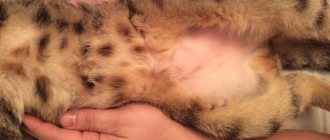
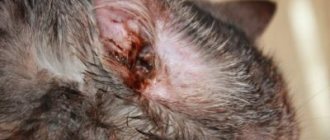
Signs of a swallowing disorder
Owners do not always pay close attention to the process of eating their pets. If an animal has congenital defects that prevent it from swallowing, and a person has no experience in caring for a cat, he may not even realize that his pet cannot eat normally. There are several main signs that allow you to suspect a swallowing disorder in your pet:
- profuse salivation, sometimes mixed with blood;
- regurgitation and coughing during or after eating;
- gagging when trying to swallow a bolus of food;
- chewing food on one side of the mouth;
- nasal discharge, crusting on the face, bad breath;
- changes in appetite and weight loss;
- general muscle weakness of the animal;
- violation of the symmetry of the head or neck.
If a cat has two or three signs, it must be shown to a specialist.
This is a voluntary process of movement of saliva secreted from the nose or food from the mouth into the pharynx, and then into the esophagus. Swallowing food can be roughly divided into 3 stages (the first 2 of them can be performed consciously, the last only automatically):
- Preparation or oral phase. Food goes through a stage of salivation and chewing. Then it is fed onto the back of the tongue to move into the pharynx.
- Pharyngeal phase. This is the section of the food tract from the oral cavity to the esophagus. Passing through this area, food enters the esophagus.
- Esophageal phase. Food moves down the esophagus towards the stomach and enters the stomach.
Swallowing liquid or saliva occurs according to the same principle: saliva or water accumulates in the oral cavity, moves towards the pharynx, a swallowing movement is made and it enters the esophagus, and then into the stomach.
The reasons for this phenomenon are very diverse. This symptom alone cannot indicate any specific ailment of the pet. You need to observe the behavior of the animal.
Nervous condition
A cat may swallow and lick its lips if it is very nervous. Her posture will be tense, her eyes attentive. As soon as the nervous tension passes, the animal will stop swallowing frequently.
A cat may swallow frequently if it feels nauseous. At the same time, she may behave nervously. This means that any diseases of the digestive system, accompanied by nausea, can cause this phenomenon (gastritis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, etc.). In this case, the cat may lick itself frequently because it is suffering from dehydration. Her stool and appetite may be disturbed, and manifestations of dyspepsia may be observed.
Helminths
Even helminthiases can cause a cat to constantly swallow. You need to pay attention to your pet’s stool and its attitude towards food. Diarrhea or constipation, problems with the general condition, apathy, and deterioration in the quality of the coat can indicate serious internal diseases of the pet. A cat may swallow frequently when vomiting, and vomiting itself may begin several hours after the start of frequent swallowing movements.
Infections
The cat may constantly swallow, make sounds similar to hiccups, and has a high fever. These signs are classified as infectious diseases of the animal. What kind of disease can only be found out from a veterinarian.
Foreign body
A cat may swallow frequently if its esophagus or stomach is clogged with fur, or if an object has become lodged in it. If your cat is choking on a fish bone or even several fish bones, she may swallow and try to push them down. Sometimes these actions are followed by gagging. If there are hairballs or rain, the cat may vomit them out.
When a needle is swallowed, if it remains in the oral cavity (for example, immersed in the tissues under the tongue), the animal’s body temperature may increase, regional lymph nodes may enlarge, the cat often swallows, and at the site of puncture by the needle (if it breaks and a fragment is stuck in the tissues) it may there may be inflammation and even necrosis.
We suggest you read: Why can a Chihuahua go bald?
Kidney pathology
With renal failure, the animal becomes apathetic, drinks a lot, refuses food, and its daily diuresis changes. At the same time, he may often swallow due to severe intoxication and nausea.
The formation of tartar, ulcers on the oral mucosa, trauma (for example, a fish bone stuck in the gum or fishing line between the teeth) can lead to hypersalivation and increased swallowing. In this case, the cat may not have time to swallow saliva and liquid literally drips from its mouth.
Oncology
Tumors that form in the mouth, affecting the tongue or salivary glands can cause excessive salivation and attempts by the cat to swallow this saliva.
If a cat makes swallowing movements all the time, drinks often and a lot, urinates often, eats with pleasure and a lot, but at the same time loses weight, he may be developing diabetes mellitus. Since the animal remains active for a long time, these signs are rarely noticed by owners in the early stages of the pathological process.
These are the main reasons why a cat often swallows. Any disease accompanied by intoxication and nausea causes excessive swallowing movements.
Although pharyngeal dysphagia in dogs and cats is more common in older animals, young animals can also have temporary symptoms. Pharyngeal dysphagia often mimics cricopharyngeal achalasia: regurgitation associated with swallowing. Pharyngeal dysphagia sometimes has more difficulty swallowing liquids than swallowing solids.
Common reasons for not eating
- Pain syndrome and stress.
- Oral diseases.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines or stomach.
- Poisoning.
- Viral infection.
- Liver, kidney and urolithiasis.
- Foreign body in the stomach or intestines.
It is worth taking a closer look at each factor that will help answer the question of what to do if a domestic cat does not want to eat?
Stress or pain syndrome
Stress in an animal can be caused by rearranging things in the house or changing place of residence.
Adult animals have difficulty getting used to a new place, so a lack of appetite is normal. The owner should observe the animal, since the cat may refuse to eat due to the fact that the feeder is in an unusual place for it. Cats are independent and prefer to eat food in a secluded place. An animal may refuse food for a day during estrus, childbirth, or castration. In this case, you should not force your cat to eat; after a while, everything will work out. The main thing is that after a hunger strike the cat does not overeat, otherwise it will lead to more serious problems. If a kitten does not eat for 3 days and only sleeps, perhaps it is adapting to a new environment; a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Pain syndrome is often caused by a chronic disease. If your cat stops eating, you should consult your veterinarian.
Oral diseases
Dental problems are fairly common reasons why a cat won't eat and only drinks water.
Why is this happening? Lack of teeth in animals is the cause of diseases of the digestive tract. This is explained by the fact that the cat experiences discomfort when absorbing this or that food, as a result, it swallows the food without chewing. This problem can be corrected by selecting the right type of feeding.
The formation of tartar provokes chronic inflammation of the gums and tooth loss. It is necessary to remove tartar in a timely manner and regularly care for the animal’s oral cavity.
Caries overcomes our smaller brothers, it is also the source of many problems. Only by identifying the cause can you cope with the consequences.
Inflammatory processes in the intestines and stomach
It happens that owners provide the necessary care for their pet, but it often gets sick. Why is this happening?
The most common reason why a cat won't eat anything is worms. Animals picked up on the street especially suffer from parasites. Anyone can identify a severe helminthic infestation. Worms are visible in the animal's feces and vomit. In this case, you should get rid of parasites under the supervision of a doctor. Self-treatment of a pet can provoke poisoning of the body and deterioration of the animal’s condition.
It also happens that a cat injures the intestines with bone that is not digested by the body. As a result, the structure of the mucous membrane is disrupted, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract appear. It is impossible to ignore alarming symptoms; this can lead to exhaustion of the cat’s body and even death.
Poisoning
The gag reflex in cats is very well developed, so many pet owners are not too worried about their pet vomiting.
It is believed that vomiting helps a cat get rid of hairballs. If the cat is active after such a procedure, there is no need to worry. You should be concerned when weakness, lethargy, muscle tremors and other “unhealthy” symptoms are attributed to vomiting. Drooling with vomiting indicates poisoning. Severe poisoning in most cases leads to the death of the animal. Missing foods, household chemicals or tablets eaten by a cat can cause severe intoxication. If your cat has eaten poison, you should immediately go to the veterinarian and tell him what kind of substance the animal was poisoned with. This will make it easier for the doctor to choose the right treatment.
Viral infection
Common symptoms of a viral infection are: sneezing and discharge from the nose and eyes, complete lack of appetite, dehydration, fever, a combination of all of the above.
Treating a cat yourself, especially if it is not vaccinated, is quite risky. Whether a cat can cope with an infection depends on its immunity. The animal may refuse food for 3 days or more, in which case it will weaken. Don’t take risks, consult a doctor who can make a diagnosis after taking a blood test from the animal.
Liver, kidney and urolithiasis
If a cat does not eat or drink, he may have urolithiasis, accompanied by the formation of stones, sand in the kidneys and bladder.
It is not difficult to identify this disease. The cat is lethargic, refuses to eat, has a constant urge to urinate, and has blood in the urine. Such symptoms indicate problems with the animal’s bladder. Take preventative measures; proper nutrition for your cat is the best prevention against urolithiasis. According to statistics, cats are three times more likely to develop kidney disease than dogs. Nutrition is directly related to kidney function. Kidney failure leads to disruption of natural processes in the animal's body. The result of advanced disease is vomiting, loss of appetite, lethargy, and bad breath. Diagnosing this disease is difficult, because the symptoms are characteristic of other diseases. Do not allow the disease to go into a chronic stage, then it will be very difficult to fight it.
Liver diseases are accompanied by the symptoms described above. A cat may not eat for 3 days or even more. To avoid these problems, you should create a competent diet for your beloved pet. Balanced food supplies the animal’s body with all the necessary elements.
Foreign body in the stomach or intestines
An intestinal obstruction in an animal is a good reason to take it to the vet. Ignoring the problem often leads to the death of the pet. Obstruction is caused by sausage skins, Christmas tree needles and rain, bones and even scraps of wool.
During obstruction, gastric juice continues to be released, but it stagnates in the stomach or intestines and is not absorbed by the body. The animal reacts to this by vomiting, during which the body is actively dehydrated. Symptoms of intestinal obstruction are: vomiting, loss of appetite and complete refusal of food, enlarged abdomen, the cat reacts painfully to its touch. Why does the animal not eat for 3 days, only drink water and sleep? What can be done?
- Do not feed the animal, this will cause vomiting.
- Do not do an enema, you risk intestinal damage.
- Do not give your cat laxatives, this will shorten the intestinal muscles.
- Do not use antiemetic drugs; they provide a temporary effect but do not eliminate the problem.
- Be sure to show the animal to the veterinarian.
Etiology
Pharyngeal dysphagia in dogs and cats occurs primarily as an acquired disorder due to neuropathy, myopathy, and synaptic dysfunction (for example, localized myasthenia gravis). Failure to form a normal food bolus at the base of the tongue and/or to push the bolus into the esophagus is often associated with damage to cranial nerves IX or X. Concurrent dysfunction of the cranial esophagus can result in food retention just behind the cricopharyngeal sphincter.
Causes of the disorder
The causes of swallowing disorders are usually divided into several large groups:
- mechanical;
- traumatic;
- caused by infectious brain damage;
- caused by damage to the cranial nerves.
Oral distress can be caused by trauma to the jaw, dental disease, or abscesses in the mouth or throat. In this case, swallowing is impaired due to acute pain. If an animal is injured, there may be visible violations of the integrity of the bones, blood in the saliva, bad breath, and an abscess leads to deformation of the jaw at the site of formation.
Lymphadenopathy (inflammation of the lymph nodes of a bacterial nature or the formation of tumors) in the submandibular region leads to visible deformation of the neck, difficulty swallowing, the animal may be apathetic, its temperature rises and all other signs of general intoxication appear.
Congenital anomalies (cleft palate or short frenulum of the tongue) make it difficult for the animal to eat without losing its appetite. With a cleft palate, some of the food gets into the nose, the animal may sneeze and cough, and choke.
Swelling of the pharynx due to allergies or inflammation leads to a narrowing of the pharyngeal ring and difficulty in moving food. Allergies can cause laryngospasm and suffocation.
Ordinary myositis, inflammation of the masticatory muscles, can lead to impaired swallowing. Due to pain and dysfunction, it is difficult for the animal to chew food. Dysphagia can be caused by infectious polymyositis caused by toxoplasmosis.
Damage to the nerves (trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, cranial) leads to the inability of the animal to move food using the tongue; it tries to solve the problem using adaptive behavior.
We suggest you read: Why does a rabbit have red urine and other dangerous ailments: symptoms and treatment
Swallowing disorders can develop after a stroke, traumatic brain injury, and some other pathologies affecting the animal’s brain. In this case, the cat experiences not only a loss of the ability to swallow, but also other disorders, paralysis, and loss of consciousness.
Autoimmune diseases, polyneuropathy, muscular dystrophy that affects the masticatory apparatus lead to the fact that the animal cannot perform the usual chewing and swallowing movements.
Some infectious diseases lead to muscle damage or disruption of the transmission of nerve impulses to the masticatory muscles, for example, botulism, rabies, tick-borne encephalitis. All these diseases are accompanied by their characteristic symptoms.
A foreign body is one of the most common causes of swallowing disorders in animals. Particularly often affected are cats whose owners feed them fish or allow them to gnaw on the tubular bones of birds. In this case, the bone can get stuck in the soft tissues of the palate or pharynx, the animal coughs, vomits, and tries to scratch with its paws near the cheeks and mouth.
Causes of swallowing disorders
Gingivitis
The swallowing process is disrupted under the influence of the following pathogenic factors:
- Mechanical: occur when a foreign object is inserted into the soft tissues of the mouth or the food tube is blocked. An embedded fish bone causes pain and interferes with the act of swallowing. A curious pet plays with small parts of toys or devices scattered on the floor, swallows them and blocks the lumen of the pharynx or esophagus.
- Traumatic: damaged soft tissues become inflamed and swollen, pain or narrowing of the food passage due to a formed scar prevents swallowing.
- Congenital: anatomical abnormalities prevent the normal passage of the food coma. Most often they occur during spontaneous selection, when mating partners are not selected taking into account pedigrees.
- Errors in feeding , in which food particles are retained on the gums. Plaque occurs, tartar forms, and gingivitis develops. The act of swallowing becomes painful.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes due to hypothermia from frozen food, burns that are too hot, and infectious diseases.
- Formation of ulcerative defects of the mouth as a result of calicivirus infection.
- Paralysis of the masticatory muscles due to tick-borne or viral infection, poisoning, autoimmune processes.
- Swelling of the pharynx under the influence of irritating factors
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Tumors.
Be sure to read:
The cat doesn’t eat, only drinks water, is lethargic: reasons for what to do if he refuses to eat and sleeps
Symptoms
- Drooling, sometimes with blood
- Gagging
- Chewing food on one side of the mouth
- Frequent swallowing movements
- Cough
- Regurgitation of food
- Change in appetite
- Weight loss
- Pain in the head, mouth or neck
- Head and neck deformity
- Nasal discharge
- Bad breath
- Weakness of muscles in other parts of the body
When your cat has a hard time swallowing and you, not knowing what to do, are looking for advice on this topic on the Internet on forums, we recommend not to self-medicate and experiment on your beloved cat. The fact is that there are many causes of dysphagia in an animal, and the consequences of your experiment may disappoint you and your family.
How is the treatment carried out?
The treatment regimen is determined by the veterinarian; self-medication is prohibited. The owner must provide the pet with proper care and nutrition. Veterinarians recommend high-quality food for gastrointestinal diseases - Royal Canin Gastro Intestinal, Purina Veterinary Diets, Hills. For esophagitis, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection. When the esophagus expands or narrows and the animal cannot feed itself, an esophagostomy is installed - a tube to provide nutritional support. Therapy for concomitant diseases is also prescribed. Surgical treatment is used to remove foreign objects, remove tumors, and suturing an organ in case of severe distension.
Care and maintenance
Follow all recommendations from your veterinarian. If your pet's condition does not improve or gets worse, you should immediately contact a veterinarian. With proper treatment and care, an animal with muscle weakness or paralysis, as well as brain nerves, can recover in a few weeks.
The condition of the dentogingival system is an indicator of order in the cat’s internal organs. If you have problems with your teeth, this is a signal of a disease not only of the digestive system, but also of problems in other systems.
It happens that a pet grinds its teeth only while eating, but it happens that the process continues constantly or occurs regardless of food intake.
Treatment and prevention
Feeding through a nasoesophageal tube
Treatment consists of eliminating the cause of the disease and diet therapy.
For conservative treatment, medications of the following groups may be needed:
- antibiotics;
- immunomodulators;
- anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drugs;
- external wound healing agents.
Since swallowing is difficult, food is served in liquid form; if it is refused, it is forcibly administered through a nasoesophageal tube.
Restorative procedures involve parenteral administration of a mixture of electrolytes and detoxifiers, and, if necessary, water-soluble vitamins.
Surgical treatment is used to remove a foreign body, remove a diseased tooth or tumor. Congenital anomalies, as well as certain traumatic injuries, cannot be treated.
Teeth cleaning
Prevention consists of the following actions:
- Complete nutrition with prepared food of at least premium class. If plaque forms, use special food to remove food debris from the teeth and gums.
- Use natural cat toothpaste and brush.
- Do not treat your pet to fish with bones that could get stuck in the mouth or throat.
- Do not scatter small parts of toys or devices on the floor that your pet could swallow.
- Do not offer frozen or too hot treats.
- Vaccinate your pet in a timely manner in accordance with the vaccination plan.
- Use insectoacaricidal agents to protect the animal from arthropods.
- Carefully select pairs for mating. Eliminate the possibility of inbreeding.
Be sure to read:
What should you do if your cat develops a lump at or near the injection site after vaccination? When does a tumor become oncology?
Causes of teeth grinding while eating
Periodontal disease
Inflammation of the gums.
A pathological degenerative condition of the periodontal tissues, when there is destruction of the dental “pocket” and a violation of the attachment of the tooth in the socket. This leads to loose teeth and excessive friction.
Tartar
Tartar in a cat.
Dense yellowish-brownish growths that occur predominantly at the enamel-gingival boundary (gingival groove).
It is impossible to remove this plaque with a regular brush, especially when the cat is resisting. Professional hygienic cleaning with an ultrasonic device and sanitation of the oral cavity with disinfecting solutions in a veterinary clinic are required.
Gingivitis
You can't give your cat bones for dogs!!!
Let's look at the causes of teeth grinding that do not depend on food intake.
The products of bile metabolism enter the blood and settle in the tissues. Bile acids and their salts are quite aggressive substances that lead to bitterness in the mouth and itchy gums.
The cat's teeth itch due to liver failure.
Therefore, the animal tries to “comb” its gums - you can hear the grinding of teeth.
Urea salts (urates) and unremoved nitrates circulate through the blood, and the body tries to remove their excess through the skin and mucous membranes. Your pet's fur and mouth begin to smell like urine.
We suggest you read: What to do and how to treat diarrhea in a cat
Urates, accumulating on the surface of the enamel, make it dull and rough. Therefore, when rubbing with teeth and chewing, a characteristic sound is heard.
Another consequence of renal failure is uremic.
Often with this pathology, reflux occurs - a reverse flow of stomach contents into the esophagus, which can reach the oral cavity. Stomach acid in combination with urea salts has a detrimental effect on enamel, contributing to its destruction.
Chlorhexidine is a reliable antiseptic.
When creaking is associated with pathologies of the dentogingival system, sanitation of the oral cavity and the use of antiseptics will help:
- hydrogen peroxide,
- Chlorhexidine,
- Furacillin solution,
- Metrogyl gel.
If teeth grinding is associated with kidney or liver failure, you need to conduct an examination of the cat’s internal organs and take a sample. The sooner the correct diagnosis is made and appropriate treatment is prescribed, the greater the chance of saving the pet.
Periodontal disease
Inflammation of the gums.
Gingivitis
Pet owners sometimes hear their cats grinding their teeth. An animal can make this sound while eating, sleeping, or being awake. The reasons may be different, but in any case it is a sign of pathology. The exception is cat breeds that squeak due to a pronounced undershot or direct bite. Misalignment of teeth causes teeth to grind, causing wear and tear on the enamel.
Replacing baby teeth doesn't always go smoothly. In cases where the owner notices that the kitten’s teeth have begun to grind, it is necessary to look into its mouth. Permanent teeth can grow next to baby teeth. Loose baby teeth cause teeth to grind. A month after the teeth change begins, the grinding disappears. An exception is preserving the baby tooth(s) when the kitten is six months old. This tooth is removed in a veterinary clinic.
The cause of teeth grinding can be neurological disorders after anesthesia. Exceeding the dose of anesthetic, a delay in removing it from the body, features of the nervous system - all this can affect the cat’s condition. In such cases, the cat’s teeth grind, regardless of time and food intake.
When a cat’s teeth grind in a dream, it means that the animal has suffered a nervous shock. The stress experienced has a delayed reaction in the form of jaw clenching in sleep.
Periodontal disease
Inflammation of the gums.
Gingivitis
Cats make swallowing movements several dozen times a day. This process begins to attract the attention of the owner when the animal swallows almost constantly, or this symptom is accompanied by other manifestations.
Stressful state
It is common for all living beings to clench their teeth when under stress. People close their jaws and clench their fists not because they are preparing for a fight, but because it is a reflex. All muscles tense, as if compressed, adrenaline enters the blood, and the brain does everything to ensure survival. In this regard, our pets are not much different from people, only stressed teeth grinding most often manifests itself as a delayed reaction.
When a cat grinds its teeth in its sleep, we can safely talk about stress bruxism. The pet could have become nervous while you were at work, seeing someone else’s cat from the window; you must admit, such a reason is extremely difficult to establish. Much depends on the type of psyche of the pet; many cats are not inclined to grind their teeth, even when they are very angry. Artificially bred breeds are more susceptible to nervous disorders, so the risk of bruxism is high.