There are a huge number of reasons why a cat scratches its ear until it bleeds. Some of them are quite harmless and can be easily eliminated.
Sometimes such changes indicate the development of diseases. The owner must determine as quickly as possible what led to the pet’s itching. Thanks to this, it will be possible to provide timely assistance and avoid serious problems.
Possible reasons
The reasons why a cat scratches its ears are as follows:
- water getting into the ear canal;
- foreign body;
- ear mite;
- otitis;
- anatomical features of the structure of the ear canals;
- bruise, hematoma formation;
- fleas;
- fungal diseases of the skin;
- infectious pathologies of the hearing organs;
- non-compliance with ear hygiene rules, the formation of wax plugs.
The following symptoms indicate pathological changes:
- head tilted to one side;
- the pet itches, tears the skin on the outside near the ear;
- the cat does not allow you to touch the affected area;
- the inside of the ear turns red, plaque and dirt with an unpleasant odor appear on it;
- squelching sound when pressing on the ear.
If the disease is neglected, the animal develops pathology, resulting in a rise in temperature and loss of appetite. The cat becomes restless and shows aggression.
Similar symptoms are observed with the development of the following diseases:
- Otodecosis (scabies caused by ear mites). As the disease develops, an inflammatory process begins, as a result of which the animal develops severe itching.
Otitis. Inflammation of the hearing organs, at the initial stage manifested by itching. Visually, the ears appear dirty and have plaque. The disease can be parasitic, bacterial, mixed.- Allergy. A negative reaction is provoked by allergens that are contained in some food products, hygiene products, household chemicals, and plant pollen.
- Neoplasms (mainly observed in adult animals).
- Notoedrosis. The causative agent of the disease is the sarcoptoid mite, which affects the hearing organs, nasal cavity, and the area above the eyes. The danger of the pathology lies in the fact that as a result of the parasite’s activity, the functioning of the nervous, reticuloendothelial and cardiovascular systems is disrupted.
What causes allergies?
Allergy is an immunopathological process. The reaction appears due to the release of specific neurotransmitters in the area of contact with the stimulus. The cat's epidermis may react with redness and irritation in response to the following:
- mold;
- household chemicals;
- cat washing products;
- drugs;
- waste products of parasites.
These types of intolerance are manifested by a complex of symptoms, the main of which is redness and swelling of the epidermis. It is quite simple to identify the irritant in these cases, and eliminating its effect quickly reduces symptoms.
The situation is more complicated with food allergies in cats. They can manifest themselves as changes in the epidermis, as well as general symptoms - lacrimation, sneezing, indigestion. If you suspect a food intolerance, you cannot do without the help of a doctor, since it is very difficult to identify the allergen on your own.
How to treat a combed area
The veterinarian should tell you what to do to eliminate the itching. Often, self-medication or delayed consultation with a doctor leads to serious problems.
At home, the most primitive activities are allowed. You can take a cotton swab, hydrogen peroxide, and treat the affected area.
Instead of peroxide, an alcohol solution or brilliant green is also used. You cannot apply ointments to your ears, use traditional medicine methods, or perform other manipulations yourself.
Diagnostic methods
To determine why your kitten is scratching its ear excessively, you need to contact your veterinarian.
You can spot ear mite infestations on your own. To do this, you need to wipe the auricle with a cotton swab, transfer the resulting material to a black cloth, and examine it through a magnifying glass.
White parasites on a black background will be clearly visible.
Other pathologies are identified in a veterinary clinic. The doctor performs a visual examination. The presence of peeling, brown discharge, and swelling will indicate dermatitis.
The following laboratory tests will help make an accurate diagnosis:
- Bacteriological culture. Often impossible due to lack of necessary equipment.
- Smear. This diagnostic procedure allows you to identify the exact cause of intense itching.
- X-ray.
- Ultrasonography.
Treatment depends on the cause of the disease. Therapy is selected on an individual basis.
Therapy methods
Treatment depends on what problem is causing the itching. This could be dermatitis, fungus, ear mites, otitis media and other pathologies.
Dermatitis should be treated with drops containing novocaine. Using a swab dipped in hydrogen peroxide, the crusts are carefully removed, and the ulcers are treated with an astringent ointment.
Fungal infections are treated with antifungal agents.
Ear mites are removed by mechanical cleaning of the ear canals. A swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide is used. Additionally, medicinal drops and ointments are used. In case of advanced disease, injections with antibiotics are prescribed.
Therapy for otitis media is selected depending on the disease. First of all, you need to treat the ears with a cotton swab with peroxide.
Immediately after these manipulations, treatment procedures using the following drugs begin:
- Leopard;
- Otoferonol premium gold;
- Aurikan;
- Oricin;
- Surolan;
- Ordermil.
Tick-borne otitis media is treated comprehensively. Drugs prescribed:
- Anandin;
- Tsipam;
- Decor.
Antimycotic agents are also used:
- Clotrimazole ointment;
- shampoos Nizoral, Sebazol.
The products are applied to the inside of the ear. They cannot be washed off, otherwise there will be no therapeutic effect.
For fungal and yeast forms of otitis, it is necessary to strengthen the animal’s immunity.
The bacterial variety of pathology often leads to the development of diseases that are difficult to treat.
Local medications are prescribed:
- Otonazole;
- Otibiovin;
- Mastitis.
Advanced forms of the disease are treated with novocaine blockades with antibiotics. After the course of treatment, preventive treatment is carried out. This way it is possible to prevent relapses .
An allergy is diagnosed when a pet scratches its ear, but there is no discharge. In this case, local and systemic antihistamines are used.
Special drops are used against fleas; they are applied to the withers. If the animal is often outdoors, then an anti-flea collar is used.
Detected hematomas, formations, and polyps are removed surgically. Identified foreign bodies are removed immediately. The animal's ears are treated with antiseptic drugs.
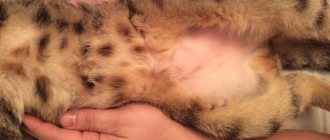
Hematoma of the auricle
A hematoma is an accumulation of blood under the skin of the ear at the site of a bruise, cut or bite.
Symptoms:
- the cat's ear swells;
- the damaged ear is hot to the touch, hard and sometimes hangs close to the head;
- a red or bluish swelling is visible on the inside of the ear;
- in chronic cases, curvature of the auricle develops;
- in severe cases, tissue necrosis or an abscess forms at the site of the hematoma.
Treatment of hematoma
If you find an ear hematoma in your cat, immediately apply a cold compress and a tight bandage to the injury site for a day. Don't delay visiting the veterinarian. The doctor should examine the sore ear and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If the cat has a mild hematoma, then it is enough to apply a tight bandage with a cold compress for 2 weeks. After this time, the hematoma will significantly decrease in size and the veterinarian will prescribe UHF therapy.
In case of severe hematoma in a cat, the doctor will puncture the source of inflammation and use a syringe to suck out the accumulated fluid. After this, a 0.5% solution of novocaine with an antibiotic and hydrocartisone will be injected into the hematoma cavity. For effective healing of the hematoma, the veterinarian may prescribe intramuscular injections of Vikasol.
For the treatment of extensive hematoma or advanced form, surgery is indicated.
The only preventative measure against a hematoma in a cat is to ensure that your ward does not get injured and avoid clashes with other animals.
Preventive actions
Preventive measures that help prevent the development of ear diseases in cats:
- Systematic cleaning and examination of the ears. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times a week. A special spray helps remove sulfur and has a disinfecting and healing effect. The product must include natural ingredients. Antibiotics in this case can only do harm, so they are not used.
- The following measures are taken against parasites: drops are applied to the withers, a collar is put on the animal to repel fleas and ticks.
- Maximum accuracy when carrying out water procedures. When bathing your pet, you need to make sure that water does not get into the ears. It is recommended to plug them with cotton wool. You can't get your head wet.
- No drafts.
- Activation of the body's protective functions. Ear diseases often develop with weak immunity. It is necessary to enrich the animal's diet with foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Physical activity, lack of stress, and good nutrition strengthen the pet’s body.
A pet may scratch its ears for a variety of reasons. Often itching in the ears is the initial stage of any disease, so this symptom cannot be ignored.
Next
Health Cloudy eyes in a cat: causes, diagnostic methods, treatment
Erosion and ulcers of the ear in a cat
Erosion and ulcers in a cat’s ears are a manifestation of diseases of various etiologies. To diagnose and identify the causes of ulcers or erosion in the animal’s ears, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination by a veterinarian. The doctor will conduct a cytological examination, hematological and biochemical tests.
Dermatitis
If the cause of erosive-ulcerative dermatitis in a cat is associated with malfunctions in the immune system, then at the initial stage the veterinarian will prescribe the use of mechanical means of protection to prevent self-injury. For example, an Elizabethan collar, overalls or anti-scratch boots.
For the treatment of immune diseases the following is used:
- corticosteroids;
- immunosuppressants.
Bacterial infections
Quite rarely, bacterial infections become the cause of ulcers and erosion in a cat’s ears. Treatment in this case consists of eliminating the cause and antimicrobial therapy. Effective methods of therapy can only be prescribed by a veterinarian after examination.
Neoplasms
It is extremely rare that papilloma, sarcoma or fibroma cause itching in a cat's ear. As these tumors grow, they lead to partial or complete hearing loss. To eliminate the tumor, the veterinarian performs surgery. In most cases, the prognosis is positive.