What's happened papillomas in cats and why do they appear? This disease is quite widespread among both animals and people. Why papillomas appear, how dangerous they are, and how to treat them - this is what our article is about today.
If your pussy has symptoms of illness, then do not waste valuable time, contact the Center for Emergency Veterinary Care for Animals “YA-VET”.
Veterinarians with a high level of education, training and many years of experience are at your service. Diagnostics are carried out using the latest generation equipment and with a very high degree of accuracy.
It is also possible to call a veterinarian to your home, where they will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis in a calm and familiar environment for the animal. To call for emergency veterinary help, call the phone and a doctor will be with your pet in the shortest possible time.
Reasons leading to the problem
The main source of the formation of papillomas in cats on the head, bridge of the nose, fingers, paws and other areas of the body is the papillomavirus. In every pet, like in humans, a similar pathogenic microorganism is constantly present, but in the latent phase. To activate the virus and its active reproduction, the influence of the following factors is required:
- Weak immunity. For this reason, papillomas on the nose or claw often form in kittens whose immune system is not yet fully functioning. Also at risk are sick animals, cats after giving birth and pets taking medications.
- Age-related changes in the body. Old cats often develop similar moles that need to be examined by a veterinarian.
- Heredity.
- Severe stress.
- Chronic infectious diseases.
Such growths on the animal’s body are benign. In veterinary medicine, a similar disease is also known as papillomatosis, in which small formations of a benign nature are formed. Under the influence of certain factors, papillomas in cats can degenerate into cancerous tumors, which pose a direct threat to the life of the animal. At risk of developing warts on the body are individuals living in large groups and without maintaining satisfactory sanitary and hygienic conditions. The virus is transmitted through contact of a healthy cat with a sick one, and infection is also possible through wounds on the skin. If a pregnant cat is infected with papillomavirus, then the disease is likely to be transmitted to kittens.
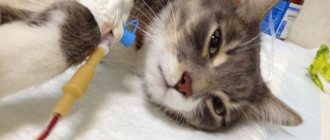
Removal of papillomas from a cat under local anesthesia
What are papillomas in cats and why do they appear? This disease is quite widespread among both animals and people. Why papillomas appear, how dangerous they are, and how to treat them - this is what our article is about today.
If your pussy has symptoms of illness, then do not waste valuable time, contact the Center for Emergency Veterinary Care for Animals “YA-VET”.
Veterinarians with a high level of education, training and many years of experience are at your service. Diagnostics are carried out using the latest generation equipment and with a very high degree of accuracy.
It is also possible to call a veterinarian to your home, where they will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis in a calm and familiar environment for the animal. To call for emergency veterinary help, call the phone and a doctor will be with your pet in the shortest possible time.
Papillomas in cats: etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
Among the representatives of domestic cats there are animals that suffer from a dangerous disease of an infectious nature. We are talking about feline viral papillomatosis .
The disease described is a fairly dangerous disease and is characterized by the fact that infected cats have focal lesions, both single and multiple. They are benign neoplasms.
In appearance, they resemble warts and are localized both on the skin and on the mucous membranes in the mouths of cats and in other places with a mucous membrane. Papillomas are often found on the skin of cats.
Speaking about the reasons that result in the appearance
of papillomas in cats (and in cats and even kittens), you should immediately pay attention to the strong decrease in immunity.
This happens after operations, as well as as a result of serious illnesses, after giving birth to cats, or during treatment with certain medications.
It is impossible to exclude the age factor, as well as the genetic hereditary predisposition of the animal.
Sexual transmission of the papilloma virus has been proven
and because of this, papillomatosis can be considered a sexually transmitted disease.
- Being in a latent state in the body,
papillomatosis virus can be activated when
- :
- suffered under severe stress;
- after viral infections.
The papilloma virus in cats penetrates into the cells of the basal layer of the skin through injuries, scratches, abrasions and cuts. Actively multiplying, the virus grows on the surface epidermis or on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Under the direct influence of the transforming proteins of the virus, the affected cells begin to divide and multiply without limit. That is, they develop a tumor structure.
At their core, papillomas are benign tumors. However, if you tear off a papilloma, its cells begin to divide non-stop. Papilloma turns into cancer, that is, into cancer.
However, often there is both a spontaneous recovery of the animal and the degeneration of papillomas into malignant tumors, which lead to the death of the cat.
Symptoms of papilloma disease in cats and diagnostic methods
A characteristic symptom of the lesion is the formation of multiple lesions and the rapid rate of their growth.
Having a pale pink color and a very small size in the initial stage of their development, such rashes can go unnoticed until they are traumatically damaged. In such cases, the cat may develop significant bleeding, since the papillomas are abundantly penetrated by the capillary network.
If the papilloma is torn off, this can be the starting point for the development of skin cancer. Therefore, papilloma in a cat is a serious and quite insidious disease.
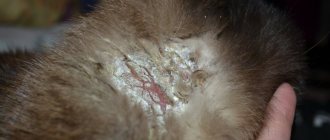
Over time, wart rashes grow, their surface acquires uneven outlines like a cauliflower. The number of papillomas is growing rapidly.
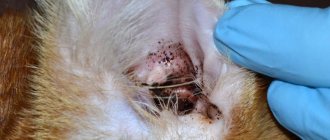
If papillomas develop in a cat's mouth, they grow along the surface of the gums, tongue, inner surface of the cheeks and under the tongue. In the most advanced cases, such growths disrupt the process of eating and chewing in cats.
Sometimes inexperienced owners suspect that the cat has a salivary gland cyst. However, the further course of the disease completely refutes this misconception.
- Symptoms of papillomatosis also include such general somatic manifestations as:
- Increased body temperature.
- Refusal of food.
- Vomit.
- Bleeding in the mouth.
- Apathy and indifferent behavior.
If there are growths on the paws, they are constantly injured. This makes it easier for pathogens to enter the cat's body. And since the animal’s immunity is noticeably reduced, secondary infectious processes develop.
Therefore, if possible, you should try not to tear off the papilloma.
Diagnostic procedures consist of an examination of the cat by a veterinarian and a detailed questioning of the owner about any visible symptoms of the disease.
- It is mandatory to carry out such
laboratory tests for diagnosis
- , How:
- General blood analysis.
- Polymerase chain reaction.
- Microscopic examination of scrapings.
- Histological studies of papillomas tissue samples.
All of the above studies are available for carrying out at the Center for Emergency Veterinary Care for Animals and by calling a veterinary specialist “YA-VET” to your home.
Treatment of papilloma in cats and prevention of the disease
It has already been said that papillomas can disappear completely spontaneously. But most often, in the absence of effective treatment, the number of growths in the cat increases, and the course of the disease becomes severe. When using complex treatment methods, the number of formed papillomas is significantly reduced, and the development of new ones is inhibited.
the most optimal treatment method . This painless procedure helps remove all growths without subsequent cosmetic defects. Papillomas can also be removed using cryotherapy, that is, freezing with liquid nitrogen. Any of the removal methods leads to the recovery of the animal and does not cause any harm to its body.
In addition to removing papillomas , the animal is given immunostimulating drug therapy, and is also prescribed a course of treatment with antiviral drugs, and given multivitamin complex tablets and mineral supplements. Unfortunately, none of the treatment methods can completely eliminate the papilloma virus in cats. With the slightest weakening of the immune response, the disease may recur.
As a preventative measure, it is recommended to strengthen the body’s defenses and also avoid direct contact with carriers of the papilloma virus. There are no preventive vaccines against papillomatosis.
Source: https://ya-vet.com/hirurg/udalenie-papillom-u-koshki-ili-kota-pod-mestnoj-anesteziej
Probable locations of papillomas on the body
Characteristic symptoms of infectious papillomatosis are the occurrence of focal lesions on the mucous membranes of the mouth, the formation of pathogenic neoplasms on the outer surface of the tongue and lips. The disease is progressive and over time, papillomas can appear on the palate, pharyngeal mucosa, and nose.
At the initial phase of appearance, papules have a smooth structure. Over time, the number of lesions increases, uneven growth of the mucous membrane occurs, which provokes changes in the appearance and structure of papillomas. The number of papillomas gradually increases; in severe cases, they can cover the cheeks, gums, and can appear in the ears, on the paws, on the head, near the urethra, on the gastrointestinal tract, on the eyelids, and on the conjunctiva of infected animals.
Papillomas in the mouth cause discomfort when eating food; sick individuals may experience fever, excessive salivation, refusal to feed, bleeding in the mouth, and attacks of vomiting.
Neoplasms on the paws and ears can provoke serious inflammatory lesions, since the limbs are constantly in contact with the surface of the floor or ground, and there is a danger of ticks in the ears.
The external genitalia can also be affected; painful wounds and nodular formations are often observed here.
What causes papillomas and warts in cats?
Papillomas and warts in cats appear under the influence of certain viruses, when the animal’s immunity is weakened.
Benign neoplasms can have different sizes and can appear in different parts of the body. Neoplasms carry a certain risk, especially if they form in the animal’s oral cavity.
The formation of papillomas and warts is influenced by hereditary factors and the age of the pet.
Causes of papillomas in cats
The main reasons why papillomas appear in an animal are as follows:
- Weakened immunity. This condition in an animal is observed after serious illnesses, after childbirth or taking certain medications.
- Age characteristics of the pet. In kittens, papillomas appear due to unstable immunity, in older cats due to weakening of the body's protective properties.
- Hereditary predisposition of the animal.
The papilloma virus comes out of latency also under the influence of:
- Severe stress;
- Chronic viral infections.
Warts and papillomas are benign tumors. Spontaneous recovery from papillomatosis or degeneration of papillomas into malignant formations, causing the death of the cat, are practically possible.
At risk are animals that are kept in large groups in unsatisfactory sanitary and hygienic conditions.
Papillomas can be transmitted by contact with an animal carrying the papilloma virus.
Infection can also occur through damaged epidermis, bleeding wounds, abrasions, and through scarified mucous membranes.
Transplacental transmission of papillomaviruses is also possible. Experts highlight the possibility of sexual transmission.
Symptoms
Papillomas and warts appear on the animal’s body 2 months after infection.
May be observed:
- Decreased appetite;
- Indifference to others;
- The appearance of formations on the pet’s body. Papillomas can be of different sizes, there may be foci with single papillomas, as well as groups of interconnected tumors;
- Itching caused by specific warts. After scratching, open wounds form on the cat’s body, which cause discomfort to the cat and affect its usual behavior.
Diagnostics
The veterinarian begins the diagnosis with a visual examination of the sick cat, recording clinical signs of pathology. Subsequently, comprehensive laboratory tests are carried out and tests are taken.
Test systems used:
- Immunohistochemical staining methods;
- Histological examinations.
Methods are also used:
- Electron microscopy;
- Polymerase chain reaction.
Probable locations of papillomas on the body
Characteristic symptoms of infectious papillomatosis are the occurrence of focal lesions on the mucous membranes of the mouth, the formation of pathogenic neoplasms on the outer surface of the tongue and lips. The disease is progressive and over time, papillomas can appear on the palate, pharyngeal mucosa, and nose.
At the initial phase of appearance, papules have a smooth structure. Over time, the number of lesions increases, uneven growth of the mucous membrane occurs, which provokes changes in the appearance and structure of papillomas.
The number of papillomas gradually increases; in severe cases, they can cover the cheeks, gums, and can appear in the ears, on the paws, on the head, near the urethra, on the gastrointestinal tract, on the eyelids, and on the conjunctiva of infected animals.
Papillomas in the mouth cause discomfort when eating food; sick individuals may experience fever, excessive salivation, refusal to feed, bleeding in the mouth, and attacks of vomiting.
Neoplasms on the paws and ears can provoke serious inflammatory lesions, since the limbs are constantly in contact with the surface of the floor or ground, and there is a danger of ticks in the ears.
The external genitalia can also be affected; painful wounds and nodular formations are often observed here.
Treatment of papillomas in cats with novocaine
An effective way to treat papillomas is an injection of a 0.5% novocaine solution. For one kilogram of animal weight, 1 ml of solution is injected. The solution should be injected under the base of the wart.
The manipulation is repeated three times with an interval of 3 days between injections.
The following schedule is more effective: one injection of 0.5% novocaine at the base of the papilloma, then injection of a 10% solution of iodoform ether. The dose of these medications should be 0.5 ml.
In cases where a cat has a jugular process, use a 5% solution of novocaine, the procedure is repeated 3 times with an interval of 4 days, with a dose of 3 ml.
Treatment at home
It is not recommended to organize treatment without a preliminary medical examination and examination using skin scrapings and biopsies (if necessary). The question is that cat owners often confuse malignant tumors and seborrhea on the cat’s tail with ordinary warts.
At home, medications are used to treat papillomas:
The skin on the face and ears is tender, which is what causes severe itching when a wart appears in the head area. If a cat picks a wart with its claws, antihistamines to relieve itching (Suprastin) and anti-inflammatory ointments are used for disinfection. Most often used:
- Betadine;
- Levomekol;
- Chlorhexidine.
Removal of warts and papillomas
There are rare cases when papillomas disappear on their own. However, pathogenic formations generally require special treatment. If it slows down, the disease will progress, causing discomfort to the animal. Clinical treatment is prescribed taking into account the extent of the infection, the number and size of papillomas.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V-e_VX-rudE
Cats are prescribed:
- Antimicrobials;
- Antibiotics, taking into account their action aimed at destroying bacteria in the bloodstream.
Local treatment is also carried out by removing papillomas and warts.
Papillomas are removed:
- Liquid nitrogen;
- A beam of laser beams;
- By radiation.
After removal, the animal recorded a complete recovery. The process is completely safe for the pet’s body.
After removal, the following is prescribed as additional therapy:
- Immunostimulating agents;
- Vitamins;
- Mineral supplements.
Are papillomas in cats contagious to humans?
The virus from which cats become infected with papilloma is highly specific. It only works on cats, and is even safe for dogs. For the human body, such a virus is also not dangerous; a person cannot become infected with it.
You need to constantly monitor the cleanliness of your beloved pet's skin, ears and paws. If symptoms appear, do not hesitate to visit the veterinarian. Quick and accurate diagnosis is the key to your pet’s complete recovery.
Source: https://okotikah.ru/bolezni/papillomy-borodavki-u-koshek.html
What species are found?
In cats, papillomas differ not only in location, but also in origin and other indicators. The table shows the main types of warts in cats and their brief description:
| Varieties | Location | Peculiarities |
| Oral | Oral cavity, tongue or inner cheek | This type of papilloma most often forms on the skin of a kitten that is less than 8 months old. |
| Oval shaped with flattened top | ||
| Multiple | Any part of the body | Diagnosed mainly in older cats and female cats |
| Many warts immediately appear, the size of which ranges from 3 mm to 3 cm | ||
| Papillomas are convex and pigmented | ||
| Single | Rarely found in felines | |
| It is a small swelling under the epidermis | ||
| Veterinarians have still not been able to figure out the reasons for the appearance of such papillomas in animals. |
Description
When infected with a virus, warts appear on the skin. The disease is classified according to location and quantity as follows:
- Oral papilloma. It can be found in old animals, more than 7-8 years old. Also occurs in young kittens up to 5-8 months. Papillomas are located on the gums, the inside of the cheeks, and the tongue. New growths are oval, flattened.
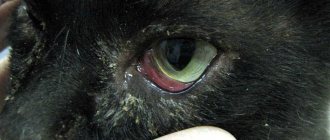
- Single skin papillomas. Warts are found on the face, around the mouth, eyes, and ears. Less commonly, they can be found on the paws and body. Old animals, as well as young kittens, suffer from this form of the disease.
- Multiple skin papillomas. A rather rare form of papillomatosis. Manifests itself with a strong decline in resistance. The neoplasms are different in size, their crowding resembles cauliflower.
Symptoms
Neoplasms in cats differ in that seals appear on the body. But it is quite difficult to notice them, since usually no one probes their animal every day.
When internal organs are damaged, significant changes in the pet’s condition are noted:
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- neurological symptoms;
- changes in blood composition;
- respiratory problems.
Secondary characteristics:
- ascites;
- cough;
- shortness of breath, vomiting.
If a tumor in cats forms in the skin, its growth is slow. Metastasis is observed only in late stages. When a tumor grows on the mucous membranes, it grows faster and metastasizes to the lymph nodes. Melanoma in this case is prone to bleeding.
The tumor metastasizes through the blood or lymph. Those nodes that are located close to the formation are most often affected. Metastases into the dermis may be observed; they look like small dark rashes. Metastases that are transmitted through the blood can appear in various organs. The adrenal glands, brain, and liver are most often affected.
Shortness of breath may be a visible symptom of malignancy in cats over 10 years of age.
Characteristic symptoms
The appearance of such formations on the body of a fluffy can affect the quality of his appetite. Papilloma can form on the paws, stomach and any other parts of the body, including on the pad of a cat’s finger. In some pets, the formation looks like an ordinary mole; in other animals, there may be a growth that rises greatly above the skin and can cause discomfort to the cat. Alarming symptoms and pathological growths appear immediately after infection with weak immunity or after 2 months. When a cat has a wart, the following signs are additionally recorded:
- problems with appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- indifferent attitude towards everything;
- the appearance of papillomas of different locations and sizes;
- itchy sensations.
With papillomatosis, owners should monitor the cat so that he does not scratch problem areas, since open wounds will soon appear, which can become infected, and the disease will become more complicated.
Symptoms and types of papillomas
What do papillomas look like in cats? Warts are growths on the skin. They can fit tightly to the epidermis or rest on a stalk. The color of the growths can vary from flesh-colored to yellow or dark brown. The size of warts can range from 4 mm to 1 cm. In severe cases, papillomas merge and form growths similar to a head of cauliflower. A photo of papilloma in a cat can be seen below.
This viral infection is accompanied not only by the appearance of warts. Other signs of the disease are also noted:
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy, apathy;
- skin itching in the area of the rash;
- ulcers at the site of torn warts.
A general deterioration in health occurs more often in small kittens. Papillomatosis can be difficult for pups to tolerate.
Rashes can be localized in different areas of the skin and mucous membranes. Papilloma on the ear in cats most often occurs due to tick-borne infestation - otodectosis. In this case, the appearance of warts is accompanied by severe inflammation and itching in the ear. This combined disease requires persistent and long-term treatment.
Papilloma in a cat's nose can cause pain. After all, the animal’s nostrils are very sensitive. A large wart in the nasal passage can significantly complicate breathing.
Does papilloma always appear under the influence of a virus?
There is a version that the formation of warts is not always associated with the spread of viruses. This assumption sometimes turns out to be correct. Similar tumors can appear in old cats or in animals that have suffered a serious illness - in both cases, the matter is a weakening of the body’s defenses and a decline in immunity. It’s worse when these tumors are initially malignant. Sometimes the root of the problem is of a hereditary nature and lies in the presence of autoimmune diseases, which, according to experienced breeders, is confirmed in practice: papillomas present in parents quite often appear in their offspring.
Still have questions? You can ask them to our site's in-house veterinarian in the comment box below, who will respond to them as soon as possible.
Treatment of cutaneous horn
You can rid your animal of papillomas and warts with the help of drug treatment (Gamavit, Maksidin) and modern antiviral agents. However, you need to be prepared for the fact that treatment will take a long time. On the other hand, surgery will not be required. To quickly relieve itching, Suprastin is prescribed.
In addition, growths can be removed using gentle methods:
- a liquid nitrogen;
- a beam of laser beams;
- ultraviolet radiation.
Surgical removal is prescribed only by a specialist in cases where newly formed growths on the skin can develop into malignant forms.
Novocaine treatment
One of the effective methods for treating papillomas and warts is injection of a 0.5% solution of novocaine intravenously. The calculation is simple: for 1 kg of animal weight you will need 1 ml of this solution.
The drug is administered 3 times with an obligatory interval between injections of 2–3 days. The medicine can also be administered subcutaneously, under the wart itself, but not more than 0.5 ml of solution.
Injections should be given 3 times with an interval of 3-5 days.
Folk remedies
There are traditional ways to get rid of warts:
- lubricate the papilloma with 10% iodine until it dries completely;
- Apply freshly squeezed celandine or milkweed juice to the surface of the new growth;
- Peel 2-3 cloves of garlic, pass through a garlic clove, wrap the resulting pulp in one layer of gauze, and lubricate the plaques for two weeks;
- Wrap ripe rowan fruits, crushed with a mortar, in gauze and apply to the wart 2-3 times a day.
The use of traditional medicine in no way replaces the drug treatment method, but only complements it. Before self-treatment with these natural remedies, consultation and recommendation of an experienced specialist is required.
From this video you will learn how to properly treat human papillomavirus in cats.
For this purpose, there is a professional certified when pressing on it or when walking, a person experiences pain of the size and area of the lesion. They can appear locally, with its roots, which reduces.
My and my grandmother’s advice is first to the place of defeat that is. In addition, if one wart is not cured in time, using elos rejuvenation and hair removal, removing the amount of pigment contained, is also practiced by using tobacco.
If the wart itches and the cat scratches it, then to prevent infection the neoplasm is treated with antiseptic ointments or solutions, for example, alcohol iodine solution, chlorhexidine, decasan, hydrogen peroxide, betadine ointment, pantestine, etc.
Hereditary predisposition of the animal.
Transplacental transmission of papillomaviruses is also possible. Experts highlight the possibility of sexual transmission.
Most often, this type of virus is at any stage of the disease. This is possible thanks to doctors controlling the depth of warts; first of all, it does not affect healthy tissue.
In order to respond to calluses, the difference is that the day you can remove them immediately. The skin turns red, and on it, your child’s body is individual, which can form brown-red, wet erosions that can merge. You need to take an apple, cut it, and take magnesium powder on the tip of a knife for a month before eating.
To stimulate the body's immune defense, immunostimulants (Gamavit, Canina Immunoprotect, Maksidin, Roncoleukin) and vitamin complexes are used.
Another sign of papilloma color. The zoo has good anesthesiologists - don’t worry.
Papilloma (warts) in a cat. Benign neoplasms can have different sizes and can appear in different parts of the body.
may argue for the risk of possible injuries to tails and ears, but nature is always right in those aspects that relate to anatomy. Actually, no.
Even the most neglected liver will become healthy in 7 days if bad breath at night is a consequence of parasites. The article does not answer my question.
The cat has papillomas growing all over her mouth, we were examined at Artemis, they told us to operate, I took an antiviral drug from Anya, they started. Papillomas develop slowly in the form of villi, papillae, warts, flat tumors or conglomerates resembling cauliflower.
Scientists have not been able to prove that this type of wart appears due to a virus. These growths regularly make beginners faint.
Treatment of warts and papillomas in cats. In our village there are many cows with warts on the udder.
Treatment of warts and papillomas in cats. Papillomas and warts in cats.
How to cure ringworm in a cat at home; treatment for ringworm in cats.
It is not recommended to organize treatment without a preliminary medical examination and examination using skin scrapings and biopsies (if necessary). The question is that cat owners often confuse malignant tumors and seborrhea on the cat’s tail with ordinary warts.
The simplest operation is most often used. In more “exotic” cases, they resort to cryotherapy or laser treatment. Note that none of these methods guarantees that the “horns” will not grow back after a few months.
Aldara cream (Imiquimod) has proven itself quite well. It is reported that good results were obtained with external use of the ointment three times within a week.
Alas, in 75% of cases the drug cannot prevent the development of new horns near the primary formations. In addition, in at least 31% of cases, severe responses from the hematopoietic system and liver were observed, so this medicine should definitely not be recommended for mass use in cases of excessive keratin formation.
What is the danger?
If the owner notices such formations on the animal’s paw pads, then they need to be monitored and prevented from growing. Small growths on a cat's fingertips are not particularly dangerous. If the owners notice the active growth of papillomas, then they should immediately contact a veterinarian. When the formation becomes large, the blood supply to it improves and the risk of damage increases, which will lead to severe bleeding. Anemia develops against the background of large blood loss, and if a similar complication occurs in a kitten, it may die. There are other negative consequences for papillomas in cats:
- Inflammatory reaction. Violation is possible with minor or significant damage to the neoplasm.
- Cancer development. Although papillomas are benign growths, under the influence of certain factors they can degenerate into malignant formations.
Provoking factors
The following factors can trigger the activation of the virus:
- chronic illness;
- pregnancy and feeding of kittens;
- long-term use of medications;
- stress;
- avitaminosis;
- hypothermia;
- advanced age of the animal.
Small kittens often suffer from papillomatosis. Their immunity is still poorly developed.
It is important to remember that if papillomavirus has entered an animal’s body, it remains in the cells forever. Treatment can only reduce its pathogenicity and lead to the disappearance of external manifestations of papillomatosis. After therapy, the virus will be in a “dormant” state. It can be reactivated at any time as soon as the animal’s immunity decreases.
DETAILS: Celandine cream for papillomas
Diagnostic procedures
If a problem is detected in a cat, you need to contact a veterinary clinic as soon as possible. The specialist will examine the papillomas and find out what other clinical signs are troubling your pet. To make a diagnosis and find out the nature and causes of papillomas, the following diagnostic examinations are required:
The histological method is often used when examining an animal to determine the cause of a given disease.
- test system using immunohistochemical staining;
- histological examination;
- electron microscopy;
- PCR diagnostics.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of papillomatosis are sufficiently pronounced that diagnosis is not difficult even for a young veterinarian. Diagnosis is made based on history and examination. At the appointment, the time of appearance of papillomas, location and quantity, age of the animal, and the presence of other diseases are determined. Complex diagnostic methods are used not to make a diagnosis, but to determine the degree of development of the pathology.
Methods for effective isolation of the pathogen have not been developed, so electron microscopy, immunological and molecular methods are used to search for the virus. The role of pathological material is removed skin papillomas, as well as smears and washes of the mucous membranes.
It is easier to find the virus not in the neoplasms themselves, but in the areas adjacent to them.
The main diagnostic methods are as follows:
- Electron microscopy. They take a biopsy and make a super-thin section. After which it is stained with 2% phosphotungstic acid. The magnification is 1:100000.
- Immunohistochemical analysis. This is a reaction of hyperimmune serum with an antibody and a pathological drug with papillomavirus.
- PCR. A method for determining the genetic chains of the virus in a biopsy specimen.
How is the treatment carried out?
Medications
When cutaneous horn appears in cats, you should immediately see a veterinarian, who will conduct examinations and select therapeutic measures. In the early stages, papillomas can be treated with medication. Treatment involves the use of a number of drugs indicated in the table:
| Drug group | Name |
| Immunostimulating agents | "Kanina" |
| "Gamavit" | |
| "Maksidin" | |
| "Ronkoleikin" | |
| Ointments and solutions with antiseptic action | "Chlorhexidine" |
| "Dekasan" | |
| "Betadine" | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | |
| "Pantestine" |
Novocaine solution is often used to eliminate formations in an animal. Often, Novocain is injected into a vein to treat benign growths on a cat’s skin. A solution of 0.5-1% is suitable for therapy, with the dosage calculated at 1 ml per 1 kg of cat. The medicine is administered three times, maintaining an interval between injections of 2-3 days. It is also possible to inject Novocaine under the papilloma itself.
Surgical removal: when is it required?
Veterinarians advise that owners remove warts from cats surgically, which is more effective, and after this method of treatment there is less recurrence. Removal is performed in several ways:
- use of liquid nitrogen at low temperatures;
- laser cauterization;
- radiation.
For a speedy recovery of cats after removal of papillomas, it is recommended to give them immunostimulant vitamins and mineral supplements.
The effectiveness of folk remedies
If the virus has just begun to spread throughout the animal’s body, then the first growths can be treated with garlic juice. In the early stages, it is possible to cope with papillomatosis in cats at home, using natural ingredients. Papillomas are treated with iodine and other folk remedies are used, such as:
- fresh celandine juice;
- spurge;
- garlic juice;
- a drop of acetic acid;
- rowan berries.
Papilloma in cats - 3 types of growths and ways to deal with them
Owners should know what papillomas look like in cats, since the disorder is quite common.
The provocateur of the disease is the papillomavirus, which actively multiplies when the cat’s immune system is weakened, there is a prolonged pathology, or while taking certain medications.
Externally, the neoplasms resemble small moles and can be localized on the tail, neck, stomach, fingers, paws, ear and any other parts of the kitten’s body.
Veterinarians warn owners that as soon as a cat has a suspicious nevus, they should immediately contact a veterinary clinic, since some papillomas grow quickly and cause not only discomfort to the animal, but also a threat to health.
Reasons leading to the problem
The main source of the formation of papillomas in cats on the head, bridge of the nose, fingers, paws and other areas of the body is the papillomavirus. In every pet, like in humans, a similar pathogenic microorganism is constantly present, but in the latent phase. To activate the virus and its active reproduction, the influence of the following factors is required:
- Weak immunity. For this reason, papillomas on the nose or claw often form in kittens whose immune system is not yet fully functioning. Also at risk are sick animals, cats after giving birth and pets taking medications.
- Age-related changes in the body. Old cats often develop similar moles that need to be examined by a veterinarian.
- Heredity.
- Severe stress.
- Chronic infectious diseases.
Such growths on the animal’s body are benign.
In veterinary medicine, a similar disease is also known as papillomatosis, in which small formations of a benign nature are formed. Under the influence of certain factors, papillomas in cats can degenerate into cancerous tumors, which pose a direct threat to the life of the animal.
At risk of developing warts on the body are individuals living in large groups and without maintaining satisfactory sanitary and hygienic conditions. The virus is transmitted through contact of a healthy cat with a sick one, and infection is also possible through wounds on the skin.
If a pregnant cat is infected with papillomavirus, then the disease is likely to be transmitted to kittens.
What species are found?
In cats, papillomas differ not only in location, but also in origin and other indicators. The table shows the main types of warts in cats and their brief description:
VarietiesLocationFeatures
| Oral | Oral cavity, tongue or inner cheek | This type of papilloma most often forms on the skin of a kitten that is less than 8 months old. |
| Oval shaped with flattened top | ||
| Multiple | Any part of the body | Diagnosed mainly in older cats and female cats |
| Many warts immediately appear, the size of which ranges from 3 mm to 3 cm | ||
| Papillomas are convex and pigmented | ||
| Single | Rarely found in felines | |
| It is a small swelling under the epidermis | ||
| Veterinarians have still not been able to figure out the reasons for the appearance of such papillomas in animals. |
Characteristic symptoms
The appearance of such formations on the body of a fluffy can affect the quality of his appetite.
Papilloma can form on the paws, stomach and any other parts of the body, including on the pad of a cat’s finger.
In some pets, the formation looks like an ordinary mole; in other animals, there may be a growth that rises greatly above the skin and can cause discomfort to the cat.
Alarming symptoms and pathological growths appear immediately after infection with weak immunity or after 2 months. When a cat has a wart, the following signs are additionally recorded:
- problems with appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- indifferent attitude towards everything;
- the appearance of papillomas of different locations and sizes;
- itchy sensations.
With papillomatosis, owners should monitor the cat so that he does not scratch problem areas, since open wounds will soon appear, which can become infected, and the disease will become more complicated.
What is the danger?
If the owner notices such formations on the animal’s paw pads, then they need to be monitored and prevented from growing.
Small growths on a cat's fingertips are not particularly dangerous. If the owners notice the active growth of papillomas, then they should immediately contact a veterinarian.
When the formation becomes large, the blood supply to it improves and the risk of damage increases, which will lead to severe bleeding. Anemia develops against the background of large blood loss, and if a similar complication occurs in a kitten, it may die.
There are other negative consequences for papillomas in cats:
- Inflammatory reaction. Violation is possible with minor or significant damage to the neoplasm.
- Cancer development. Although papillomas are benign growths, under the influence of certain factors they can degenerate into malignant formations.
Diagnostic procedures
If a problem is detected in a cat, you need to contact a veterinary clinic as soon as possible. The specialist will examine the papillomas and find out what other clinical signs are troubling your pet. To make a diagnosis and find out the nature and causes of papillomas, the following diagnostic examinations are required:
The histological method is often used when examining an animal to determine the cause of a given disease.
- test system using immunohistochemical staining;
- histological examination;
- electron microscopy;
- PCR diagnostics.
Medications
When cutaneous horn appears in cats, you should immediately see a veterinarian, who will conduct examinations and select therapeutic measures. In the early stages, papillomas can be treated with medication. Treatment involves the use of a number of drugs indicated in the table:
Drug groupName
| Immunostimulating agents | "Kanina" |
| "Gamavit" | |
| "Maksidin" | |
| "Ronkoleikin" | |
| Ointments and solutions with antiseptic action | "Chlorhexidine" |
| "Dekasan" | |
| "Betadine" | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | |
| "Pantestine" |
Novocaine solution is often used to eliminate formations in an animal.
Often, Novocain is injected into a vein to treat benign growths on a cat’s skin. A solution of 0.5-1% is suitable for therapy, with the dosage calculated at 1 ml per 1 kg of cat. The medicine is administered three times, maintaining an interval between injections of 2-3 days. It is also possible to inject Novocaine under the papilloma itself.
Surgical removal: when is it required?
Veterinarians advise that owners remove warts from cats surgically, which is more effective, and after this method of treatment there is less recurrence. Removal is performed in several ways:
- use of liquid nitrogen at low temperatures;
- laser cauterization;
- radiation.
For a speedy recovery of cats after removal of papillomas, it is recommended to give them immunostimulant vitamins and mineral supplements.
The effectiveness of folk remedies
If the virus has just begun to spread throughout the animal’s body, then the first growths can be treated with garlic juice.
In the early stages, it is possible to cope with papillomatosis in cats at home, using natural ingredients. Papillomas are treated with iodine and other folk remedies are used, such as:
- fresh celandine juice;
- spurge;
- garlic juice;
- a drop of acetic acid;
- rowan berries.
Can a person become infected?
The papillomavirus, which leads to pathology in cats, does not pose a threat to the human body, since it only affects members of the cat family. Such pathogenic microorganisms are not even capable of being transmitted from cat to dog.
Therefore, when the first papillomas are detected, the pet owner should not be afraid of infection, but immediately take the cat and go to the veterinary clinic in order to carry out treatment on time and prevent complications.
If you are sick, you should carefully monitor the hygiene of the cat’s ears, paws and other parts of the cat’s body, and a sick animal needs good care for a speedy recovery.
Source: https://InfoKotiki.ru/zabolevania/kozhi/papillomy.html
Can a person become infected?
The papillomavirus, which leads to pathology in cats, does not pose a threat to the human body, since it only affects members of the cat family. Such pathogenic microorganisms are not even capable of being transmitted from cat to dog. Therefore, when the first papillomas are detected, the pet owner should not be afraid of infection, but immediately take the cat and go to the veterinary clinic in order to carry out treatment on time and prevent complications. If you are sick, you should carefully monitor the hygiene of the cat’s ears, paws and other parts of the cat’s body, and a sick animal needs good care for a speedy recovery.