inclined to look for predisposing diseases of fungal origin, since pathogenic fungi greatly reduce immunity and are difficult to treat.
Is there any treatment for Jacobs ulcer in cats? There is, and in many cases it is very effective and allows you to quickly cope with the disease. Sick cats are prescribed corticosteroids, including prednisolone. As a rule, after a single use the positive effect is clearly visible. Depo-Medrol and Sulfetrim have proven themselves very well. The average therapeutic course lasts about three weeks. Here's how to treat this disease.
Unfortunately, all of the above applies only to relatively mild cases. If it comes to holes in the cheeks and the formation of pronounced defects over a large area, then surgical intervention cannot be avoided. Note that advanced cases of Jacobs ulcer quite often “transform” into sarcoma, and this disease requires completely different treatment.
Things to remember
When treating or diagnosing Jacobs ulcer, one must remember that this disease often manifests itself as one of the varieties of a large complex of eosinophilic granuloma.
In addition to ulcers, it can “give out”:
- Eosinophilic plaques.
- Eosinophilic granulomas.
- Allergic milliary dermatitis.
Why does the average cat owner need all this information? It just happens that all these lesions are grouped and occur in the same animal. Therefore, cases where Jacobs ulcer has spread to the abdomen are precisely a systemic complex of eosinophilic granuloma.
All diseases in this group respond to the same therapy and are diagnosed in the same way. It’s just that in case of damage to large surfaces of the body, you need to understand that something is seriously wrong with the animal’s immunity. It may be worth suspecting the presence of some kind of autoimmune disease.