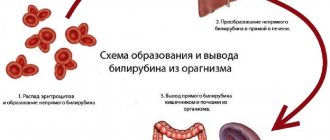
If alkaline phosphatase or bilirubin in a cat is elevated, this indicates diseases such as cirrhosis, hyperparathyroidism, osteodystrophy, pancreatitis, cancerous tumors, and heart disease. In addition to alkaline phosphatase, deviations are observed in cholesterol, albumin, and creatinine. The owner should know when the test is indicated, the rules for donating blood, as well as ways to normalize the condition.
According to statistics from veterinarians, changes in the level of alkaline phosphatase in 23% of cases are affected by hepatitis, and in 13.8% - by metastatic tumors and are found in cats of all age categories.
What it is
Amylase is an enzyme that a cat's body needs for normal digestion. This substance is produced in the pancreas and parotid salivary glands.
About 40% of the enzyme is produced by the pancreas. Otherwise it is called pancreatic amylase. This substance promotes the digestion of food mass in the duodenum.
The remaining 60% of the enzyme is produced in the salivary parotid glands. This part of amylase is necessary for processing food in the mouth.
Amylase is involved in the digestion of carbohydrates. The level of this enzyme increases during the day when the cat eats food. At night, its concentration in the blood decreases.
The enzyme is divided into 3 fractions:
- alpha amylase;
- beta amylase;
- gamma amylase.
Only alpha-amylase can be detected in the animal's blood plasma. The concentration of this particular substance is important for diagnosing diseases.
How to test alpha-amylase levels in cats
Alpha-amylase levels are examined through a biochemical blood test.
The material for research is blood serum, less often plasma. The sampling is carried out on an empty stomach. Typically, such an analysis is done before making a diagnosis or starting treatment. The blood is placed in a dry tube and tested. During the study, the age of the animal being examined should be taken into account. Young animals have a higher level.
Alpha-amylase levels can be detected by blood tests.
Amylase in the blood is increased
This enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of amino acids that make up cell membranes and tissues. AST is not active in all organs. Moreover, this type of aminotransferases can be classified as specific enzymes, the excess activity of which indicates a fairly narrow range of pathological conditions. Most of AST is found in the myocardium, cardiac muscle, hepatocytes of liver tissue, neurons of the brain and muscle tissue of skeletal muscles. This is explained by a fairly high level of metabolic processes in them and the need for maximum cell adaptability to maintain its structure. This enzyme helps them with this. As long as the structure of cells containing AST is not disturbed, the amount of this enzyme in the plasma is minimal and does not exceed normal limits. As soon as their integrity is disrupted, this leads to its excessive release into the systemic circulation. This phenomenon will be recorded in the form of a natural increase in AST activity. The dependence should be directly proportional: the more active the cytolysis, the higher the AST level.
What test do you need to take?
To find out your amylase level, you need to take a blood biochemistry test. It can also be used to determine the content of liver enzymes, cholesterol, bilirubin and other metabolic indicators. To correctly diagnose an animal, a veterinarian evaluates all analysis data in a comprehensive manner.
Venous blood is taken from the vessels of the front paw for examination. To obtain accurate data, you must follow the following rules for preparing the sample:
- This test is taken only on an empty stomach. It is necessary to stop feeding the animal 8-10 hours before blood sampling. On the eve of the test, the cat should only be given clean water to drink.
- Animals often experience fear of veterinary procedures. Stress and anxiety can negatively affect analysis data. Therefore, you should try to calm your pet before taking blood. It is advisable to call a veterinarian at home; in a familiar environment, cats behave calmer.
- If your animal is taking any medications, you should notify your veterinarian.
How is the analysis carried out?
The main way is to take blood plasma for analysis. The test will allow you to determine deviations, determine the course of treatment and carry out proper monitoring of the animal’s condition.
There are several restrictions when taking the test. Firstly, the procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours must have passed since your last meal.
Secondly, it would be better to invite a doctor to your home. Your cat may become agitated or aggressive in the clinic. In the arms of the owner with her favorite toy, she will feel calm and will easily give her paw for an injection.
Thirdly, if your pet is taking any medications, you should notify the doctor. Taking any medications can easily distort the results of the study.
ATTENTION! Amylase levels alone provide little information about health status. Only a comprehensive examination will allow you to make a correct diagnosis.
Elevated amylase in the blood of cats can cause many serious diseases. The owner should closely monitor the condition of the pet and, at the first suspicion, contact a specialist.
Possible diseases
If cats have elevated amylase and there are abnormalities in other biochemical parameters, this may indicate the following pathologies:
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- renal failure;
- intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis;
- mumps;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
Making a diagnosis on your own at home is quite difficult. However, you should pay attention to your pet’s behavior in order to notice warning signs in time.
Next, we will take a closer look at possible diseases in which cats have elevated alpha-amylase.
When do alpha-amylase levels increase in a cat's blood?
The level increases during inflammatory processes or obstruction.
It is also possible to increase the level of alpha-amylase in pathologies of the small and large intestines, skeletal muscles, and ovaries. The normal range for cats is 580–1720 units.
Alpha amylase levels should be between 580 and 1720 units.
High enzyme levels
High levels of the enzyme are observed in the following diseases:
- pancreatitis;
- mumps;
- renal failure;
- intoxication due to poisoning;
- diabetes;
- acute hepatitis;
- biliary cirrhosis of primary origin;
- volvulus of the stomach or intestines;
- peritonitis;
- imbalance of electrolyte metabolism.
Low enzyme levels
A decrease in enzyme levels occurs in cases of chemical poisoning.
At the same time, a decrease in the level of the enzyme occurs with necrotic pathology of the pancreas, thyrotoxicosis, and poisoning with toxic chemicals.
De Ritis coefficient in dogs and cats
The coefficient in animals is determined in the same way as in humans - the ratio of two enzymes - aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT). These enzymes are synthesized by the liver and myocardium.
Heart diseases accompanied by necrosis (infarction, ischemia) increase the level of AST in the blood by approximately 8-10 times. At this time, ALT is also increased, but less - 2-2.5 times.
If an animal has liver problems, the level of ALT in the blood increases by about 8-10 times, but AST increases by about 2 times.
The de Ritis ratio is determined by the ratio of AST to ALT. The resulting value of the indicator is determined in units/l. The norm for dogs and cats is 1.33-1.75 units/l.
Description of the study
In animals, only alpha-amylase is present. Amylase hydrolyzes complex carbohydrates. The pancreas, liver, and small intestine are sources of serum amylase. In a healthy animal, the source of serum amylase is extrapancreatic sources and this amount usually does not exceed 1000 U/l. Lipase and amylase are inactivated in the kidneys and are excreted from the body in the urine (if the excretory function of the kidneys is impaired, these enzymes remain in the bloodstream longer and their activity increases) A breed predisposition to acute pancreatitis has been noted: • Middle-aged dogs of breeds such as miniature schnauzer, miniature poodle and cocker -spaniel • Middle-aged Siamese cats
Inflammation of the pancreas
This pathology is otherwise called pancreatitis. The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. Most often, older cats suffer from inflammation of the pancreas.
The chronic form of the disease can occur without obvious pathological manifestations. Acute pancreatitis is accompanied by severe symptoms:
- diarrhea or stool retention;
- unpleasant sour odor from feces;
- drowsiness and apathy;
- plaintive meowing during an attack of pain;
- frequent vomiting after eating;
- fever;
- heavy breathing.
Similar manifestations are observed during exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
The analysis showed that the cat had elevated pancreatic amylase, liver enzymes, cholesterol and glucose. Due to diarrhea and vomiting, dehydration occurs, so the calcium level in the blood is reduced.
Animals require a strict diet. The cat needs to be fed often, but in small portions. It is advisable to switch your pet to special medicated food. The use of painkillers, antacids and antiemetics is indicated. In case of severe dehydration, drip administration of saline solutions is necessary.
Treatment method and prognosis
As a rule, the dog is prescribed a course of medications aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that caused the increase in enzymes. So, if the process has developed against the background of liver pathology, the drug Essentiale is prescribed, which stabilizes liver function. The dosage is determined by the veterinarian.
At the end of treatment, a biochemical blood test is done again. Enzyme levels at the same level or their increase indicate that the treatment was ineffective. In this case, there is a need for surgery to remove the affected organ.
In the postoperative period, the level of phosphatase is also increased, but this is not considered a pathology. Over time it will normalize.
During the treatment and postoperative period, the owner must strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or prescribe medications without consulting a veterinarian.
As for the prognosis, it all depends on how timely and competently the treatment (surgery) was carried out. The development of pathology leads to chronic organ diseases.
Diabetes
Elevated pancreatic amylase in cats may be one of the signs of diabetes mellitus. Obese animals are especially susceptible to this disease. The cause of the pathology is a decrease in the production of the hormone insulin.
The owner should be wary of the following pathological manifestations in the pet:
- urinating too frequently;
- strong thirst;
- lethargy;
- bad breath with the smell of acetone;
- changes in appetite (gluttony or refusal to eat);
- deterioration in wool quality;
- causeless weight loss.
The concentration of glucose and creatinine in the blood also increases.
Cats have two types of diabetes. In type 1 pathology, the animal requires constant and lifelong administration of insulin. For type 2 diabetes, taking pills that lower glucose levels in the body is indicated. It is also helpful to purchase a veterinary glucometer to monitor your blood sugar levels.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to establish a diagnosis of pancreatitis based solely on the symptomatic picture . The specialist prescribes several analyzes and tests, the results of which will be the basis for the correct diagnosis. If necessary, additional tests are prescribed to rule out other variants of the disease.
The most common options for examining cats :
- X-ray of the abdominal area. Aimed at identifying any foreign bodies in the intestines, as well as effusion or coprostasis.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity allows you to diagnose the condition of all organs involved in digestion. Particular attention is paid to the pancreas, which increases in size during inflammation and is well fixed by the device. This method is considered the most effective in making a diagnosis.
- Blood tests are performed in several variations - biochemical and general. The information obtained allows us to identify both pancreatitis and concomitant diseases.
- Invasive interventions are performed in complex cases of disease, when traditional treatment does not change the condition of the sick animal. The study is carried out using laparoscopy, which allows you to exclude blockage of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as assess the real condition of the pancreas. This method helps diagnose neoplasms, abscesses, cysts, perforated ulcers or abdominal effusions.
Histological studies do not always reflect the real picture of the animal’s condition, so material for a biopsy is not taken often. This type of study can reveal ductal hyperplasia, the process of fibrosis, as well as pancreatic necrosis in cats.
Blockade with novocaine has a good therapeutic effect, which leads to the cessation of vomiting in cats after surgical procedures.
Pancreatic amylase in cats, like lipase, cannot be considered a hallmark of pancreatitis, as occurs with inflammation of the pancreas in humans.
Pancreatic amylase may be elevated as a result of the presence of a foreign object in the cat's digestive tract, or during enteritis.
Inflammatory processes in the pancreas do not increase either amylase or lipase, and the stool test will show the norm of pancreatic elastase. There is a special test for cats for pancreatitis , it was developed in the USA, but today it has not become widespread in veterinary hospitals in Russia.
When does a cat have insufficient alpha-amylase?
Problems in the animal’s body can also be judged if the analysis reveals a lack of amylase. So, if the amount of enzyme is much lower than normal, you can suspect the following ailments:
- Pancreatic insufficiency
- with insufficient production of digestive enzymes, cats may experience weight loss with a good appetite, constipation and diarrhea, which alternate (the color of the stool may be whitish, the smell - sour and fetid), flatulence, rapid heartbeat, vomiting. Most often, this disease is diagnosed in older diabetic cats;
Myocardial infarction
– with the development of necrotic processes in the muscular middle layer of the heart in cats, paleness of the skin and mucous membranes, pain in the elbow area on the left, and agitation are encountered. Most often, infarction occurs in animals with heart disease and vasculitis;
Oncology of the stomach, liver or intestines
– with cancer, cats quickly lose weight, become lethargic, eat little, and suffer from temperature fluctuations. When the liver is damaged, the mucous membranes turn yellow, and if the stomach or intestines are damaged, there may be blood in the stool, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea. More often, oncology is diagnosed in cats in old age, in animals with low immunity, in pets suffering from hormonal disorders;
Pancreatic necrosis
– when pancreatic tissue dies, cats suffer from severe vomiting, high fever, bloating, and pain in the peritoneum. The pets' skin takes on a bluish color. Most often, necrosis develops in cats with gallbladder problems, poor diet, and uncontrolled medication use;
- Hepatitis
- amylase can be reduced during diffuse processes occurring in the liver. Symptoms of hepatitis are weakness, jaundice, vomiting, and sometimes blood in the stool. As a rule, hepatitis develops against the background of advanced helminthiasis, during poisoning, or as a complication after infectious diseases.
So, we found that an increase or decrease in alpha-amylase levels in a cat's blood can signal major health problems. An experienced doctor, who will have the test result at his disposal, will help you find out exactly what disease has affected the animal.
Signs of low amylase
A lack of amylase can also lead to problems with cat health. Let us note some diseases and their symptoms.
Pancreas problems
Reduced secretion of amylase leads to malfunction of the digestive organs. Let us note the symptoms that lead to pathologies in the pancreas:
- loss of appetite;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- changes in the color of feces and a sour, foul odor;
- bloating and excess intestinal gas;
- cardiopalmus;
- vomit.
The disease is typical for older cats.
This group also includes necrosis of the pancreas . In fact, this is the death of living cells. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- elevated temperature;
- severe vomiting;
- bloating;
- abdominal pain on palpation;
The lower abdomen turns blue. The death of pancreatic cells is associated with poor nutrition, abuse of cheap dry food, and excessive use of medications.
Cancer of the digestive system
A terrible disease, of course, cannot appear only because of a low level of amylase in the blood. But the very fact of hormone deficiency can clearly indicate an incipient disease:
- the mucous membranes of the digestive organs acquire a yellow tint;
- bloody diarrhea;
- constipation;
- gases in the intestines;
On the positive side, it can be noted that older pets with weakened immunity and disruptions in the hormonal system are susceptible to the disease.
Hepatitis
Unfortunately, a lack of amylase can lead to hepatitis. Among the main symptoms it is worth noting:
- weakness, unsteadiness of gait;
- vomit;
- the mucous membrane acquires a yellow coating;
- feces with blood.
Hepatitis is often caused by poisoning and infection by pathogenic microorganisms.
Myocardial infarction
Heart problems are also a consequence of low amylase. The disease exhibits the following symptoms:
- excitation;
- mucous membranes turn white, as do individual areas of the skin;
- chest pain.
Most often, myocardial infarction is preceded by heart disease and vasculitis.
Intestinal obstruction
This pathology in cats occurs due to volvulus of intestinal loops. It is accompanied by pronounced symptoms:
The cause of volvulus can be too much food, frequent constipation, as well as excessive activity of the animal after eating. This is a very dangerous pathology that can quickly lead to the death of a pet. An emergency operation is required, during which the veterinarian will remove the intestinal obstruction.
When volvulus occurs in cats, amylase is increased and protein content is decreased. However, a blood test is usually not required for this pathology. This disease is diagnosed using an x-ray or ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Drug treatment of pancreatitis
Treatment of pancreatitis in cats is carried out after a preliminary diagnosis. The acute form of the disease is dangerous with sepsis or painful shock , so waiting for research results can be fatal.
Compensation for water and salt losses
Since diarrhea and vomiting removes essential fluids and salts from the cat’s body , it is necessary to restore the balance with the following solutions:
- Trisol;
- saline;
- Ringer;
- Acesol.
The medicine Reamberin is also used, which has the ability to reduce blood glucose levels and also reduces its acidity. The above solutions are administered intravenously warm, but at a very low speed. Since the volume of the solution is quite large, the cat can remain under the IV for hours.
Reference!
It is possible to add vitamins and antioxidants to the solutions - Mexidol, vitamin C, Emidicin.
Decoding the biochemical blood test in cats
A biochemical blood test allows you to evaluate the functioning of the internal organs of cats and dogs.
The following main indicators: bilirubin, total protein, creatinine, urea, glucose, cholesterol.
Example of biochemical blood test
Enzymatic activity is assessed by: ALT (alanine aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), amylase and alkaline phosphatase.
Also, according to indications, the study includes indicators such as electrolytes (phosphorus, potassium, calcium, sodium, chlorine, iron) and magnesium.
The following indicators are considered normal:
| Index | Units | Norm |
| Bilirubin | µmol/l | 3-12 |
| Total protein | g/l | 54-77 |
| Creatinine | µmol/l | 70-165 |
| Urea | µmol/l | 5,4-12,1 |
| Glucose | mmol/l | 3,3-6,3 |
| Amylase | mg/(s*l) | 8-32 |
| Cholesterol | mmol/l | 1,6-3,7 |
| AST | U/l | 9,2-39,5 |
| ALT | U/l | 0-95 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | U/l | 39-55 |
| Phosphorus | mmol/l | 1,1-2,3 |
| Calcium | mmol/l | 2-2,7 |
Peritonitis
Inflammation of the peritoneum in cats is most often of bacterial or viral origin. Pathology can occur in the following forms:
- Exudative. Fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. This type of inflammation is diagnosed in 70% of cases.
- Dry. There is no accumulation of fluid in the abdomen. Foci of inflammation are observed in the peritoneal tissues.
The symptoms of the pathology are as follows:
- severe pain syndrome;
- vomit;
- fever (temperature is not reduced by antipyretics);
- complete refusal of food;
- diarrhea;
- abdominal retraction;
- reduced blood pressure.
The cat has increased amylase and globulins, and albumins are sharply decreased. Due to fluid loss during vomiting and diarrhea, the content of sodium, potassium and chlorine decreases.
Cats are prescribed antibiotics, analgesics and immunomodulators. For severe pain, it is recommended to apply cold compresses to the abdomen. In case of exudative form of pathology, drainage of the abdominal cavity is performed.
Symptoms of pancreatitis in cats
The high effectiveness of treatment of pancreatitis in cats is entirely determined by timely and correct diagnosis. Often the signs have a general clinical picture and are mild, so pancreatitis is difficult to identify even for an experienced veterinarian .
The unique course of the disease in cats is determined by its invisibility, since the animal simply sleeps a lot. Chronic and acute pancreatitis is manifested by the following symptoms :
- The gag reflex is characteristic both during an exacerbation and during an advanced disease. Vomiting is manifested by continuous urges, this extremely exhausts the animal.
- Dyspeptic symptoms - diarrhea with particles of undigested food, fetid stool, flatulence.
- Against the background of vomiting and intestinal dysfunction, a water-salt imbalance develops .
- Painful sensations , which are manifested by loud meowing or strong excitement.
- Abdominal muscle tone.
- Lack of energy and tone in the cat, ignoring games and communication with family members. The animal tries to hide in a dark corner.
- Acute attacks are characterized by fever.
- With pathology of the bile ducts, the mucous tissues of the cat may become yellow.
- Refusal of food, weight loss.
- Dysfunction of the cardiac or respiratory system.
The severity of the symptoms directly depends on the degree of damage to the pancreas; the acute form of the disease has more noticeable symptoms. Symptoms and treatment may vary depending on the causes of the disease, so therapy is prescribed by a veterinarian after all the necessary tests.
Reference!
Often, pancreatitis affects the functioning of other organs - the liver, heart or lungs, as well as the functioning of the entire digestive tract. The entry of toxins into the animal’s bloodstream leads to extensive damage to the entire body.
Kidney failure
Kidney failure most often affects cats over the age of 8 years. The animal exhibits the following symptoms:
- frequent urination;
- discoloration of urine;
- thirst;
- swelling of the paws and body;
- blanching of mucous membranes;
- smell of ammonia from the mouth;
- sudden weight loss;
- dulling of fur;
- severe lethargy;
- frequent licking of the perineum.
As the pathology develops, the amount of urine decreases sharply. The cat has increased amylase, as well as creatinine, magnesium and urea. In the chronic form, there is a decrease in calcium and potassium levels.
Kidney failure cannot be completely eliminated. You can only achieve long-term remission. To eliminate dehydration, animals are given IVs with salt solutions and prescribed corticosteroids and potassium supplements. In later stages, diuretics are indicated. In advanced cases, dialysis must be performed regularly.
Diet plays an important role in treatment. Protein foods should be excluded from the diet. Veterinarians recommend giving sick animals special dietary foods.
Causes
During a pathological process in the body, the permeability of cell membranes increases, as a result of which the cells are destroyed. This is how alkaline phosphatase, or rather its excess, penetrates the blood. This can be confirmed by the result of a biochemical blood test.
This does not always mean the development of serious pathologies in the body. For example, in puppies and young animals, enzyme levels may increase due to intensive skeletal and bone tissue development.
An increase in phosphatase in animals after fractures, as well as in bitches during pregnancy, is not a deviation from the norm.
Another common cause of elevated enzymes is the use of certain medications, such as steroid hormones, anticonvulsants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
An increase in phosphatase can occur with calcium deficiency and consumption of fatty foods, as well as with the development of serious pathologies in the dog’s body: cirrhosis of the liver, Cushing’s syndrome in dogs, oncology of the mammary glands, bone tissue, biliary tract, pancreatitis.
And this is not a complete list of life-threatening diseases. That is why, if suspicious signs are detected, it is so important to contact a veterinarian in a timely manner.
Liver diseases
With hepatitis, biochemical blood parameters deviate sharply from the norm. The cat has elevated amylase and liver enzyme ALT. There is also a high iron content in plasma.
Unlike people, cats do not suffer from viral hepatitis. This disease in animals is of bacterial or parasitic origin. There is also a toxic form of liver inflammation that develops after poisoning.
The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- yellow color of the whites of the eyes and oral mucosa;
- severe itching;
- vomiting with bile;
- loss of appetite;
- irregular bowel movements (diarrhea alternates with constipation);
- light-colored feces;
- darkening of urine;
- thirst.
Animals are prescribed hepatoprotectors, immunomodulators and antihistamines. For the infectious form of the pathology, antibiotics are indicated, and for toxic hepatitis, the introduction of antidotes. If the disease is caused by parasites, then anthelmintic therapy is necessary.
The most dangerous liver pathology is cirrhosis. This disease is very difficult to recognize at an early stage, since symptoms may be completely absent. Signs of the disease appear in advanced cases, when it is already very difficult to cure the cat.
Most often, cirrhosis develops as a complication of hepatitis. The disease is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- bloating due to fluid accumulation;
- drowsiness;
- thirst;
- sudden weight loss;
- seizures;
- causeless aggression;
- unsteady gait;
- decreased visual acuity.
Biochemical blood parameters in cirrhosis are the same as in hepatitis.
It is impossible to completely cure cirrhosis that has already begun. In this disease, healthy organ cells are replaced by fibrous tissue. You can only stop the development of pathological changes. It is necessary to take hepatoprotectors, diuretics and vitamins. Sick cats are prescribed a diet with limited protein and fatty foods.
Significance of indicator changes
So, the animal got sick, after donating blood for a biochemical analysis, it is clear that the dog’s de Ritis coefficient is reduced. What does this mean? This indicator indicates an increase in the level of alanine aminotransferase.
If it is below 1.33 units/l, but above one, this means that the animal has chronic liver disease. If the indicator drops below one, this indicates acute liver damage. When the coefficient is equal to one, this indicates viral hepatitis, piroplasmosis, babesiosis and other acute pathologies.
An increase in the de Ritis coefficient in the analysis indicates an increase in aspartate aminotransferase in the blood. Most often, this indicator indicates myocardial infarction. This is an extremely rare pathology for animals; it occurs mainly in old dogs and cats. Sometimes this situation occurs when there is a congenital vascular pathology or in case of poisoning with cardiotoxic poisons.
An increased de Ritis ratio may also indicate liver pathologies. This is typical for cirrhosis. In humans, this situation is a typical sign of alcohol impairment.
But alcoholic cirrhosis does not occur in cats and dogs, so an increased de Ritis coefficient indicates chronic toxic lesions or as a consequence of long-term hepatitis.
The Ritis coefficient also determines how effective the treatment of the disease is. A decrease in this value indicates correctly selected treatment. But when treating acute hepatitis, it is important to monitor the overall AST indicator - it should also decrease.
How to check amylase levels
To determine the level of amylase, a cat's blood or plasma is taken for biochemical analysis. It is done to make a diagnosis, determine a treatment regimen for the animal, and control the course of the disease. The collected sample is placed in a test tube and sent to the laboratory for testing.
In order to prepare a cat for testing, you need to follow several rules.:
- Minimize stress and keep your pet calm. It is better to call the veterinarian home.
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach. You cannot feed your cat for at least 8 hours before the procedure. Otherwise, the results may be erroneous.
- If your animal is taking medications, notify your doctor.
When conducting animal analysis, the age of the cat is taken into account. In young animals the level of indicators is higher.
The level of amylase in the blood of a cat, unlike dogs, does not provide any information. If all other indicators are normal, then there is no cause for concern.
In order for a cat to be healthy and live a long life, you need to carefully monitor its behavior. If signs of illness appear, you need to show it to the doctor. Only a specialist will take the necessary tests and correctly interpret the results. You should not treat yourself. And the cat will give its warmth to its owner for a long time.
Mumps
With pathologies of the parotid glands in cats, amylase is increased. The cause of this is most often mumps. In humans, this disease is known as mumps. It is accompanied by inflammation of the salivary glands. The causative agent of the pathology is paramyxovirus. Often mumps occurs as a complication of stomatitis, pharyngitis or plague.
The disease begins acutely. The animal quickly develops the following signs of pathology:
- swelling of the muzzle (unilateral or bilateral);
- pain when opening the mouth;
- fever;
- increased salivation;
- formation of ulcers on the skin in the affected area;
- sudden weight loss;
- refusal of food.
In severe cases, the salivary glands become suppurated and a painful abscess appears on the skin.
Treatment of a viral infection can only be symptomatic. It is necessary to provide the cat with complete rest. It is recommended to give the animal only liquid food. Vitamin preparations and immunomodulators are prescribed, as well as warming physiotherapy. When the glands become suppurated, the abscess is opened surgically.
Elimination of nausea and vomiting
During vomiting, inflammation of the esophagus occurs, and dehydration occurs. If vomiting continues in cats while refusing food, they must be stopped with medication .
For this purpose the following drugs are used:
- Cerucal, administered by injection once every 8 hours;
- Zofran, applied once every 12 hours;
- Sereniya is used once a day.
Before using Cerucal, you should exclude the possibility of a foreign body in the intestinal cavity, since the drug activates the digestive tract.
The drug Sereniya is the best option because it relieves the gag reflex, regardless of the cause of its onset, by acting on the nerve centers.