A state of decreased functionality of the gastrointestinal tract - intestinal atony in cats is manifested by disturbances in digestion and excretion of waste products. The disease is caused by internal pathological processes, the creation of improper conditions for keeping the animal, or damage to the pelvic organs. If you contact a veterinarian in a timely manner, the animal’s health will be fully restored.
Intestinal atony in cats - causes and treatment of the disease
A state of decreased functionality of the gastrointestinal tract - intestinal atony in cats is manifested by disturbances in digestion and excretion of waste products. The disease is caused by internal pathological processes, the creation of improper conditions for keeping the animal, or damage to the pelvic organs. If you contact a veterinarian in a timely manner, the animal’s health will be fully restored.
Treatment
Treatment of intestinal obstruction in a cat most often begins from the moment of admission to the clinic: even at the diagnostic stage, the animal is given a drip with an infusion solution that replenishes fluid lost during vomiting.
Restoring fluid loss
Next, after carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures, the veterinarian develops further tactics. If the diagnosis of acute intestinal obstruction is confirmed, then the cat requires urgent surgery. During the intervention, the cause of the obstruction is eliminated. In some cases, especially with volvulus or torsion, the non-viable part of the intestine is removed.
Sometimes intestinal obstruction is incomplete, that is, the intestinal lumen is not completely blocked. In case of incomplete obstruction, the veterinarian may decide on conservative treatment, that is, therapy without surgery.
It is recommended to administer IVs with infusion solutions, and take the pet with antispasmodics, vitamins, and, if indicated, antibiotics. The cat must be closely monitored, since if treatment is ineffective and the obstruction turns into acute, surgery will still have to be performed.
Intestinal atony in a cat contributes to the development of mechanical intestinal obstruction. Atony requires treatment of the underlying disease that caused the lack of peristalsis, for example, the use of drugs that improve neuromuscular conduction.
Causes of pathology
Atony in cats develops due to a weakening of the intestinal muscles and a decrease in the activity of digestive processes with a gradual increase in the difficulty of defecation.
Veterinarians identify the main causes of the disease:
- hereditary predisposition;
- congenital disorders of intestinal development and formation in kittens;
- natural aging of the body and weakening of muscles;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- improper feeding;
- blockage of intestines with fur;
- lack of fiber in food;
- low physical activity;
- intestinal infections;
- extensive helminth infestation;
- malignant neoplasms;
- overfeeding, obesity;
- inflammatory diseases of the stomach.
Failure to comply with pet hygiene rules can cause illness.
The following factors have additional adverse effects:
- adhesions as a result of surgery;
- taking and side effects of medications;
- psychological tension and stress;
- a dirty litter tray and the cat’s reluctance to empty itself;
- decreased intestinal vascular tone.
Return to contents
Treatment of intestinal obstruction in cats
As a result of establishing the cause, further actions can be judged: either conservative therapeutic treatment of the sick animal is carried out, or emergency surgery is performed to eliminate the cause of blockage of the intestinal lumen (if a foreign body, hernia, tumor, etc. is detected).
Surgery is also necessary if symptoms persist or worsen, or if signs of peritonitis are noted.
In all cases, special attention should be paid to stabilizing the animal and restoring fluid and electrolyte balance after surgery.
Symptoms of the disease
A decrease in the activity of the intestines and stomach in cats is manifested by disruption of digestive processes and a further deterioration of the general condition. Main symptoms of atony:
- decreased appetite;
- vomit;
- decreased intestinal motility;
- significant reduction in feces excreted;
- change in consistency and addition of an unpleasant odor from feces;
- weakness, lethargy.
One of the symptoms of the disease is a significant increase in the abdominal cavity.
- abdominal tension;
- lack of appetite, refusal of any food;
- sagging abdomen;
- weight loss;
- deterioration of coat condition;
- blanching of mucous membranes;
- aggressive reaction when touching the stomach due to pain.
Return to contents
Symptoms and diagnosis
When intestinal obstruction occurs in cats, the following symptoms are observed:
- Vomiting that gets worse over time. Often, owners mistake this symptom for incipient poisoning and offer the cat plenty of fluids to replenish fluid losses. However, if there is intestinal obstruction, drinking fluids only aggravates the animal’s condition.
- Decreased appetite, gradual refusal of any food and drink.
- Bloating, tenderness and tension in the abdomen. Since gases and partially digested food debris accumulate in the intestines due to the obstruction, the abdomen increases in size and becomes hard.
- The animal makes frequent attempts to defecate, strains a lot, but this does not bring any results. At first, defecation may persist, but when the intestines are freed all the way below the obstruction, it stops completely.
- The general condition of the cat suffers greatly: it becomes lethargic, apathetic, and restless.
All of the above symptoms suggest the development of intestinal obstruction in the cat. At the slightest suspicion, you should immediately contact a veterinary clinic, where a specialist will confirm or refute your fears.
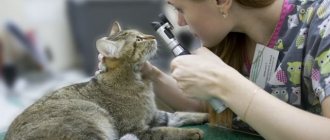
Visit to the veterinarian
The veterinarian will examine the cat and draw blood to perform the necessary tests. The most revealing diagnostic method is an x-ray using a contrast agent, which allows you to determine the exact location and level of intestinal blockage, as well as the size and nature of the foreign body, if present.
Attention! There are cases when all these diagnostic methods are not enough and they do not give a clear idea of the nature of the obstruction and the place in the intestine where the problem is located. In this case, a diagnostic surgical intervention is performed - laparotomy, which in most cases ends with surgery.
Diagnostics
To determine treatment tactics, it is necessary to find out the cause of atony. A veterinarian performs a visual examination of the cat with palpation of internal organs. The diagnosis is based on pathological history, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. Basic laboratory tests:
- Blood chemistry. A detailed study of the work of internal organs.
- Coprogram. Stool analysis assessing the functioning of the digestive and excretory systems and the presence of parasites.
Instrumental diagnostics includes the following examinations:
- Radiography. The organs of the gastrointestinal tract and intestinal structures are visualized.
- Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound). Checking the condition and contents of internal organs.
- X-ray with contrast. The work of the intestines is examined one by one after the administration of barium sulfate (jejunum, cecum and colon after 4-6 hours, rectum after 7).
- Diagnostic laparotomy. A surgical intervention that identifies damage to the digestive organs through an incision in the abdominal wall.
Return to contents
Prevention measures
To avoid the development of intestinal obstruction in your pet, you must follow the following preventive measures:
- Monitor the quality and diet of the cat. If the animal eats special food, it is better to choose one that has the ability to gently remove hair from the gastrointestinal tract. You also need to remember that your cat should always have access to a sufficient amount of clean drinking water.
Proper nutrition
- Cats walking outside clear their stomachs of accumulated hair by eating grass and causing vomiting. If your pet does not go outside, you should provide it with special grass produced for this purpose.
- It is necessary to supervise the cat and not allow it to play with small objects that it might swallow.
Attention! Plastic bags, candy wrappers, and foil are especially dangerous, since these items can easily get stuck in the intestinal lumen due to their friability and are completely indigestible.
- Regular deworming will help avoid the accumulation of parasites in the intestines.
Treatment of pathology
The choice of methods for treating intestinal atony in cats depends on the cause of defecation difficulties, the duration and severity of manifestations, the age of the animal and concomitant diseases. The veterinarian chooses from the following treatment methods:
- therapeutic nutrition;
- administering enemas with an antiseptic;
- administration of medications;
- surgical intervention.
The therapeutic diet is based on enriching the diet with fiber to stimulate digestive processes and irritate intestinal receptors. The veterinarian selects the appropriate ready-made food in accordance with the clinical picture. If the cat has eaten natural food, the doctor draws up a menu for the treatment period. Additional gentle means to facilitate bowel movements are:
- specially grown medicinal herbs (sold at a veterinary pharmacy);
- Vaseline oil;
- fiber in the form of dietary supplements.
The main means of therapy and their effects are presented in the table:
| Group of drugs | Therapeutic effect |
| Prokinetics | Stimulates intestinal contractions |
| Strengthens the functioning of the excretory system | |
| Laxatives | Liquefies feces |
| Increase intestinal activity | |
| Gastroprotectors | Protects the gastric mucosa |
| Increases resistance to external irritants | |
| Probiotics | Restore intestinal microflora |
| Antispasmodics | Remove spasms |
| Antibiotics | Eliminate infectious pathogens |
| Analgesics | Relieves pain |
| Anthelmintic | Destroy and remove parasites |
In some cases, the only treatment option is surgery.
If atony in cats is caused by fecal stones, malignant neoplasms, congenital malformations of the excretory system, or the intestines are clogged with helminths, surgical intervention is performed to eliminate the negative factors that interfere with the natural process of defecation.
Diagnosis and treatment
If the pathology is noticed in time and it is limited to constipation, you can give your pet Vaseline oil and put him on a starvation diet. In another situation, the cat must be taken to the clinic. Diagnosis is made based on clinical examination and history. If necessary, laboratory tests are carried out, as well as instrumental studies. If intestinal obstruction is detected, surgery is performed. If constipation occurs, they give a laxative and prescribe a daily fasting diet.
The main treatment is diet therapy. On the first day the pet is given 1/3 of the norm. Within 3–4 days, feed intake is restored to normal. The best option is to use wet veterinary food. It contains all the necessary components, including fiber and prebiotics, which help restore beneficial intestinal microflora. Followers of natural foods should include vegetables in their diet, as well as prebiotics or probiotics.
The best option during treatment is wet veterinary food.
Prevention of atony
To prevent difficulties in the digestive system and bowel movements, veterinarians at various clinics recommend that the cat owner follow the following rules:
- Feed the animal with high-quality feed or products.
- Ensure the supply of all necessary nutrients.
- Avoid hypothermia and stressful situations to normalize the animal’s psycho-emotional state.
- Be sure to play with your cat to increase muscle tone and physical health.
- Maintain cleanliness of the pet's premises and personal belongings.
A prerequisite for maintaining the health and well-being of a cat is the regularity and timeliness of preventive examinations, vaccinations and deworming. If negative symptoms occur, it is important to seek professional help and treat any underlying conditions.
Source of the article: https://infokotiki.ru/zabolevania/zhkt/atoniya-kishechnika-u-koshek.html
What is considered constipation?
Constipation (constipation) - irregular bowel movements with increased intervals, the feces are dry and dense. Chronic and episodic constipation can be distinguished. Chronic refers to regular or recurrent episodes of difficult bowel movements. Constipation is called episodic if it happened once and after solving the problem did not recur. Older animals with other chronic diseases are more susceptible to chronic constipation. Episodic constipation can happen at any age.
Atony in cats - what is it, types of atony, causes and symptoms
Atony is a condition in which muscle fibers lose their physiological tone. The pathological condition in cats in the intestinal tract is provoked by a number of factors, among which the leading place is occupied by an incorrectly formulated diet.
A deficiency of plant fiber leads to relaxation of the intestinal muscle fibers, resulting in atony. Inexperienced owners of domestic cats assume that intestinal atony develops against the background of excessive or insufficient food intake.
In fact, the cause of atony in the intestinal area is precisely a deficiency of fiber of plant origin. It has a coarse fibrous structure and irritates the intestinal walls. Violation of intestinal motility entails a number of problems. So, if treatment is not provided in a timely manner, the cat develops intestinal obstruction, resulting in the death of the pet.
The owner’s main task is to notice changes in the cat’s well-being and take him to the veterinary clinic. Based on the results of the studies, the specialist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the most appropriate therapy to avoid the development of complications.
Experts note that the earlier atony was detected, the higher the chances of a complete cure for the cat with restoration of impaired digestive functions. In addition to intestinal atony, bladder atony is often diagnosed in domestic cats. This type of pathological condition provokes not only problems in the digestive system (regular constipation), but also provokes disturbances in the process of urination.
Reasons for appearance
Intestinal obstruction in cats can be mechanical and dynamic (functional).
With mechanical intestinal obstruction, the intestinal lumen is blocked by some formation or object.
Sick animal
Types of mechanical intestinal obstruction in cats:
- As a result of the formation of a hairball. For long-haired cats, this type of obstruction is the most relevant.
- A foreign object gets stuck in the intestinal lumen. Sometimes an animal, for example, during play, can swallow a small object that can easily pass through the esophagus and stomach. But for unhindered passage in the intestinal lumen it may be too large.
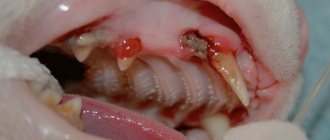
- A ball of helminths. Parasitic worms are creatures capable of rapid reproduction. Therefore, sometimes there are so many of them in the intestines that they can form a ball, which can lead to partial or complete obstruction.
- Fecal stone. There are cases when the formed feces turn out to be so hard that they form a fecal stone, which is extremely difficult to move through the intestinal lumen. This condition is most often observed with the wrong approach to feeding the cat, as well as in old animals.
- Tumor. A tumor growing into the intestinal lumen is another cause of intestinal obstruction. This is usually a rather slow and gradual process, accompanied by additional symptoms such as weight loss, weakness, and apathy.
- Intestinal volvulus. It is formed as a result of torsion of a loop of intestine around its own axis or even the formation of nodes from intestinal loops. Due to intestinal volvulus, the progress of the food bolus may not only stop, but also the death of a section of the intestine that is crushed by the loop may develop. This type of obstruction is one of the most dangerous and requires emergency surgery.
Dynamic or functional intestinal obstruction is a condition associated with impaired peristalsis, as a result of which the bolus of food stops its movement. Functional obstruction develops most often as a consequence of the adhesive process, as well as in some diseases of the nervous system.
What is atony and its causes
Muscle fibers in cats, as well as in other warm-blooded domestic animals, are represented not only by skeletal muscles. Muscles are present wherever contraction occurs - the uterus, esophagus, stomach, bladder, respiratory system, heart.
The muscle tissue structures of the small and large intestines are represented by striated and smooth fibers located on the inside of the intestine. Innervation is carried out using nerve fibers located in the area of the intestine itself. Thanks to nerve impulses, the intestinal muscles contract.
This process is called peristalsis. A complex mechanism consisting of innervation and subsequent contraction of the intestinal muscles makes it possible to move the food bolus through the loops. With intestinal atony, food remains in the body longer than expected due to the lack of normal peristalsis. The main reason for the development of atony in cats is a lack of plant fiber in the diet.
Atony in cats occurs when exposed to certain factors. Among the main ones are:
- Lack of plant fiber in the daily diet. As a result of a deficiency of plant fibers in food, receptors located on the inside of the intestine do not recognize signals in a timely manner. Problems with peristalsis, leading to the appearance of atony, develop regardless of the breed predispositions of the animal and its age. Chronic constipation, which develops in kittens from a very early age, can develop into partial blockage and intestinal obstruction.
- Infection with worms. Helminthiasis in domestic animals does not seem to be a serious problem at first glance. In fact, in addition to regular irritation of cellular structures and traumatization of intestinal tissues, helminths, in the course of their life activity, produce toxic substances that poison the cat’s body. Regular irritation and minor injuries lead to the fact that the receptors responsible for conducting nerve impulses atrophy. Against this background, atony develops.
- Physiological changes (age-related). As your pet grows up and subsequently ages, physiological changes develop. The walls of the intestines and bladder are not able to contract with their inherent peculiarity. Old cats begin to experience problems when going to the toilet and suffer from frequent constipation. In addition, problems arise with the act of urination. The main task of the cat owner is to create maximum conditions for good bowel function. This includes the mandatory inclusion in the diet of foods with plant fibers, as well as foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
Diagnosing intestinal obstruction at home
Considering that a clinical examination includes an x-ray, in which the area and degree of blockage are visible visually, your “master’s” task is to distinguish and correctly compare the first signs of the disease:
- Poor appetite and complete ignoring of food, after a few hours - refusal of water.
- Unsuccessful attempts to go to the toilet, while the cat meows, groans, and groans. Nausea, vomiting.
- Visually noticeable bloating, pain on palpation.
If we notice something like this, we pack up and go to the veterinary clinic, and on the way we remember: what the pet ate for the last 24 hours, how it behaved, whether it showed interest in eating inedible things, when they “chased” the worms, in what sequence the symptoms appeared.
The presence of the following symptoms against the background of swelling indicates an acute condition and requires immediate surgery:
- Vomiting of feces - we do not give antiemetics.
- Dehydration - do not inject saline, it reduces the temperature. To replenish the fluid supply and partially relieve toxicity, Ringer’s solution is suitable from the “handy” solution.
- If the base body temperature drops below 37° , wrap the animal in a sweater or blanket and apply a heating pad.
Important! The appearance of an extensive hematoma or bruise on the side signals a rupture of the intestine and the entry of feces into the body cavity, and may be accompanied by extensive internal bleeding. Time ticks by in minutes! Either the veterinarian will open the animal and remove the lesion, or the cat will die.
Bladder atony in cats
Problems with bladder tone arise due to the formation of stones and sand accumulated in the organ. Most often, bladder atony develops in older cats against the background of senile changes. The progression of the disease is often facilitated by untimely castration (at a late age).
Disturbances in the diet, especially if the diet predominates with fish products (raw fish), as well as a large amount of dry food, can cause the development of urolithiasis. The owner’s task is to constantly monitor the health of the animal, especially when it is older. Symptoms of bladder atony in a cat are as follows:
- change in the nature of urination - a decrease or, on the contrary, an increase in frequency;
- changes in the shade of excreted urine - the presence of inclusions of blood, turbidity;
- pain during urination;
- increased body temperature;
- severe lethargy and apathy, refusal to feed.
Treatment of bladder atony in cats at the earliest stages is carried out with the help of B vitamins (in particular B12), as well as by prescribing other medications. In advanced cases of the pathological process, surgical intervention is recommended - urethrostomy. During the surgical procedure, a catheter is inserted directly into the patient's ureter, allowing urine to pass out of the body without any problems.
After surgery, it is recommended that the animal remain in the hospital’s hospital for some time. It is then possible to continue treatment on an outpatient basis. Disturbances in bladder muscle tone are sometimes caused by diseases of the spine. In such cases, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause, and only then treat the secondary problem.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the development of atony of the large intestine in a cat can be different. It all depends on the degree of neglect of the pathological process and the factors that provoked the violation of peristalsis. In veterinary medicine, there are a number of main signs indicating the presence of pathology:
- dyspeptic disorders - chronic constipation, followed by diarrhea;
- signs of bloating (increased gas formation and discharge of flatus);
- eruption of gastric contents;
- the appearance of a repulsive odor from the cat’s mouth;
- increased body temperature (in some cases);
- lethargic and apathetic state of the pet;
- decreased or increased appetite;
- a decrease in the daily amount of feces excreted;
- the appearance of mucous discharge from the anal area with a repulsive odor when the cat tries to go to the toilet;
- pronounced sagging of the peritoneum or, on the contrary, increased tone of the muscle fibers of the peritoneum;
- aggressiveness in the animal when the owner tries to palpate the affected area (associated with severe pain of an acute paroxysmal nature).
Symptoms
- frequent debilitating vomiting;
- loss of appetite, refusal of food and favorite treats;
- lethargy, decreased activity, weakness;
- loss of body weight;
- unstable stool (diarrhea, constipation);
- acute pain on palpation of the abdomen, tight tummy;
- deterioration of coat condition.
Some cats have an increased appetite, but at the same time the daily number of bowel movements decreases, which can cause severe intoxication of the body. The act of defecation is difficult, cats experience pain when visiting the litter box. Mucous membranes are icteric, anemic.
With atony of the bladder, the symptoms are mainly manifested by difficulty urinating. There may be flakes, blood clots, and bloody threads in the urine. The rest of the symptoms are the same as with atony of the gastrointestinal tract muscles.
Intestinal obstruction in cats: prevention
If you want to save your cat from severe suffering, and yourself from mental anguish and serious material costs, then take care to remove small objects and toys from the animal’s field of view
, which it can chew and swallow.
Especially when a curious and omnivorous kitten lives in the house. Make sure that the cat does not climb into the trash can
, where there is a certain risk for the cat to try a lot of inedible, but tasty-smelling things. Sausage skins, threads, strings, pieces of paper and foil are dangerous for cats. Christmas tree “rain” and tinsel for the New Year tree are also prohibited.
In our veterinary clinic, thanks to the efficiency and professionalism of the veterinary team, we have the opportunity to quickly help with any life-threatening and health-threatening conditions in animals. One call and emergency veterinary care will be provided at home, 40 minutes after the call. This is of great importance when there is a threat of acute intestinal obstruction.
If you notice the first symptoms, do not waste time, call us to get a free consultation to provide first aid to your pet. Perhaps everything will work out and he will only need outpatient treatment under the supervision of a specialist. If necessary, our center will provide effective inpatient treatment and surgical care. Treatment drugs are sold at transparent prices that are favorable to you, since we cooperate with manufacturing plants without intermediaries. Call us, we are always happy to listen and help our clients!
Causes
The development of intestinal atony in cats is provoked by a lack of plant-based fiber in the animal’s diet. Some owners mistakenly believe that intestinal atony is caused by an excess or lack of food.
A deficiency of essential fiber in the resulting food provokes insufficient irritation of the walls of the small and large intestines. As a result, disturbances arise that provoke disturbances in peristalsis, and in advanced cases, with untimely diagnosis and treatment, intestinal obstruction develops. It can cause death.
There are many reasons for the development of atony in a cat, but the basic ones are:
- A sharp deficiency of plant-based fiber in the animal’s daily diet. With a lack of plant fiber, the receptors on the inside of the intestine do not receive the signal. Impaired peristalsis with further development of atony in a pet is possible regardless of the age of the cat. Chronic constipation in kittens can later cause blockage and partial intestinal obstruction.
- Helminthiasis. Infection with helminths in an animal provokes serious complications. In addition to injury and irritation of the intestinal walls of a mechanical nature, waste products of worms (toxic substances) poison the body. Constant irritation provokes atrophy of the receptors of nerve endings, which ultimately leads to the development of atony.
- Changes in the body of a physiological nature. With age, the body of animals and humans undergoes changes. Against the background of senile changes, the intestinal walls, as well as the muscles of the bladder, lose their functionality. The animal experiences problems with urination and defecation. The owner’s task is to provide his pet with food that is as easy to digest as possible, preferably with a high content of fiber and vitamins.
It is extremely important to notice changes in your pet's health. This will allow you to timely diagnose dangerous conditions and begin adequate treatment, avoiding possible complications.
In the initial stages of intestinal atony, it is possible to completely cure the pet with further restoration of all digestive functions.
With intestinal atony, the bladder works as usual. If the pet has a delay not only in defecation, but also in urination, suspicion falls on the development of urolithiasis, and not a violation of intestinal motility.